
트리
특징
1. 연결 그래프
2. 방향을 무시하였을 때, 싸이클이 존재하지 않는다.
3. 트리의 간선개수는 정점 개수보다 1작다.트리의 서브트리는 절대로 영역이 겹치지 않음 -> 분할정복, DP로 장난을 잘 칠 줄 알아야 한다.
순회 방법
트리의 순회 방법은 3가지다.
1. 전위 순회 (root -> left -> right)
2. 중위 순회 (left -> root -> right)
3. 후위 순회 (left -> right -> root)보통 BFS, DFS로 구현한다.
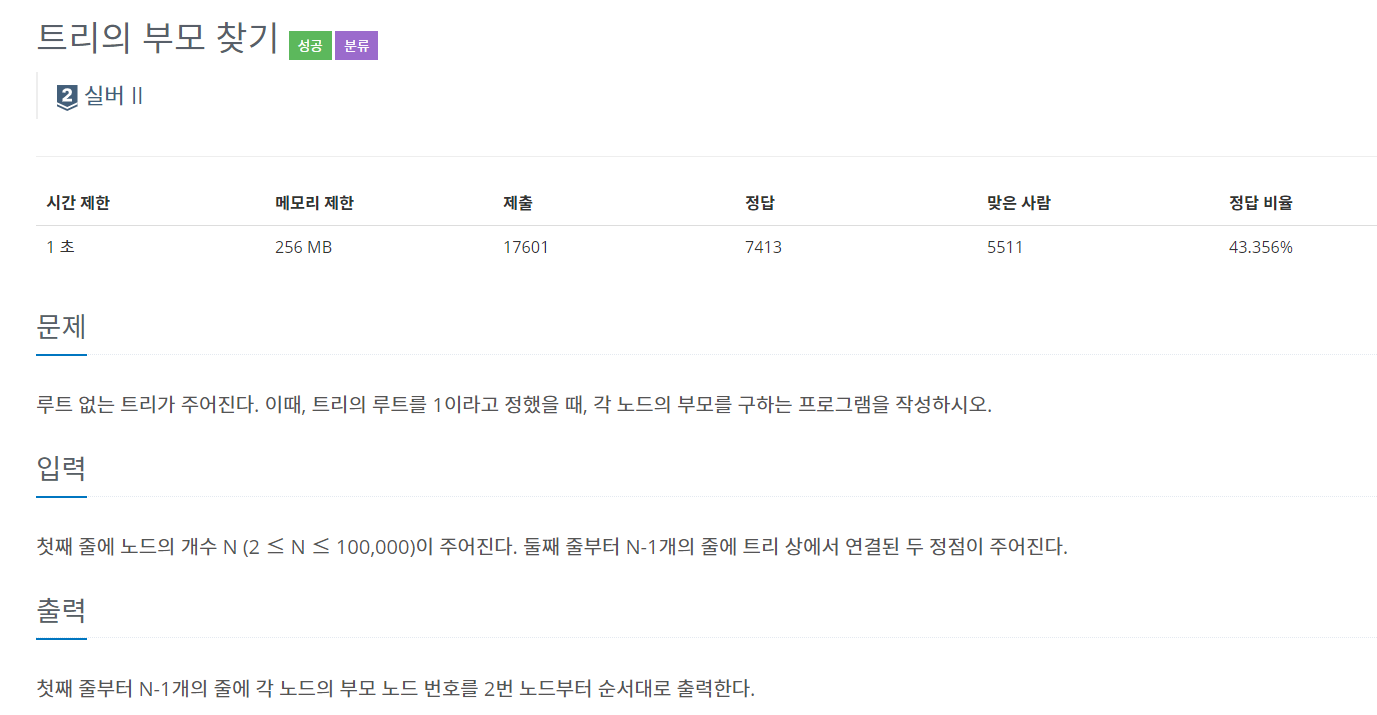
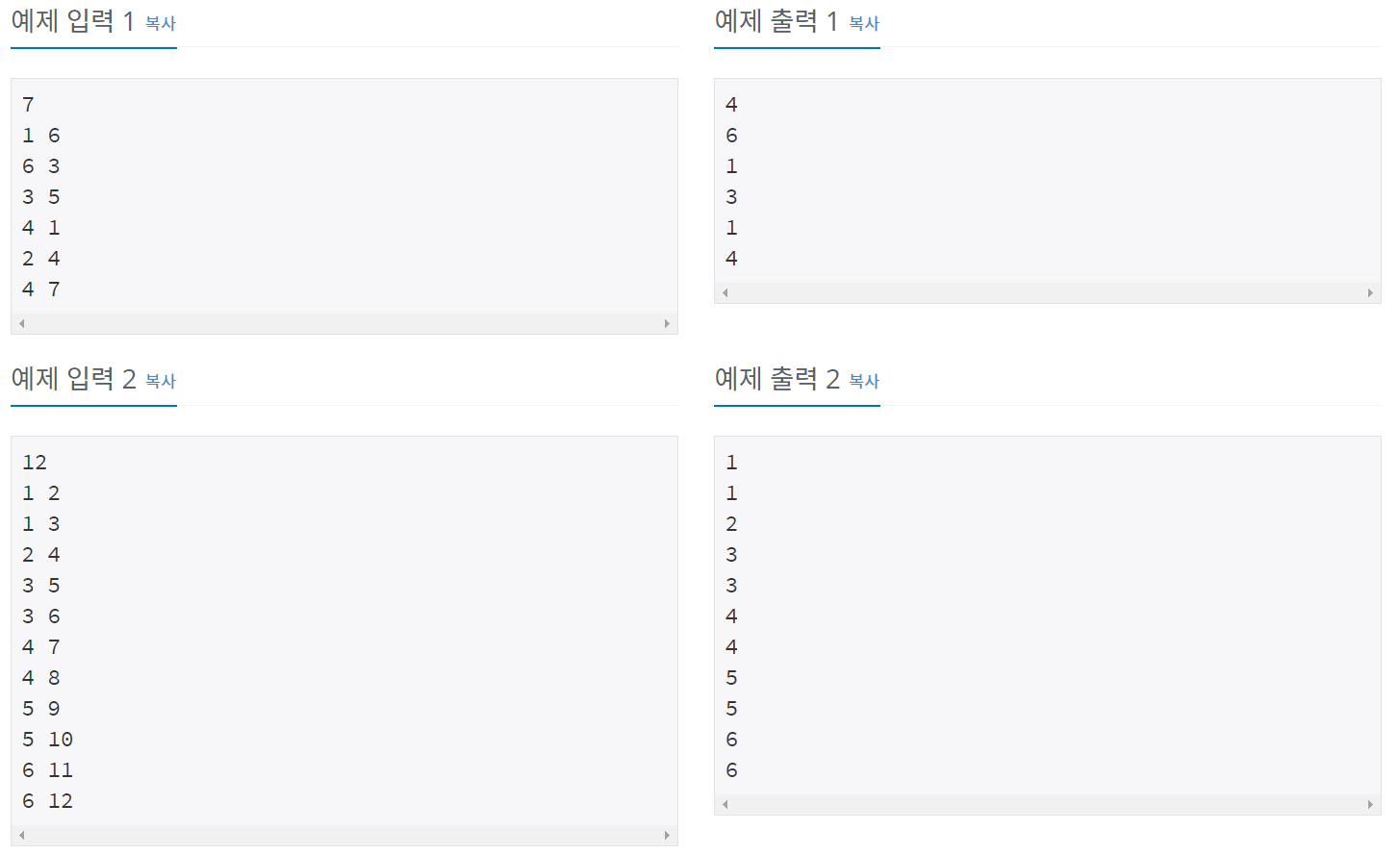
[백준 11725] - 트리의 부모찾기
풀이
BFS, DFS를 사용해 탐색하는 방식으로 구현했다.
package package27;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class num11725 {
static int N;
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> tree;
static StringBuilder sb;
static int[] result;
static boolean[] visited;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
tree = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
sb = new StringBuilder();
int N = stoi(br.readLine());
result = new int[N+1];
visited = new boolean[N+1];
for(int i=0; i<=N; i++) {
tree.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
for(int i=0; i<N-1; i++) {
String[] edge = br.readLine().split(" ");
int node1 = stoi(edge[0]);
int node2 = stoi(edge[1]);
tree.get(node1).add(node2);
tree.get(node2).add(node1);
}
// dfs(1);
bfs();
for(int i=2; i<=N; i++) {
System.out.println(result[i]);
}
}
private static void dfs(int num){
if(visited[num]){
return;
}
visited[num] =true;
for (int node: tree.get(num)) {
if(!visited[node]){
result[node] = num;
dfs(num);
}
}
}
public static void bfs() {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
for(int value : tree.get(1)) {
result[value] = 1;
queue.add(value);
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
int node = queue.remove();
for(int value : tree.get(node)) {
if(result[value] == 0) {
result[value] = node;
queue.add(value);
}
}
}
}
public static int stoi(String string) {
return Integer.parseInt(string);
}
}
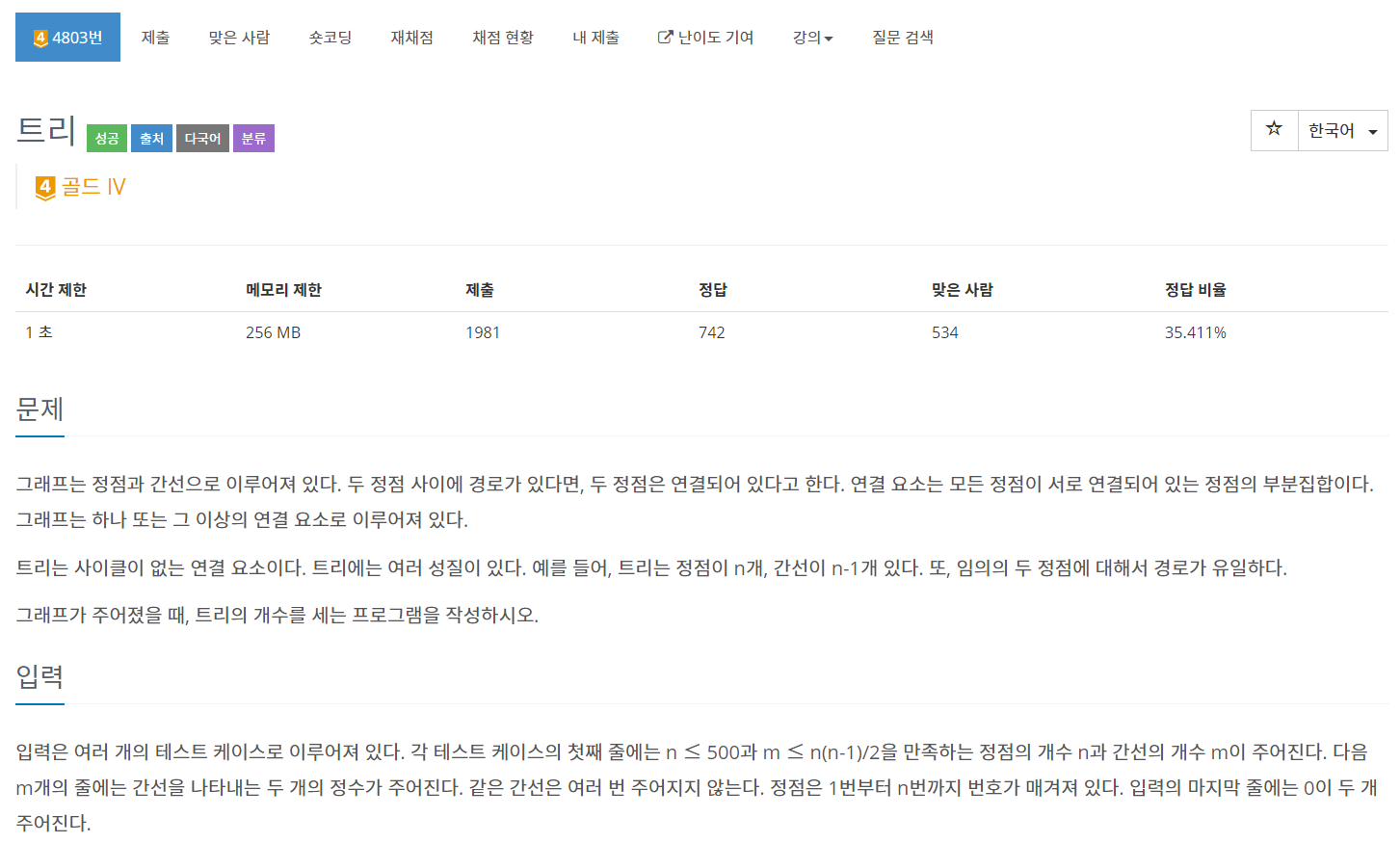
[백준 4803] - 트리
풀이
아… 이거 풀다가 책상 부실뻔 했다. 너무 헤맸다… ㅜㅜ
일단 문제에 T는 트리의 개수다.
dfs로 입력받은 노드 모두 탐색하고, cycle이 존재하면 no tree로 출력하게 짰는데 계속 틀렸다고 나왔다. ㅎㅎ 정답을 알려줘
열받아서 마포 코딩박님 블로그 dfs 부분을 참고해서 코드 작성했다.
일단 정답은 맞췄다고 나오는데
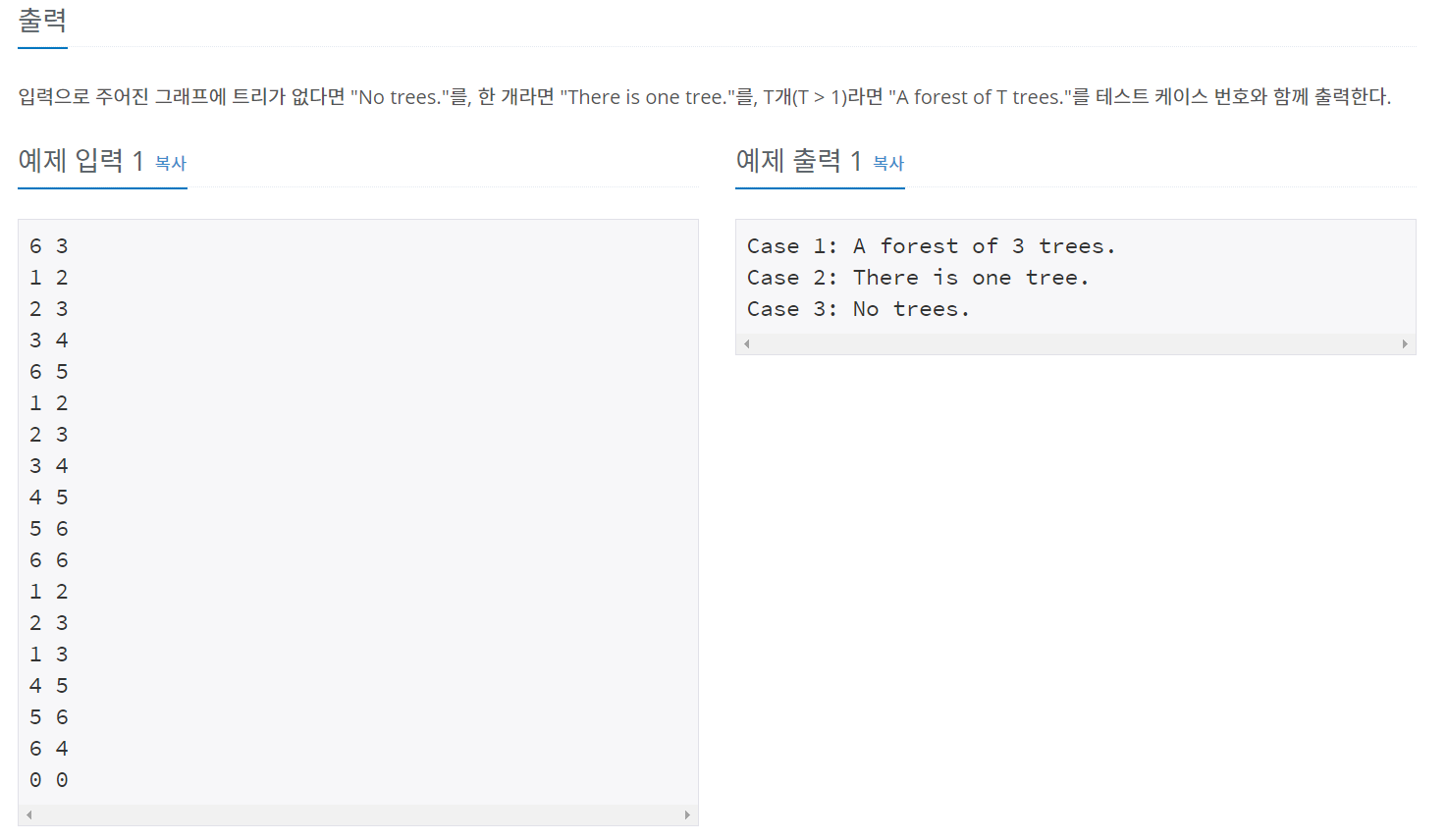
입력값
7 4
1 2
2 3
3 1
6 7
0 0
출력값
Case 1: A forest of 3 trees.이렇게 나오는데 이거 틀린거 아님? cycle 있으면 트리 없다고 나와야 하는거 아닌가 아시는 분 알려주세요ㅜㅜㅜㅜㅜ
아 짜증나 ㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋ 화 좀 식히고 나중에 생각나면 다시 봐야겠다…
package package27;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class num4803 {
static int N, M, count, caseIndex = 0;
static StringBuilder sb;
static BufferedReader br;
static ArrayList<Integer>[] graph;
static boolean[] visited;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
sb = new StringBuilder();
while(true) {
String[] NM = br.readLine().split(" ");
N = stoi(NM[0]);
M = stoi(NM[1]);
graph = new ArrayList[N+1];
visited = new boolean[N+1];
if(N==0 && M==0) {
break;
}
resetData();
inputTreeData();
checkTree();
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
public static void inputTreeData() throws IOException {
for(int i=0; i<M; i++) {
String[] Edge = br.readLine().split(" ");
int v1 = stoi(Edge[0]), v2 = stoi(Edge[1]);
graph[v1].add(v2);
graph[v2].add(v1);
}
}
public static void checkTree() {
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++) {
if(!visited[i]) {
if(dfs(i, 0))
count++;
}
}
if(count == 1) {
sb.append("Case "+caseIndex+": There is one tree.\n");
}else if(count==0){
sb.append("Case "+caseIndex+": No trees.\n");
}else {
sb.append("Case "+caseIndex+": A forest of "+count+" trees.\n");
}
}
public static boolean dfs(int num, int prev) {
visited[num] = true;
for(int node : graph[num]) {
if (node == prev) continue;
if (visited[node]) return false;
if (dfs(node, num) == false) return false;
}
return true;
}
public static void resetData() {
for(int i=0; i<=N; i++) {
graph[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
visited[i] = false;
}
count = 0;
caseIndex++;
}
public static int stoi(String string) {
return Integer.parseInt(string);
}
}
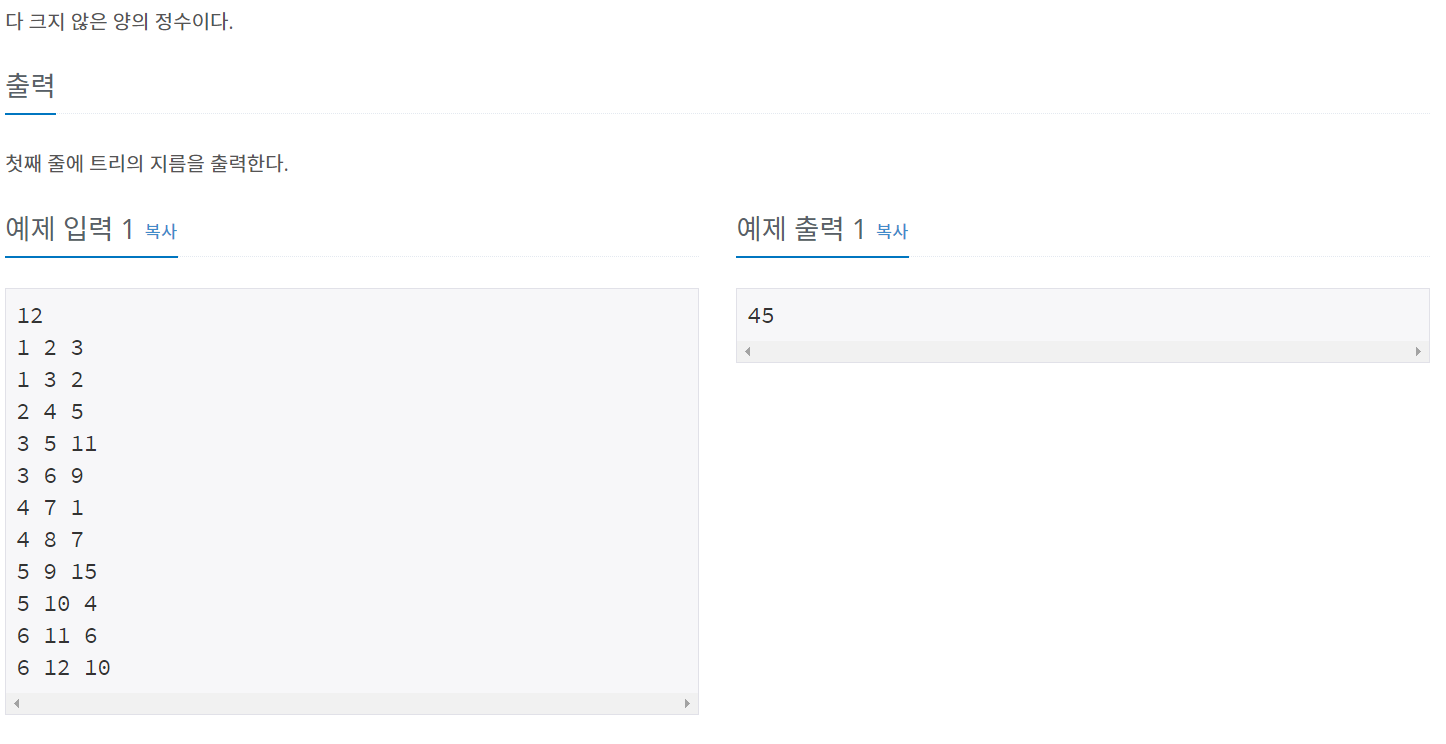
[백준 1967] - 트리의 지름
처음에 문제 접근하는 법을 잘못해서 좀 헤맸다.
트리의 지름을 구하는 방법은 다음과 같다.
1. 트리의 임의의 정점(x)에서 가장 먼 정점(y)을 찾는다.
2. 가장 먼 정점(y) 에서 가장 먼 정점(z)을 찾는다.
=> 지름은 y - z 까지의 거리다.증명이 궁금하면 전명우님 블로그 - 트리의 지름 구하기 에 쉽게 설명한 글이 있다.
-> 한줄 요약 : 어떤 한 점에서 가장 먼 점이 지름에 무조건 포함된다 (포함 안되는 경우를 증명)

package package27;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class num1967 {
static int N, result = 0, start;
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Edge>> Vertex;
static boolean[] visited;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = stoi(br.readLine());
Vertex = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Edge>>();
for(int i=0; i<=N; i++) {
Vertex.add(new ArrayList<Edge>());
}
for(int i=1; i<N; i++) {
String[] inputData = br.readLine().split(" ");
int node1 = stoi(inputData[0]);
int node2 = stoi(inputData[1]);
int w = stoi(inputData[2]);
Vertex.get(node1).add(new Edge(node2, w));
Vertex.get(node2).add(new Edge(node1, w));
}
visited = new boolean[N+1];
visited[1] = true;
dfs(0, 1);
visited = new boolean[N+1];
visited[start] = true;
dfs(0, start);
System.out.println(result);
}
public static int dfs(int len, int now) {
if (result < len) {
result = len;
start = now;
}
System.out.println(now);
for (Edge node: Vertex.get(now)) {
if(!visited[node.e]){
visited[node.e] = true;
dfs(len + node.w, node.e);
}
}
return result;
}
public static int stoi(String string) {
return Integer.parseInt(string);
}
static class Edge{
int e, w;
Edge(int e,int w){
this.e = e;
this.w = w;
}
}
}
트리의 지름 - 백준1167번 비슷한 문제다.
[백준 2250] - 트리의 높이와 너비
이문제 풀면서 많이 헤맸다ㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋ
배열 만들어서 깊이마다 맨 오른쪽 값을 맨 왼쪽 값 빼면 될 것 같다는 생각을 했는데…
양심고백을 조금 해보면 오늘 삽질을 너무 많이 해서 고민 많이 안해보고 정답 해결 방법부터 찾아봤다.
쾌락코딩님 블로그 - 백준2250번 문제(트리의 높이와 너비) with Java글을 참고했다.
문제의 포인트는 3가지다.
1. 문제에서 루트가 정해져 있지 않다
-> 루트를 확인할 수 있는 뭔가 방법이 필요
2. 트리의 높이마다 가장 오른쪽 값, 가장 왼쪽값 저장
-> 오른쪽 - 왼쪽 + 1
3. 중위 순회로 순회
-> 그림보면 왼쪽 - 루트 - 오른쪽 순으로 index가 표시되있음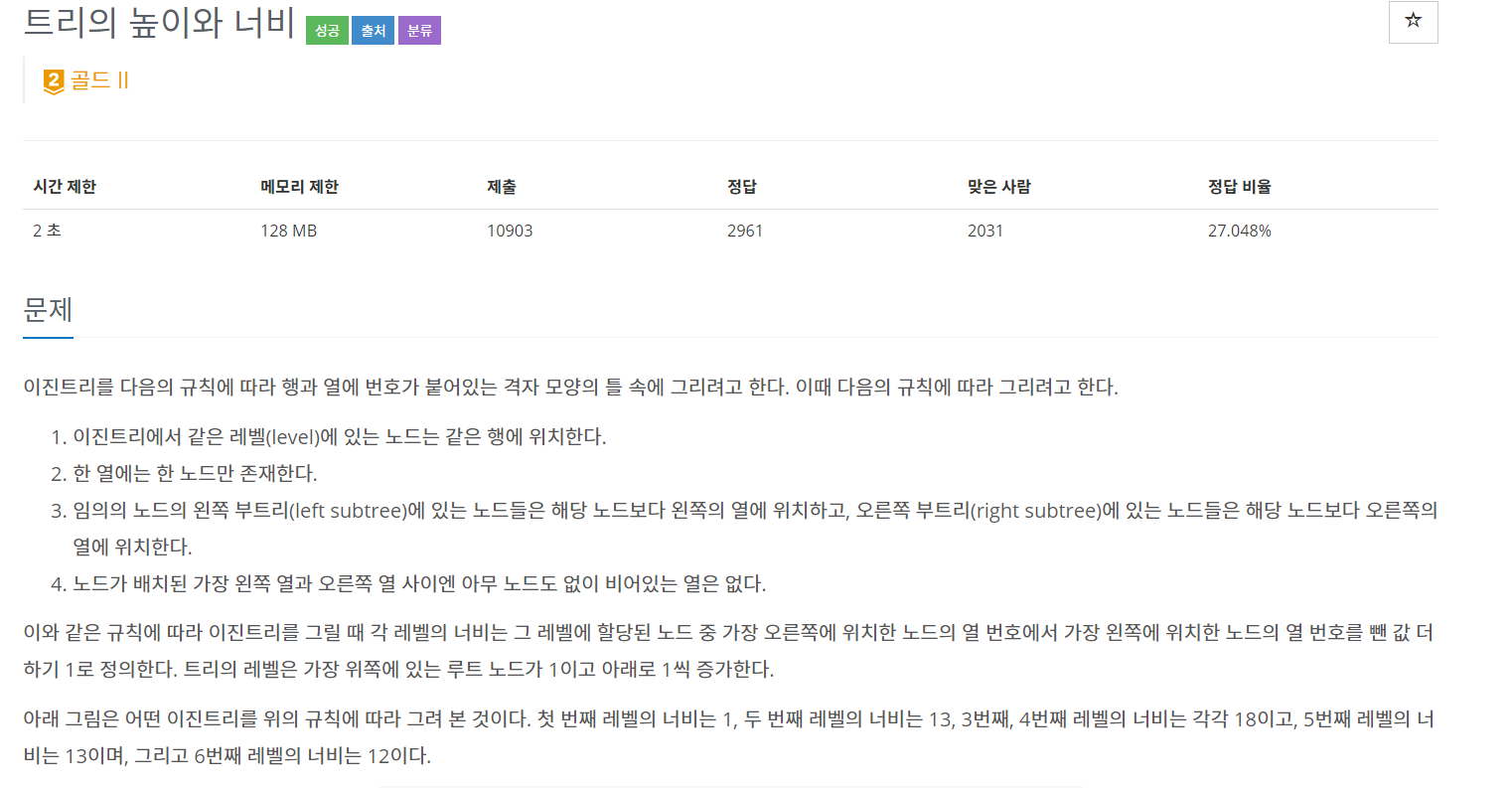

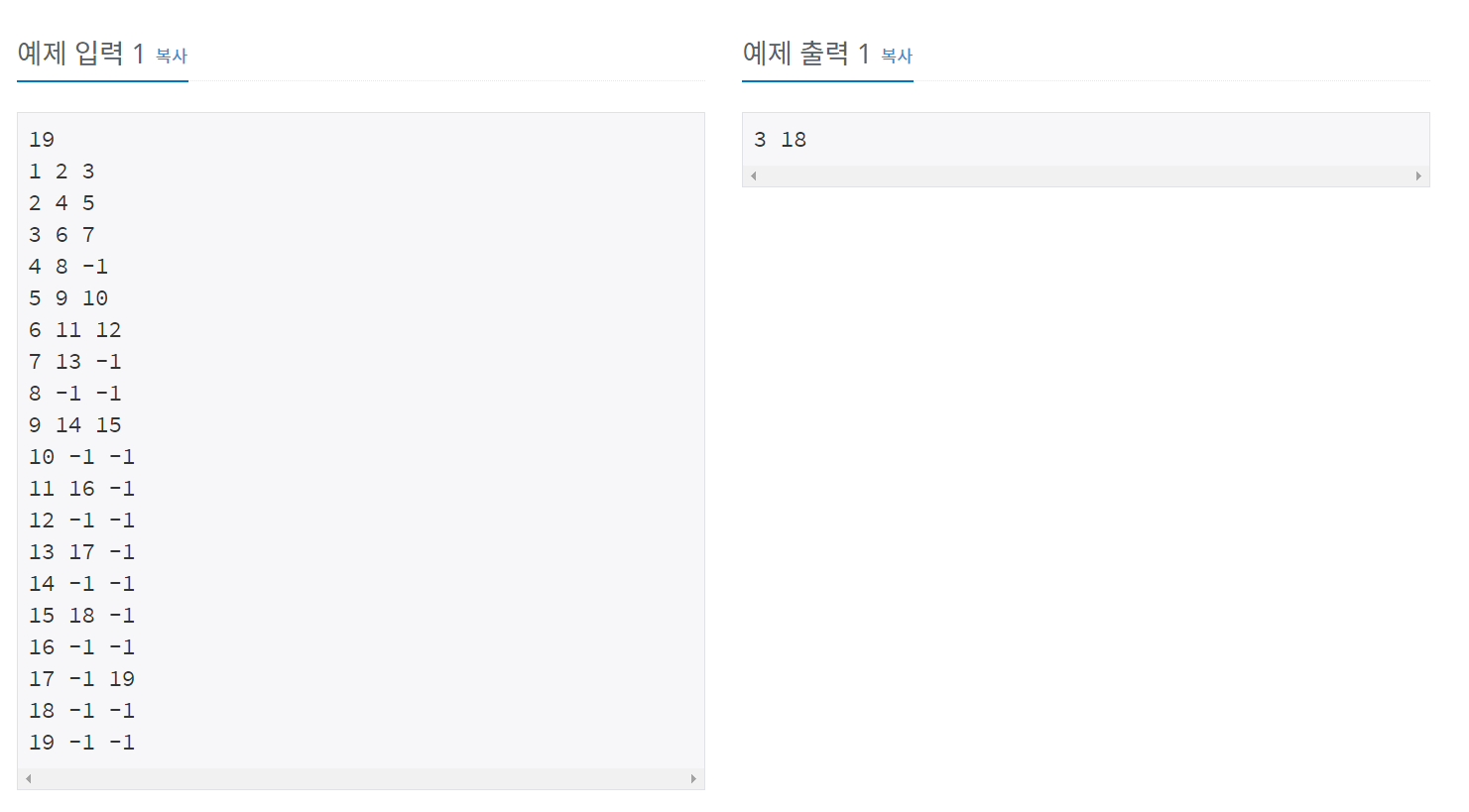
풀이
package package27;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class num2250 {
static int N, maxWidth, maxDepth, root, vCount = 1;
static Node[] tree;
static int[] depthLeft;
static int[] depthRight;
static BufferedReader br;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = stoi(br.readLine());
init();
inputTreeData();
searchRootIndex();
inOrder(root, 1);
printResult();
}
public static void init() {
tree = new Node[N+1];
depthLeft = new int[N+1];
depthRight = new int[N+1];
for(int i=0; i<=N; i++) {
tree[i] = new Node(-1, -1, -1);
depthLeft[i] = N+1;
}
}
public static void inputTreeData() throws IOException {
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
String[] inputData = br.readLine().split(" ");
int num = stoi(inputData[0]);
int left = stoi(inputData[1]);
int right = stoi(inputData[2]);
tree[num].left = left;
tree[num].right = right;
if(left != -1)
tree[left].parent = num;
if(right != -1)
tree[right].parent = num;
}
}
public static void searchRootIndex() {
for(int i=1; i <= N; i++) {
if(tree[i].parent == -1) {
root = i;
break;
}
}
}
public static void inOrder(int parentIndex, int depth) {
Node root = tree[parentIndex];
if(maxDepth < depth) maxDepth = depth;
if(root.left != -1) {
inOrder(root.left, depth + 1);
}
depthLeft[depth] = Math.min(depthLeft[depth], vCount);
depthRight[depth] = vCount++;
if(root.right != -1) {
inOrder(root.right, depth + 1);
}
}
public static void printResult() {
int index = 1;
int maxWitdh = depthRight[1] - depthLeft[1] + 1;
for(int i=2; i <= maxDepth; i++) {
int tmp = depthRight[i] - depthLeft[i] +1;
if(maxWitdh < tmp) {
index = i;
maxWitdh = tmp;
}
}
System.out.println(index + " " + maxWitdh);
}
public static int stoi(String string) {
return Integer.parseInt(string);
}
static class Node{
int parent, value, left, right;
Node(int value, int left, int right){
this.parent = -1;
this.value = value;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
정리
사실 트리는 학교 알고리즘 시간에 다뤄봐서 정리하는데 오래걸리지 않을 줄 알았는데 생각보다 오래걸렸다 ㅜㅜㅜㅜ 문제도 많이 풀어봐야 할 듯…
정.말.알.고.리.즘.문.제.풀.이.는.너.무.재.밌.다.하.하.하.하.하.하.하.하.하.하.하.하.하
오늘 정리한 문제들은 dfs, bfs로 탐색하는 문제들이었다.
아래 사진같은3 유형의 문제들도 있던데…
 빠른 시일내로 4문제 풀어봐야겠다. (조금 무서워 보인다ㅋ)
빠른 시일내로 4문제 풀어봐야겠다. (조금 무서워 보인다ㅋ)
Reference
라이님 블로그
전명우님 블로그
쾌락코딩님 블로그 - 백준2250번 문제(트리의 높이와 너비) with Java
마포 코딩박님 블로그