
최단거리 경로복원
Algorithm
2021.01.25.
Series
백준 11779, 11780, 1738번 문제를 통해 최단경로의 경로출력을 정리해보려고 한다.
백준 11779 - 다익스트라
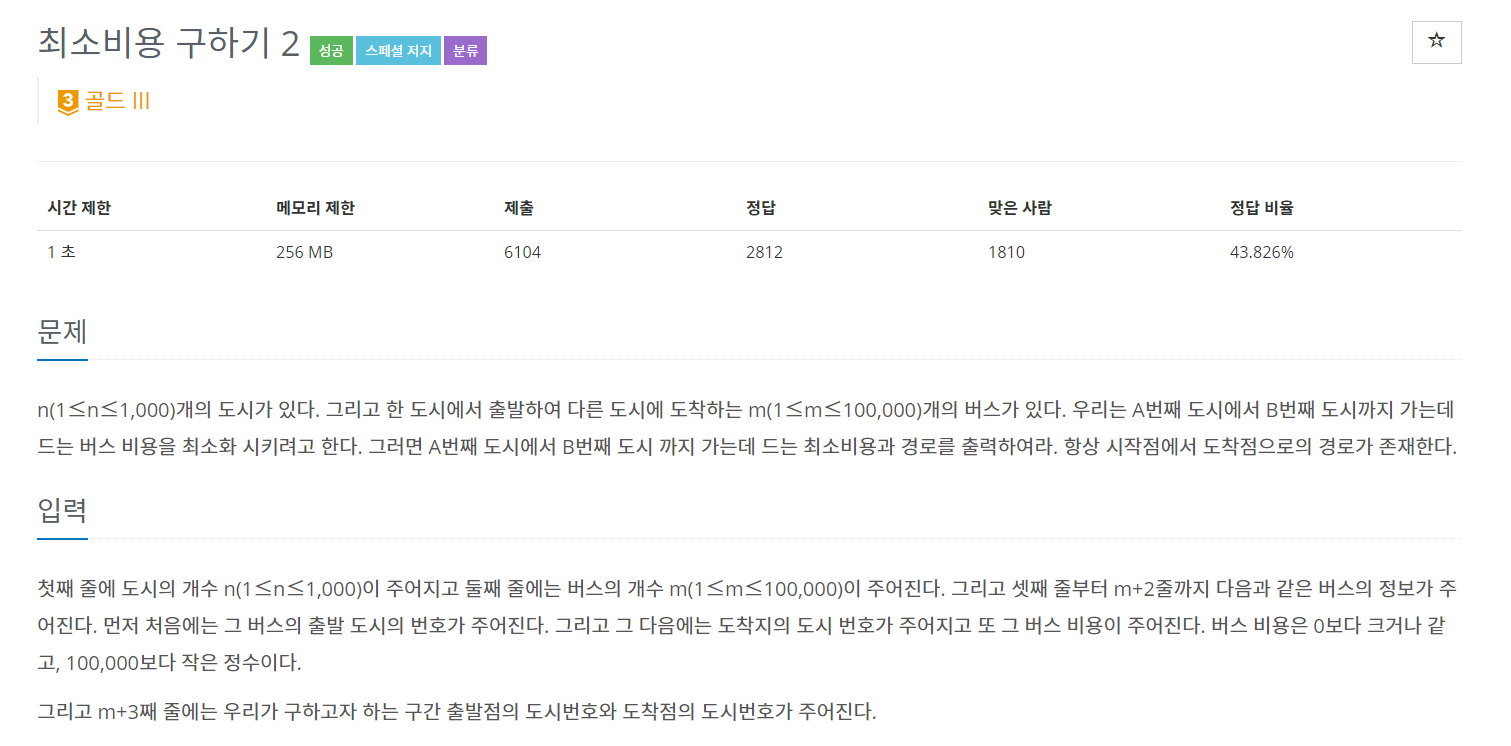
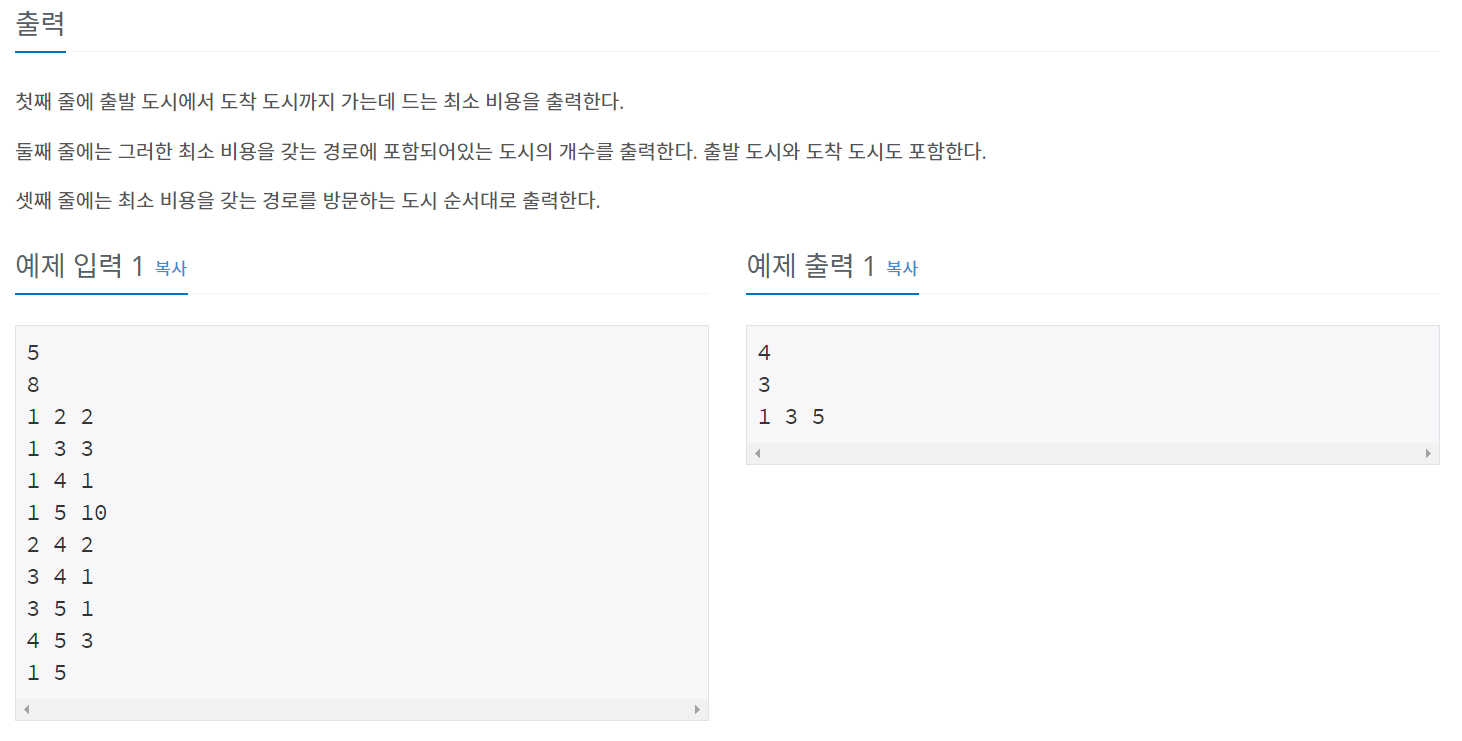
소스를 간략히 설명하면
다익스트라 알고리즘에 값이 조건에 맞아 갱신될 때 배열의 값에 이전 노드를 저장한다.
첫 노드부터 순서대로 출력하기 위해 stack을 사용했다.
package pakcage26;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Stack;
public class num11779 {
static int N, M, count=2,INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Edge>> Vertex;
static int[] dist, pre;
static boolean[] visited;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = stoi(br.readLine());
M = stoi(br.readLine());
Vertex = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Edge>>();
dist = new int[N];
pre = new int[N];
visited = new boolean[N];
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
Vertex.add(new ArrayList<Edge>());
dist[i] = INF;
}
for(int i=0; i<M; i++) {
String[] uvw = br.readLine().split(" ");
int u = stoi(uvw[0])-1;
int v = stoi(uvw[1])-1;
int w = stoi(uvw[2]);
Vertex.get(u).add(new Edge(v,w));
}
String[] point = br.readLine().split(" ");
int start = stoi(point[0])-1;
int end = stoi(point[1])-1;
dijkstra(start, end);
long answer =dist[end];
Stack<Integer> st = new Stack<Integer>();
st.add(end);
while (pre[end] != start) {
st.add(pre[end]);
end = pre[end];
count++;
}
st.add(start);
System.out.println(answer);
System.out.println(count);
while (!st.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(st.pop()+1 + " ");
}
}
public static void dijkstra(int start, int end) {
dist[start] = 0;
PriorityQueue<Edge> q = new PriorityQueue<Edge>();
q.add(new Edge(start, 0));
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
Edge now = q.remove();
if(!visited[now.e]) {
visited[now.e] = true;
for(Edge next : Vertex.get(now.e)) {
if(!visited[next.e] && dist[next.e] >= dist[now.e] + next.w) {
dist[next.e] = dist[now.e] + next.w;
q.add(new Edge(next.e, dist[next.e]));
pre[next.e] = now.e;
}
}
}
}
}
public static int stoi(String string) {
return Integer.parseInt(string);
}
static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge>{
int e, w;
Edge(int e, int w){
this.e = e;
this.w = w;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge o){
return w - o.w;
}
}
}백준 11780 - 플로이드
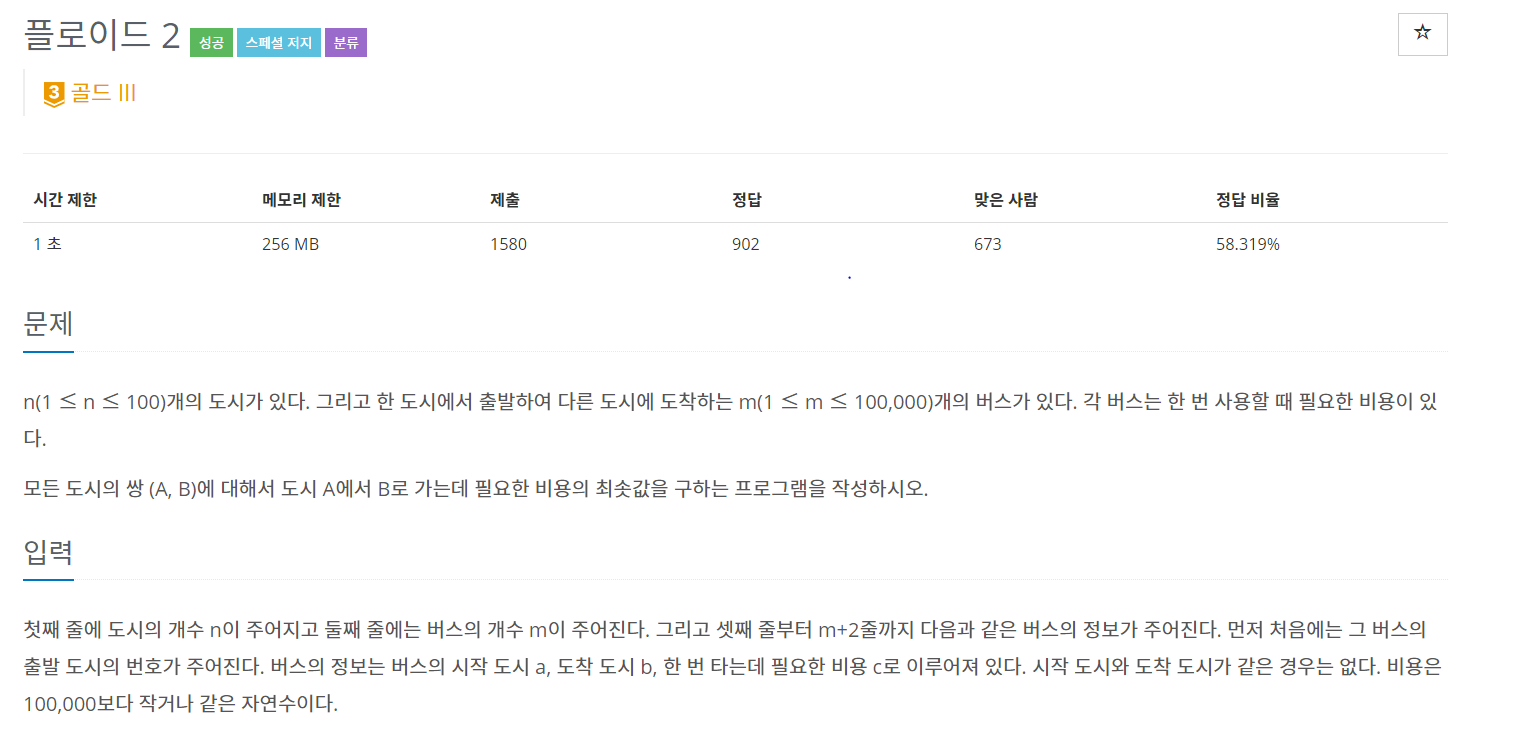
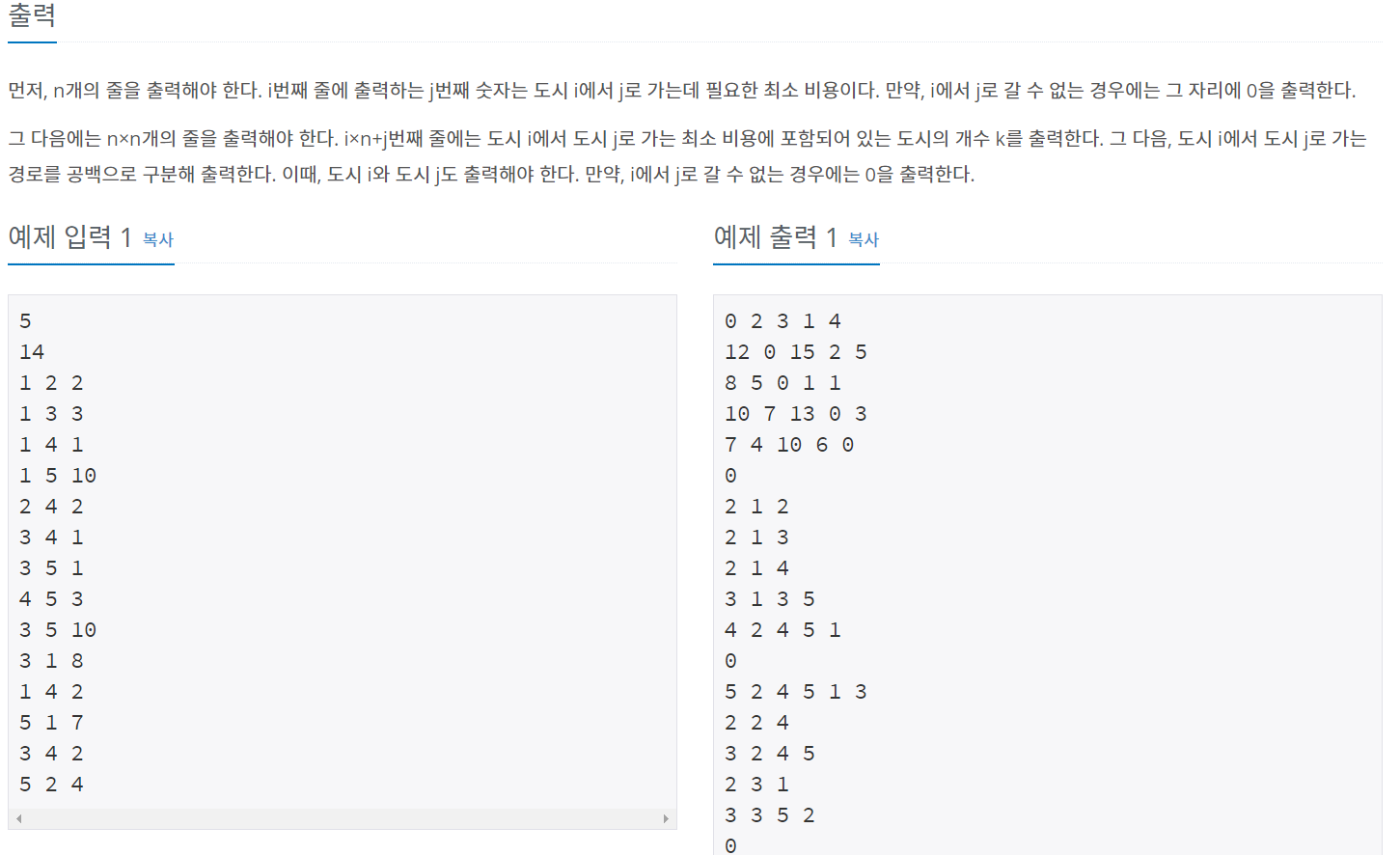
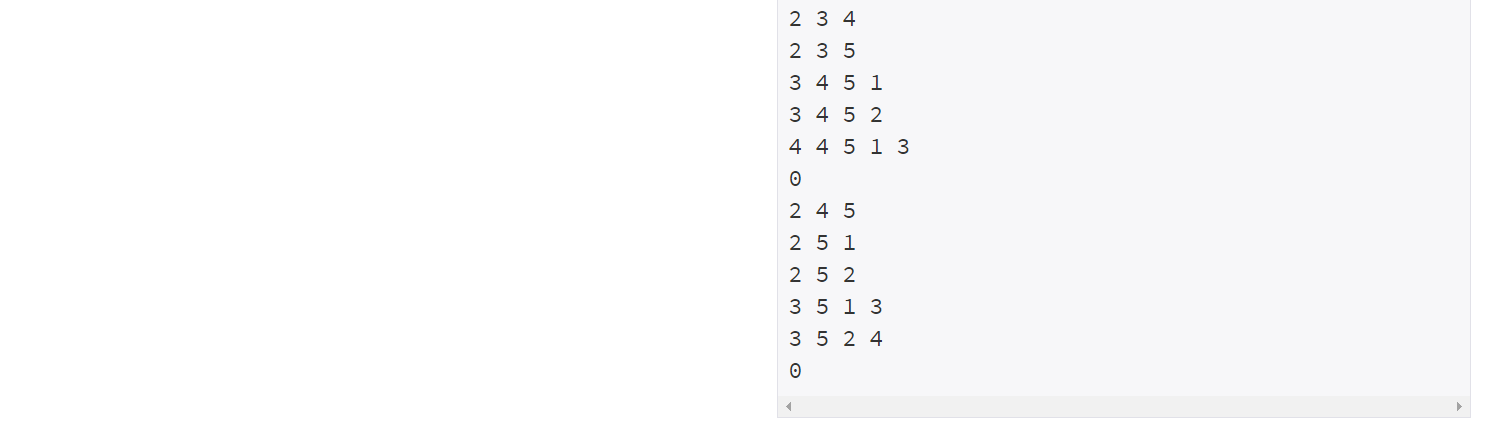
next배열은 a(정점) -> b(정점) 일 때, 출발 정점(a)의 값을 가지고 있다.
플로이드 알고리즘은 i -> k -> j 의 거리가 짧을 경우 최단거리(dist배열)을 갱신해준다.
동일하게 최단거리가 짧은 경우 출발 노드(next배열)을 k로 바꿔서 갱신해준다.
package pakcage26;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Stack;
public class num11780 {
static int N, M, INF = 100000000;
static int[][] dist, next;
static boolean[][] visited;
static Stack<Integer> stack;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
N = stoi(br.readLine());
M = stoi(br.readLine());
dist = new int[N][N];
next = new int[N][N];
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<N; j++) {
dist[i][j] = i == j ? 0 : INF;
next[i][j] = INF;
}
}
for(int i=0; i<M; i++) {
String[] abc = br.readLine().split(" ");
int a = stoi(abc[0])-1;
int b = stoi(abc[1])-1;
int c = stoi(abc[2]);
dist[a][b] = Math.min(dist[a][b], c);
next[a][b] = a;
}
floyd();
printPath();
}
public static void floyd() {
for(int k = 0; k<N; k++) {
for(int i = 0; i<N; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<N; j++) {
if(dist[i][j] > dist[i][k] + dist[k][j]) {
dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] +dist[k][j];
next[i][j] = next[k][j];
}
}
}
}
}
public static void printPath() {
for(int[] a : dist) {
for(int b: a) {
System.out.print(b + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<N; j++) {
if(next[i][j]==INF)
System.out.println(0);
else {
stack = new Stack<>();
int pre = j;
stack.push(j);
while(i != next[i][pre]) {
pre = next[i][pre];
stack.push(pre);
}
System.out.print((stack.size()+1)+" ");
System.out.print(i+1+" ");
while(!stack.empty())
System.out.print(stack.pop()+1+" ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
public static int stoi(String string) {
return Integer.parseInt(string);
}
}벨만포드 - 백준 1738

일차원 배열을 선언해 이전 경로의 값을 가지고 있는다.
기존의 벨만 포드 알고리즘과는 달리 음의 싸이클이 있으면 끝이 아니라,
음의 싸이클에 도착점으로 도달 가능해야 답이 -1이다.
4 4
1 4 3
2 3 1
3 2 1
4 2 1위의 테스트 케이스를 통과해야 정답이다.
이거 때문에 삽질 좀 했다 ㅜㅜ
package MinPath;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Stack;
public class num1738 {
static int N, M, INF = 987654321, INF2=-987654321;
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Edge>> Vertex;
static int[] preVertex;
static long[] dist;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] NM = br.readLine().split(" ");
N = stoi(NM[0]);
M = stoi(NM[1]);
dist = new long[N];
Vertex = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Edge>>();
preVertex = new int[N];
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
Vertex.add(new ArrayList<Edge>());
dist[i] = INF;
preVertex[i] = -1;
}
for(int i=0; i<M; i++) {
String[] uvw = br.readLine().split(" ");
int u = stoi(uvw[0])-1;
int v = stoi(uvw[1])-1;
int w = stoi(uvw[2]);
Vertex.get(u).add(new Edge(v, -w));
}
bellmanFord();
printPath();
}
public static void bellmanFord() {
dist[0] = 0;
preVertex[0] = 0;
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<N; j++) {
for(Edge edge : Vertex.get(j)) {
int next = edge.e, weight = edge.w;
if(dist[j]!=INF && dist[next] > dist[j] + weight) {
dist[next] = (dist[j] + weight);
preVertex[next] = j;
if(i == N-1) {
dist[next] = INF2;
}
}
}
}
}
}
public static void printPath() {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
if(dist[N-1] == INF || dist[N-1] == INF2)
sb.append("-1");
else{
for (int i = N-1 ; i != 0; i = preVertex[i]) {
if(dist[i] == INF2) {
System.out.println(-1);
return;
}else{
stack.push(i);
}
}
stack.push(0);
for (int i = stack.size(); i > 0; --i)
{
sb.append(stack.pop()+1+" ");
}
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
static class Edge{
int e, w;
Edge(int e, int w){
this.e = e;
this.w = w;
}
}
public static int stoi(String string) {
return Integer.parseInt(string);
}
}정리
세가지 알고리즘 모두 최단거리를 추적하면서
경로를 저장할 공간을 만들어서 저장하는 방식이다.