

React Hooks & Http Request
이번 포스팅에선 리액트 어플리케이션을 만들기 위해 사용하는 중요한 Hooks와 Http 요청에 대해 정리한다.
Side Effects(Refs) & More Hooks
Side Effects
함수가 실행되면서 함수 외부에 존재하는 값이나 상태를 변경시키는 등의 행위
(비동기로 처리되어야 하는 부수적인 효과)
ex) 브라우저 스토리지에 값 저장, 타이머, 백엔드 서버에 HTTP 요청 등
UseEffect()
Side Effect 처리를 위해 필요
useEffect(() => {}, [dependencies])useEffect함수는 2개의 매개 변수를 받음
1. 콜백함수,
2. 값이 변할 경우 콜백함수를 실행시키고 싶은 변수
-> 빈 배열이면 Component가 처음 마운트 되고 렌더링 될 때만 실행
-> 콜백함수 내부에서 사용하는 모든 변수는 배열에 추가되어야 한다- 첫번째 인자인 callback의 return 값으로 함수 반환 -> cleanUp 함수
- clean up 함수는 1번째 인자값으로 받은 함수(사이드 이펙트 함수)가 실행되기 전에 실행
(최초 실행시 동작x) - useEffect로 작성된 함수는 Promise객체를 반환 하면 에러
-> 함수를 따로 만들어 사용
Debouncing
연이어 호출되는 함수들 중 마지막 함수(또는 제일 처음)만 호출되도록 하는 것
useEffect(() => {
const identifier = setTimeout(() => {
setFormIsValid(
enteredEmail.includes('@') && enteredPassword.trim().length > 6,
)
}, 500)
// cleanUp 함수
return () => {
clearTimeout(identifier)
}
}, [enteredEmail, enteredPassword])ex) Form 태그 하위 요소 입력값 검증, AJAX 요청
Throttling
마지막 함수가 호출된 후 일정 시간이 지나기 전에 다시 호출되지 않도록 하는 것
ex) scroll 동작 시
Tip!!
- Debouncing, Throttling -> lodash 활용 가능
useReducer()
복잡한 state를 관리할 때 사용 다른 state기반으로 한 state를 업데이트 할 때 사용 (하나의 state로 병합)
일반적인 경우, 데이타 변경이 잦은 경우 -> useState사용
const [state, dispatchFn] = useReducer(reducerFn, initialState, initFn)첫번째 인자 reducer 함수
두번째 인자 initial State
세번째 인자 초기 state를 계산하는 함수
reducer함수는
첫번째 인자 - 현재 상태
두번째 인자 - 액션 객체 를 파라미터로 받아와 새로운 상태를 반환해주는 함수 반환
보통 dispatch함수의 액션 Type은 대문자로 명칭을 정해준다.Context API
어떤 컴포넌트에서라도 직접 다른 컴포넌트에 전달할 수 있게 해준다. props chain을 없앨 수 있음
앱 전체나 여러 컴포넌트에 영향을 주는 state 관리에 적합 (자주 바뀌는 경우 적합하지 않음)
import React from 'react';
const AuthContext = React.createContext({
iosLoggedIn: false,
});
export default AuthContext;React.createContext로 반환되는 값은 컴포넌트나 컴포넌트를 포함한 객체
만든 컴포넌트를 전역적인 위치에서 감싸준다.
// App.js
function App() {
// ...
return (
<AuthContext.Provider
value={{
isLoggedIn: isLoggedIn,
}}
>
<Header>
<Main>
</AuthContext.Provider>
);
}값을 받아오는 방법은 2가지
Consumer , react hooks 사용
- 사용하는 곳에서 Consumer 컴포넌트로 감싸 값을 가져옴
const Main = (props) => {
return (
<AuthContext.Consumer>
{(ctx) => {
return (
{ctx.isLoggedIn && (
<li>
<a href="/">Users</a>
</li>
)}
);
}}
</AuthContext.Consumer>
);
};- useContext()
const Main = (props) => {
const ctx = useContext(AuthContext);
return (
{ctx.isLoggedIn && (
<li>
<a href="/">Users</a>
</li>
)}
);
};state, state를 수정하는 로직을 모아서 사용 가능
// auth-context.js
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
// 선언을 해주면 IDE 자동 완성 가능
const AuthContext = React.createContext({
iosLoggedIn: false,
onLogout: () => {},
onLogin: () => {},
});
export const AuthContextProvider = (props) => {
const [isLoggedIn, setIsLoggedIn] = useState(false);
useEffect(() => {
const storedUserLoggedInInformation = localStorage.getItem('isLoggedIn');
if (storedUserLoggedInInformation === true) {
setIsLoggedIn(true);
}
}, []);
const logoutHandler = () => {
localStorage.setItem('isLoggedIn', true);
setIsLoggedIn(false);
};
const loginHandler = () => {
localStorage.removeItem('isLoggedIn');
setIsLoggedIn(true);
};
return (
<AuthContext.Provider value={{ isLoggedIn: isLoggedIn, onLogout: logoutHandler, onLogin: loginHandler }}>
{props.children}
</AuthContext.Provider>
);
};
export default AuthContext;
// index.js
root.render(
<AuthContextProvider>
<App />
</AuthContextProvider>,
);
// App.js
import React, { useContext } from 'react';
function App() {
const ctx = useContext(AuthContext);
return (
<React.Fragment>
<MainHeader onLogout={ctx.onlogout} />
<main>
{!ctx.isLoggedIn && <Login />}
{ctx.isLoggedIn && <Home />}
</main>
</React.Fragment>
);
}
export default App;Rules of Hooks
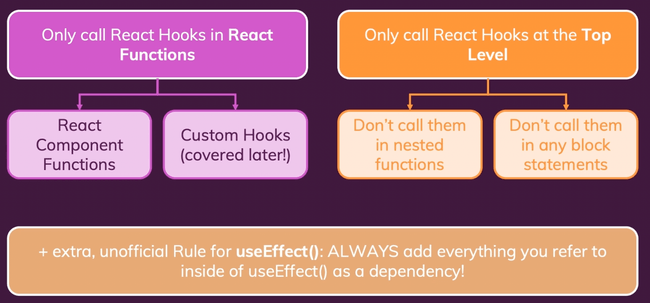
- 리액트 훅을 호출 시 1) 컴포넌트 함수, 2) 커스텀 훅에서만 사용
- 리액트 훅은 최상위 부분에서 호출
Forward Refs
React.forwardRef
부모 컴포넌트에서 하위 컴포넌트로 ref전달
useImperativeHandle
ref를 사용하는 부모 측에서 커스터마이징된 메서드를 사용 가능
ex) focusing, scrolling
useImperativeHandle(ref, createHandle, [deps])ref : 프로퍼티를 부여할 ref createHandle : 객체를 리턴하는 함수. 해당 객체에 추가하고 싶은 프로퍼티를 정의
// Login.js
const login = (props) => {
const emailInputRef = useRef();
const passwordInputRef = useRef();
...
const submitHandler = (event) => {
event.preventDefault();
if (formIsValid) {
authCtx.onLogin(emailState.value, passwordState.value);
} else if (!emailIsValid) {
emailInputRef.current.focus();
} else {
passwordInputRef.current.focus();
}
};
return (
<form onSubmit={submitHandler}>
<Input
ref={emailInputRef}
id="email"
label="E-Mail"
type="email"
isValid={emailIsValid}
value={emailState.value}
onChange={emailChangeHandler}
onBlur={validateEmailHandler}
/>
<Input
ref={passwordInputRef}
id="password"
label="Password"
type="password"
isValid={passwordIsValid}
value={passwordState.value}
onChange={passwordChangeHandler}
onBlur={validatePasswordHandler}
/>
<div className={classes.actions}>
<Button type="submit" className={classesbtn}>
Login
</Button>
</div>
</form>
);
}
// input.js
// React.forwardRef 메서드로 감싸줌
const Input = React.forwardRef((props, ref) => {
const inputRef = useRef();
const activate = () => {
inputRef.current.focus();
};
// 1) ref객체 , 2) 기능 트리거 될 함수 객체 리턴하는 익명 함수
useImperativeHandle(ref, () => {
return {
focus: activate,
};
});
return (
<div className={`${classes.control} ${props.isValid === false ? classes.invalid : ''}`}>
<label htmlFor={props.id}>{props.label}</label>
<input
ref={inputRef}
type={props.type}
id={props.id}
value={props.value}
onChange={props.onChange}
onBlur={props.onBlur}
/>
</div>
);
});React memoization
Component의 props, state, 부모 컴포넌트 렌더링에 따라 다시 실행 되는데 성능상의 이슈로 인해 리렌더가 일어나지 않도록 최적화 해주는 방법
React에서 컴포넌트가 렌더링 하는 규칙에는 크게 3가지
- state/props 변경 시
- forceUpdate() 실행 시
- 부모 컴포넌트가 렌더링 되었을 때
React.Memo()
같은 props를 받을 때 같은 결과를 렌더링한다면 React.memo를 사용하여 불필요한 컴포넌트 렌더링을 방지
다음 렌더링이 일어날 때 props가 같은 경우 성능향상
// 1
const Header = React.memo(() => {
return ()
})
// 2
export default React.memo(Header);
- 컴포넌트를 감싸서 사용
- 비교 방식을 커스텀하고 싶으면 두번째 인자로 비교하는 함수 추가
React.memo()를 사용하지 말아야 할 때
- 렌더링 될 때 props가 다른 경우가 대부분인 컴포넌트일 경우
-> 메모제이션 기법의 이점을 얻기 - 클래스 기반의 컴포넌트 일 경우 -> PureComponent, shouldComponentUpdate() 메서드를 구현해 사용하는 것이 적절
useMemo()
함수에 의해 나온 결과값을 메모리에 저장해서 컴포넌트가 반복적으로 렌더링 되어도 이미 가져온 결과값을 메모리에서 꺼내와 재사용 (값을 반환)
React.memo가 props, state에 의해 re-render를 관리한다면
useMemo는 함수의 결과 값을 memoizing하여 연산을 관리한다
const sortedList = useMemo(() => {
return items.sort((a, b) => a - b);
}, [items]);
console.log("DemoList RUNNING");useCallback()
특정 함수를 새로 만들지 않고 재사용하고 싶을때 사용 (함수를 반환)
const changeTitleHandler = useCallback(() => {
setListTitle('New Title');
}, []);dependency 배열에는 useEffect와 동일하게 어떤값이 변경되면 다시 생성할지에 대한 값들이 들어감
useEffect내부에 함수를 사용할 경우, 디펜던시 배열에 함수를 추가하면 무한 루프가 발생
-> 즉, useCallback 함수는 useEffect내부에서 사용하는 함수를 useCallback으로 감싸 동일한 객체를 사용할 수 있도록 사용
useCallback(fn, deps)은 useMemo(() => fn, deps)와 같음
useState, useReducer
컴포넌트가 초기화 될 때만 갱신된다.
성능 측정은 Dev tools Profiling 탭을 통해 가능하다.
Class Component
Function Component : 일반 컴포넌트와 달리 state, 라이플 사이클 기능 제거
-> 일반 클래스형 함수보다 빠르다
React life cycle은 React document 참고
| function | state | 기능 |
|---|---|---|
| useEffect(…, []) | componentDidMount() | 초기화 될 때마다 실행 |
| useEffect(…, [someValue]) | ComponentDidUpdate() | State가 없데이트 될 때 마다 실행 |
| useEffect(() => r{eturn () => {}}, []) | componentWillUnmount() | 컴포넌트가 실행되기 전에 실행 |
대체적으로 함수형으로 작성한게 this. 구문도 없애주고 깔끔한 코드를 작성할 수 있게 해주지만 에러를 잡아주는 부분은 클래스 컴포넌트로만 잡아줄 수 있다.
Error boundary
// ErrorBoundary.js
import { Component } from 'react';
class ErrorBoundary extends Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = { hasError: false };
}
componentDidCatch(error) {
console.log(error);
this.setState({ hasError: true });
}
render() {
if (this.state.hasError) {
return <p>에러 발생</p>;
}
return this.props.children;
}
}
export default ErrorBoundary;이런 식으로 componentDidCatch를 사용하는 ErrorBoundary 컴포넌트를 만들어 탐지하고 싶은 컴포넌트에 감싸서 사용한다
Forms, Http Request & Custom Hooks
Http Request
React에서 Http 요청을 하기 위한 2가지 방법
- axios
- fetch
비동기 처리를 위해 async, await 구문을 사용한다.
Custom Hooksre
로직 재사용(공유)을 위해 Hook 만들어 사용
- 함수의 이름은 use로 시작한다.
- Custom Hook을 통해 만들어진 상태는 각각의 컴포넌트마다 따로 상태 관리
// use-Https.js
import { useCallback, useState } from 'react';
const useHttp = () => {
const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(false);
const [error, setError] = useState(null);
// 1) 어떤 종류의 요청이든 가능하게
// 2) 어떤 데이터 변환도 가능하게
// 3) 로딩과 에러 상태 관리
const sendRequest = useCallback(async (requestConfig, applyData) => {
setIsLoading(true);
setError(null);
try {
const response = await fetch(requestConfig.url, {
method: requestConfig.method ? requestConfig.method : 'GET',
headers: requestConfig.headers ? requestConfig.headers : {},
body: requestConfig.body ? JSON.stringify(requestConfig.body) : null,
});
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error('Request failed!');
}
const data = await response.json();
// 2번째 인자로 받은 request 요청 후 처리 함수 실행
applyData(data);
} catch (err) {
setError(err.message || 'Something went wrong!');
}
setIsLoading(false);
}, []);
return {
isLoading,
error,
sendRequest,
};
};
export default useHttp;
// other Component
const [tasks, setTasks] = useState([]);
const { isLoading, error, sendRequest: fetchTasks } = useHttp();
useEffect(() => {
const transformTasks = (tasksObj) => {
const loadedTasks = [];
for (const taskKey in tasksObj) {
loadedTasks.push({ id: taskKey, text: tasksObj[taskKey]text });
}
setTasks(loadedTasks);
};
fetchTasks({ url: url }, transformTasks);
}, []);
Form
사용자의 입력값을 검증하는 방법 3가지
| 동작 | 장점 | 단점 |
|---|---|---|
| Form 요청을 제출 | 불필요한 알림을 줄일 수 있다 | 사용자에게 알리는 시점이 늦다 |
| Input 포커스 해제 | 폼 데이터를 제출하기 전에 사용자에게 알릴 수 있다 | 포커스를 잃었을 때만 동작 |
| 사용자의 키 입력마다 | 빠른 피드백 가능 | 사용자의 입력을 전부 받기 전에 알림 |
비즈니스 요구사항에 따라 적절히 조합해 값 검증
Tip!!
태그의 속성들을 객체로 만들어 속성값을 한번에 넘겨서 사용하면 깔끔한 코드 작성 가능
// Component
return = (
...
<Input
label="Amount"
input={{
id: 'amount_' + props.id,
type: 'number',
min: '1',
max: '5',
step: '1',
defaultValue: '1',
}}
/>
...
)
// input.js
const Input = (props) => {
return (
<div>
<label htmlFor={props.input.id}>{props.label}</label>
<input {...props.input} />
</div>
);
};
export default Input;
reducer 함수 작성 시 배열값을 추가할 때 concat으로 값을 추가하면 새로운 객체로 값을 생성해서 이전 상태를 바꾸지 않고 처리 가능
React는 함수 내 상태를 업데이트하는 여러개의 함수가 있어도 하나의 동기화 프로세스에서 같이 실행한다