
구간합(Prefix Sum) 배열
Algorithm
2021.02.02.
구간합 배열
전처리를 통해 모든 부분합을 O(1)으로 구할 수 있는 방법
1. 원래 배열 이외에 pSum배열을 추가로 하나 만들어 준다.
2. pSum[x] 배열에는 앞에서 부터 x개 원소의 합을 저장한다.
-> pSum[i+1] = pSum[i] + A[i]
백준 11659 - 구간 합 구하기4
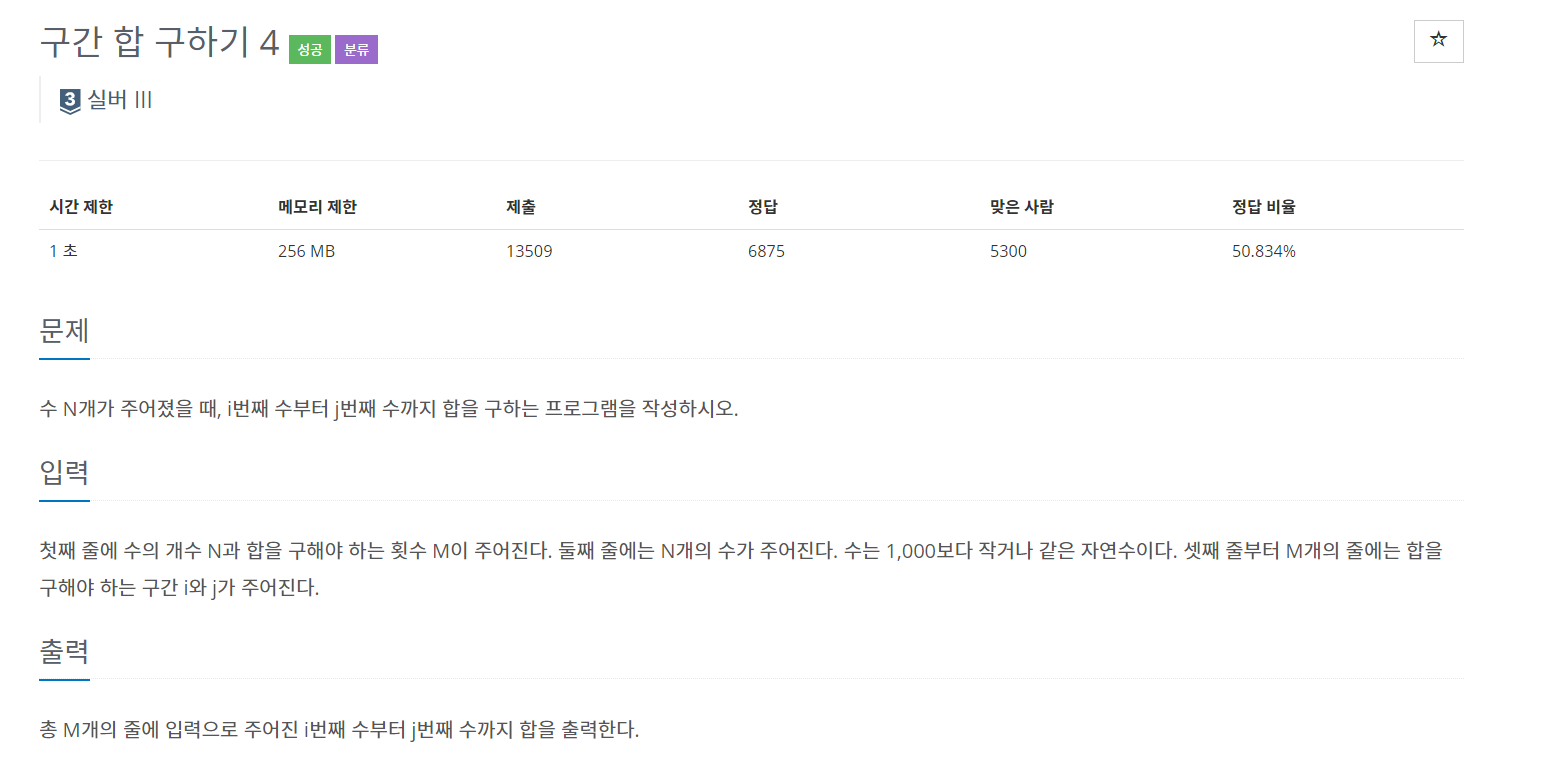
풀이
pSum[i+1] - pSum[j]를 해주면 된다.
package sumOfInterval;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class num11659 {
static int N, M;
static int[] arr, pSum;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
String[] NM = br.readLine().split(" ");
N = stoi(NM[0]);
M = stoi(NM[1]);
arr = new int[N];
pSum = new int[N+1];
String[] arrData = br.readLine().split(" ");
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
arr[i] = stoi(arrData[i]);
pSum[i+1] = arr[i] + pSum[i];
}
for(int i=0; i<M; i++) {
String[] AB = br.readLine().split(" ");
int a = stoi(AB[0])-1;
int b = stoi(AB[1])-1;
sb.append(pSum[b+1] - pSum[a] + "\n");
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
public static int stoi(String string) {
return Integer.parseInt(string);
}
}
백준 11660 - 구간 합 구하기5
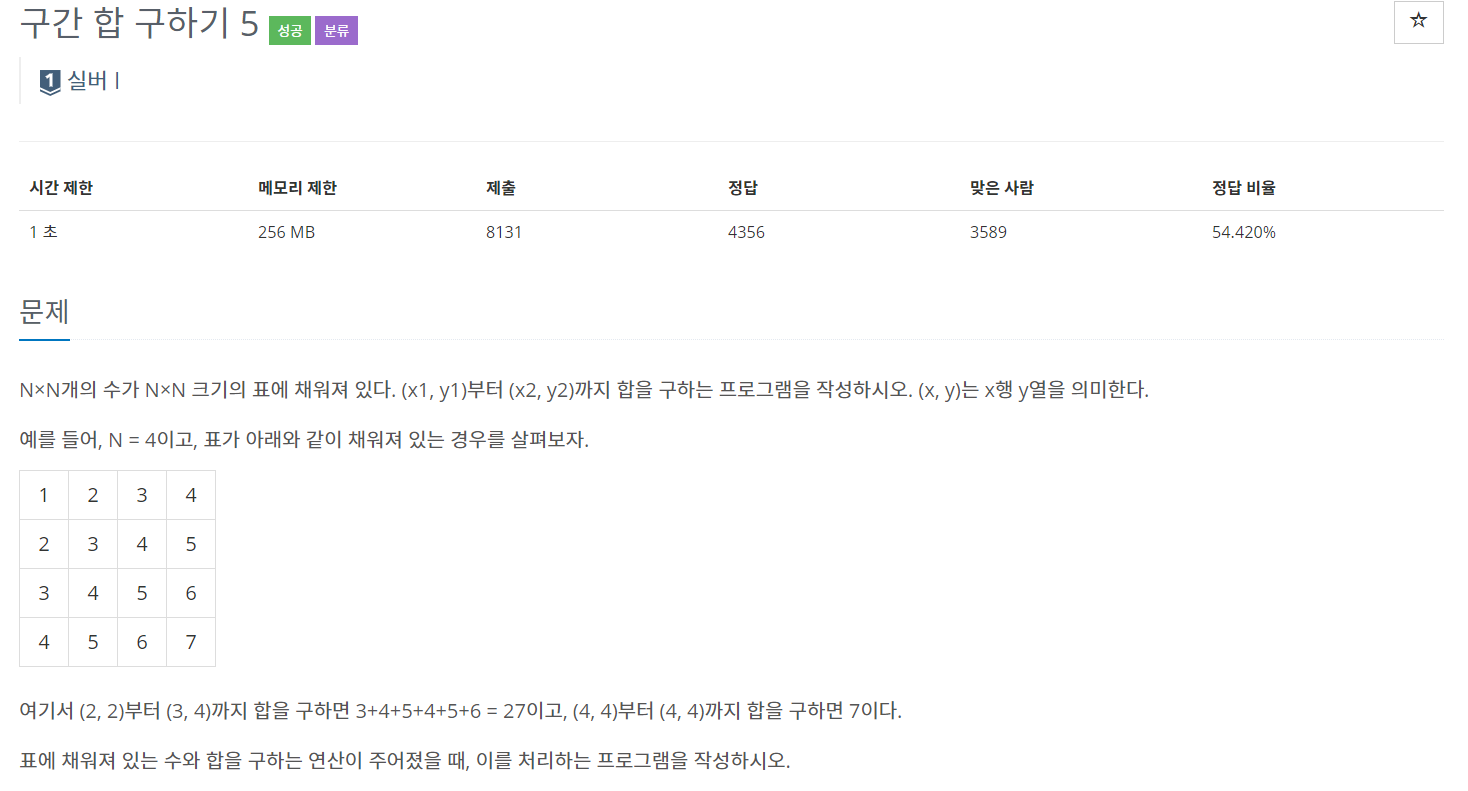
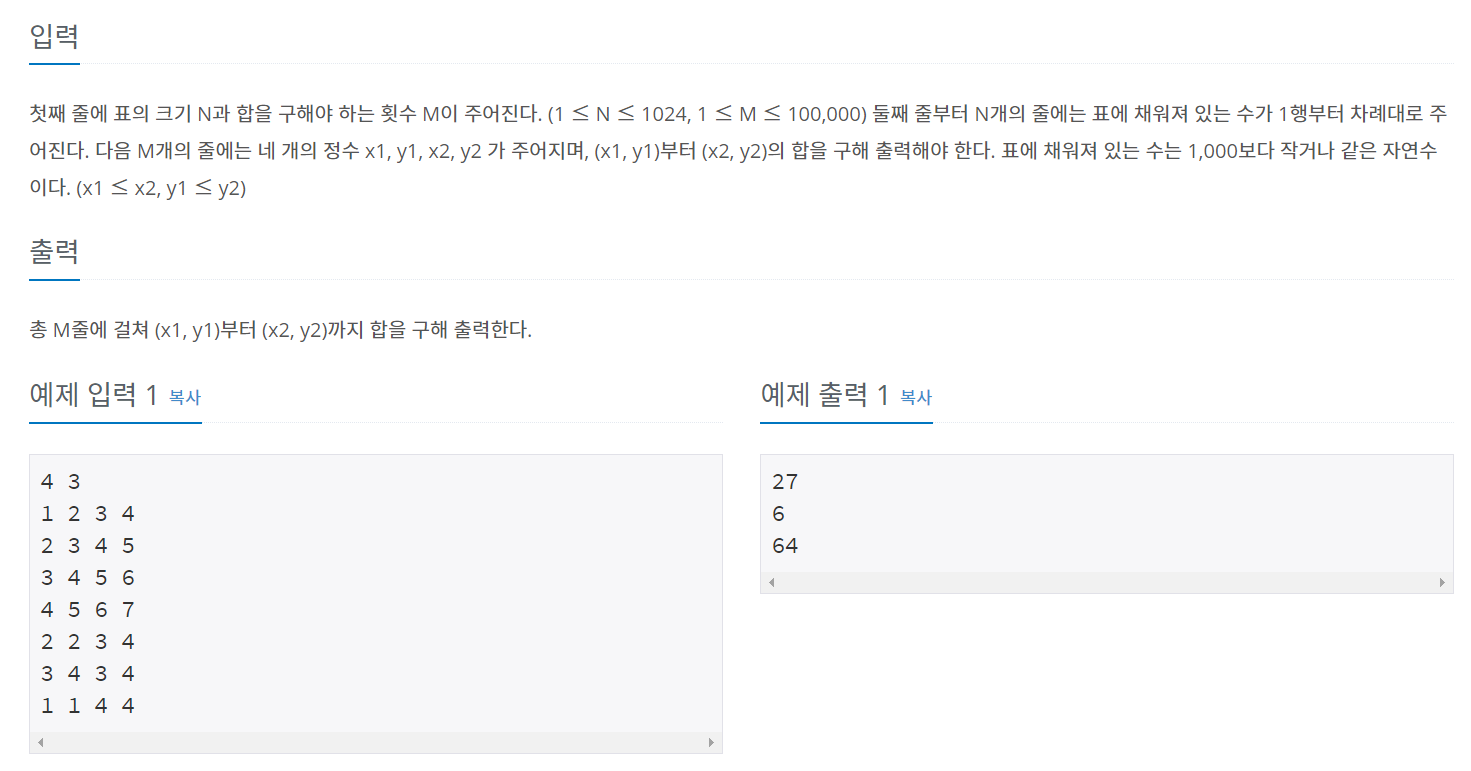
풀이
이전 문제와 비슷한데 2차원 배열을 사용해 pSum을 저장한다.
빼줄 때 범위 설정에 주의한다.
package sumOfInterval;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class num11660 {
static int N, M, x1, x2, y1, y2;
static int[][] map, pSum;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
String[] NM = br.readLine().split(" ");
N = stoi(NM[0]);
M = stoi(NM[1]);
map = new int[N+1][N+1];
pSum = new int[N+2][N+2];
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
String[] row = br.readLine().split(" ");
for(int j=0; j<N; j++) {
map[i][j] = stoi(row[j]);
pSum[i+1][j+1] = pSum[i+1][j] + pSum[i][j+1] - pSum[i][j] + map[i][j];
}
}
for(int i=1; i<=M; i++) {
String[] point = br.readLine().split(" ");
x1 = stoi(point[0]);
y1 = stoi(point[1]);
x2 = stoi(point[2]);
y2 = stoi(point[3]);
sb.append(pSum[x2][y2] - pSum[x1-1][y2] - pSum[x2][y1-1] + pSum[x1-1][y1-1] + "\n");
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
public static int stoi(String string) {
return Integer.parseInt(string);
}
}
백준 10211 - Maximum Subarray
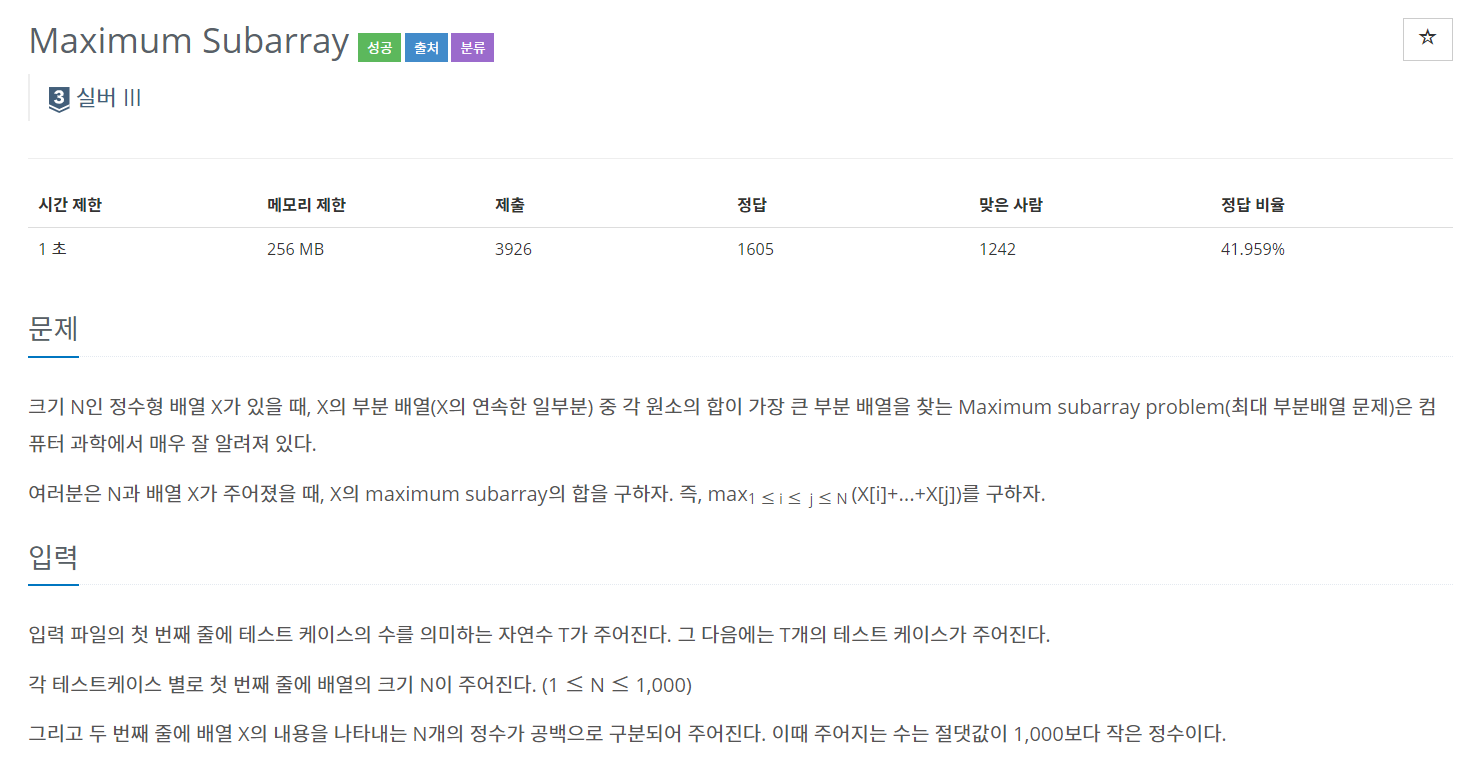
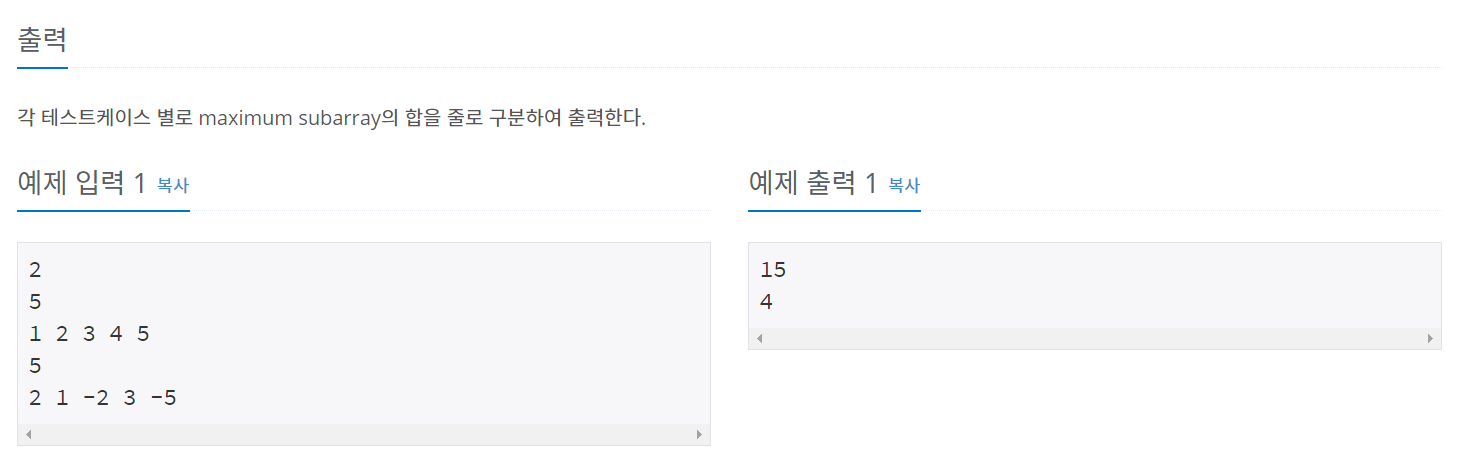
풀이
1
2
-7 5별 생각 없이 풀다가 위 CASE에 걸리는 걸 알았다.
전까지 합이 음수고, 새롭게 들어온 값이 양수라면 새롭게 들어온 값부터 더해준 값이 최대값이다.
위 문장에 대한 처리를 해야한다.
package sumOfInterval;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class num10211 {
static int N, X, MAX;
static int[] arr, pSum;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
N = stoi(br.readLine());
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
MAX = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
X = stoi(br.readLine());
String[] arrData = br.readLine().split(" ");
arr = new int[X];
pSum = new int[X+1];
for(int j=0; j<X; j++) {
arr[j] = stoi(arrData[j]);
pSum[j+1] = Math.max(pSum[j], 0) + arr[j];
MAX = MAX > pSum[j+1] ? MAX : pSum[j+1];
}
sb.append(MAX+"\n");
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
public static int stoi(String string) {
return Integer.parseInt(string);
}
}
백준 10986 - 나머지 합
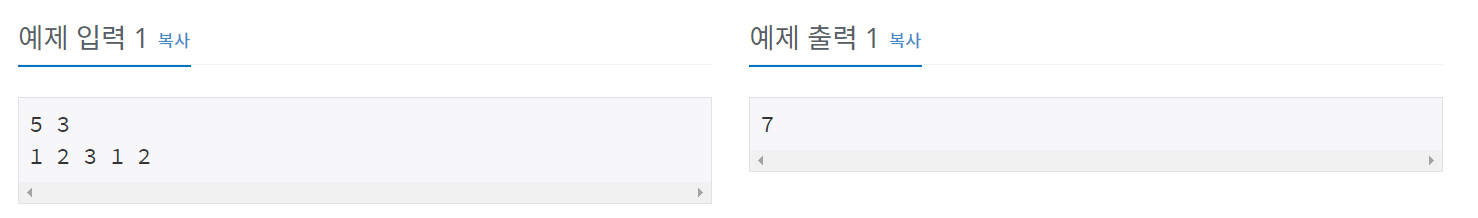
풀이
이 문제는 발상의 전환이 필요하다.
pSum[j] % M 와 pSum[i] % M 나머지가 같으면 나누어 떨어지는 구간이다.
-> M으로 나눴을 때 나머지를 저장하는 누적합 배열을 만든다.
-> 나머지의 개수를 저장하는 배열을 하나 더 만들어서 나머지에 대한 개수를 저장한다.
-> 나머지의 순서에 상관없이 2개씩 뽑는 개수를 모두 더한다.
package sumOfInterval;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class num10986 {
static long N, M, ans;
static long[] cnt, pSum;
static final int MAX = 1000000 + 1;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] NM = br.readLine().split(" ");
N = stol(NM[0]);
M = stol(NM[1]);
cnt = new long[(int)M];
pSum = new long[(int)N+1];
String[] arrData = br.readLine().split(" ");
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++) {
long num = stol(arrData[i-1]);
pSum[i] = (pSum[i - 1] + num) % M;
cnt[(int) pSum[i]]++;
if(pSum[i] == 0) ans++;
}
for(int i = 0 ; i < M ; ++i) {
ans += cnt[i] * (cnt[i] - 1) / 2;
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
public static long stol(String string) {
return Long.parseLong(string);
}
}