순열, 조합, 중복 순열, 중복 조합, 부분 집합
Algorithm
2022.10.31.
n, m, arr을 받아 순열, 조합, 중복 순열, 중복 조합 전부 출력하는 형태로 구현 해보자
정리하고 백트래킹 문제 좀 풀어봐야 겠따
| 종류 | 정의 | 중복 | 순서 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 순열 | n개의 원소 중 r개를 순서를 고려 해 나열 | X | O |
| 중복 순열 | n개의 원소 중 r개를 중복을 허용하고, 순서 고려해 나열 | O | O |
| 조합 | n개의 원소 중 r개를 순서 생각하지 않고 나열 | X | X |
| 중복 조합 | n개의 원소 중 r개를 중복을 허용하고, 순서를 생각하지 않고 | O | X |
순열
// static int arr[], n, r, totalCnt / ArrayList<int[]> res; / boolean[] visited
public static void permutation(int cnt, int[] selected) {
if (cnt == r) {
totalCnt++;
int[] saveArr = selected.clone();
res.add(saveArr);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (visited[i]) {
continue;
}
visited[i] = true;
selected[cnt] = arr[i];
permutation(cnt + 1, selected);
visited[i] = false;
}
}visited배열을 사용해서 방문체크를 해 중복 제거하며 전체를 돌 수 있게 한다
중복 순열
// static int arr[], n, r, totalCnt / ArrayList<int[]> res; / boolean[] visited
public static void rePermutation(int cnt, int[] selected) {
if (cnt == r) {
totalCnt++;
int[] saveArr = selected.clone();
res.add(saveArr);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
selected[cnt] = arr[i];
rePermutation(cnt + 1, selected);
}
}순열에서 중복 된 값을 처리해주는 visited 배열 제거
조합
// static int arr[], n, r, totalCnt / ArrayList<int[]> res;
public static void combination(int idx, int cnt, int[] selected) {
if(cnt == r) {
totalCnt++;
int[] saveArr = selected.clone(); // 객체 복사 - 원본 배열과 별개의 주소값으로 새로운 객체 생성
res.add(saveArr);
return;
}
for(int i = idx; i<n; i++){
selected[cnt] = arr[i];
combination(i + 1, cnt + 1, selected);
}
}index를 변경해 이전 수 참조할 수 없게 다음 값을 인덱스로 전달
중복 조합
// static int arr[], n, r, totalCnt / ArrayList<int[]> res;
public static void reCombination(int idx, int cnt, int[] selected) {
if (cnt == r) {
totalCnt++;
int[] saveArr = selected.clone(); // 객체 복사 - 원본 배열과 별개의 주소값으로 새로운 객체 생성
res.add(saveArr);
return;
}
for (int i = idx; i < n; i++) {
selected[cnt] = arr[i];
reCombination(i, cnt + 1, selected);
}
}s중복 조합은 조합 소스에서 index를 자기 자신은 가능하지만, 이전 값들을 다시 쓸 수 없게 구현하면 된다.
전체 소스
package math;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class example {
static int arr[], n, r, totalCnt;
static boolean visited[];
static ArrayList<int[]> res;
static String[] commands = {
"permutation", "rePermutation", "combination", "reCombination"
};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] nr = br.readLine().split(" ");
n = stoi(nr[0]);
r = stoi(nr[1]);
arr = new int[n];
String[] input = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = stoi(input[i]);
}
for (String command : commands) {
run(command);
}
}
public static void run(String command) {
init();
switch (command) {
case "permutation":
permutation(0, new int[r]);
break;
case "rePermutation":
rePermutation(0, new int[r]);
break;
case "combination":
combination(0, 0, new int[r]);
break;
case "reCombination":
reCombination(0, 0, new int[r]);
break;
}
printResult(command);
}
public static void init() {
totalCnt = 0;
res = new ArrayList<>();
visited = new boolean[n];
}
// static int arr[], n, r, totalCnt / ArrayList<int[]> res; / boolean[] visited
public static void permutation(int cnt, int[] selected) {
if (cnt == r) {
totalCnt++;
int[] saveArr = selected.clone();
res.add(saveArr);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (visited[i]) {
continue;
}
visited[i] = true;
selected[cnt] = arr[i];
permutation(cnt + 1, selected);
visited[i] = false;
}
}
// static int arr[], n, r, totalCnt / ArrayList<int[]> res; / boolean[] visited
public static void rePermutation(int cnt, int[] selected) {
if (cnt == r) {
totalCnt++;
int[] saveArr = selected.clone();
res.add(saveArr);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
selected[cnt] = arr[i];
rePermutation(cnt + 1, selected);
}
}
// static int arr[], n, r, totalCnt / ArrayList<int[]> res;
public static void combination(int idx, int cnt, int[] selected) {
if (cnt == r) {
totalCnt++;
int[] saveArr = selected.clone(); // 객체 복사 - 원본 배열과 별개의 주소값으로 새로운 객체 생성
res.add(saveArr);
return;
}
for (int i = idx; i < n; i++) {
selected[cnt] = arr[i];
combination(i + 1, cnt + 1, selected);
}
}
// static int arr[], n, r, totalCnt / ArrayList<int[]> res;
public static void reCombination(int idx, int cnt, int[] selected) {
if (cnt == r) {
totalCnt++;
int[] saveArr = selected.clone(); // 객체 복사 - 원본 배열과 별개의 주소값으로 새로운 객체 생성
res.add(saveArr);
return;
}
for (int i = idx; i < n; i++) {
selected[cnt] = arr[i];
reCombination(i, cnt + 1, selected);
}
}
public static void printResult(String command) {
System.out.print(command);
System.out.print("( ");
for (int n : arr) {
System.out.print(n + " ");
}
System.out.println(")");
System.out.println("totalCount : " + totalCnt);
for (int[] list : res) {
for (int item : list) {
System.out.print(item + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
}
public static int stoi(String s) {
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}
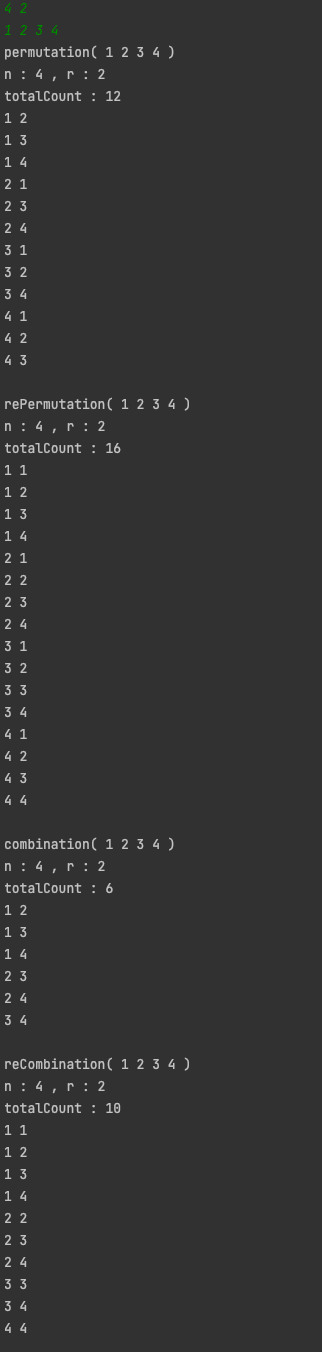
결과
백준 N과 M ( 1 ~ 4 )문제가 순서대로 순열, 조합, 중복순열, 중복 조합 문제
(검증하기 좋다 ㅎㅎ)