
최소 신장 트리 정리
신장 트리(Spnning Tree)
하나의 그래프가 있을 때 모든 노드를 포함하면서 사이클이 존재하지 않는 부분 그래프
최소 신장 트리(Minimum Spanning Tree)
트리의 간선마다 가중치가 있을 때, 간선의 가중치 합이 최소인 트리
신장 트리의 최소비용을 구하는 크루스칼 알고리즘, 프림 알고리즘 2가지 알고리즘에 대해 정리한다.
크루스칼 알고리즘
간선 선택 기반의 알고리즘으로, 탐욕적인 방법을 이용, 간선을 하나씩 선택해서 MST를 찾는 알고리즘입니다.
특징
- 그리디 알고리즘의 일종 -> 작은 간선부터 훑기 때문에
- 시간 복잡도 : O(ElogE)
-> 가중치 별로 정렬 : O(ElogE) + 정점이 같은 컴포넌트에 속해있는지 확인 : 약 O(1) = O(ElogE)
구현 방법
1. 간선을 비용에 따라 오름차순으로 정리하고, 정점을 초기화한다
2. 간선을 하나씩 확인하며 간선이 싸이클을 발생시키지 않으면 간선을 포함시킨다.
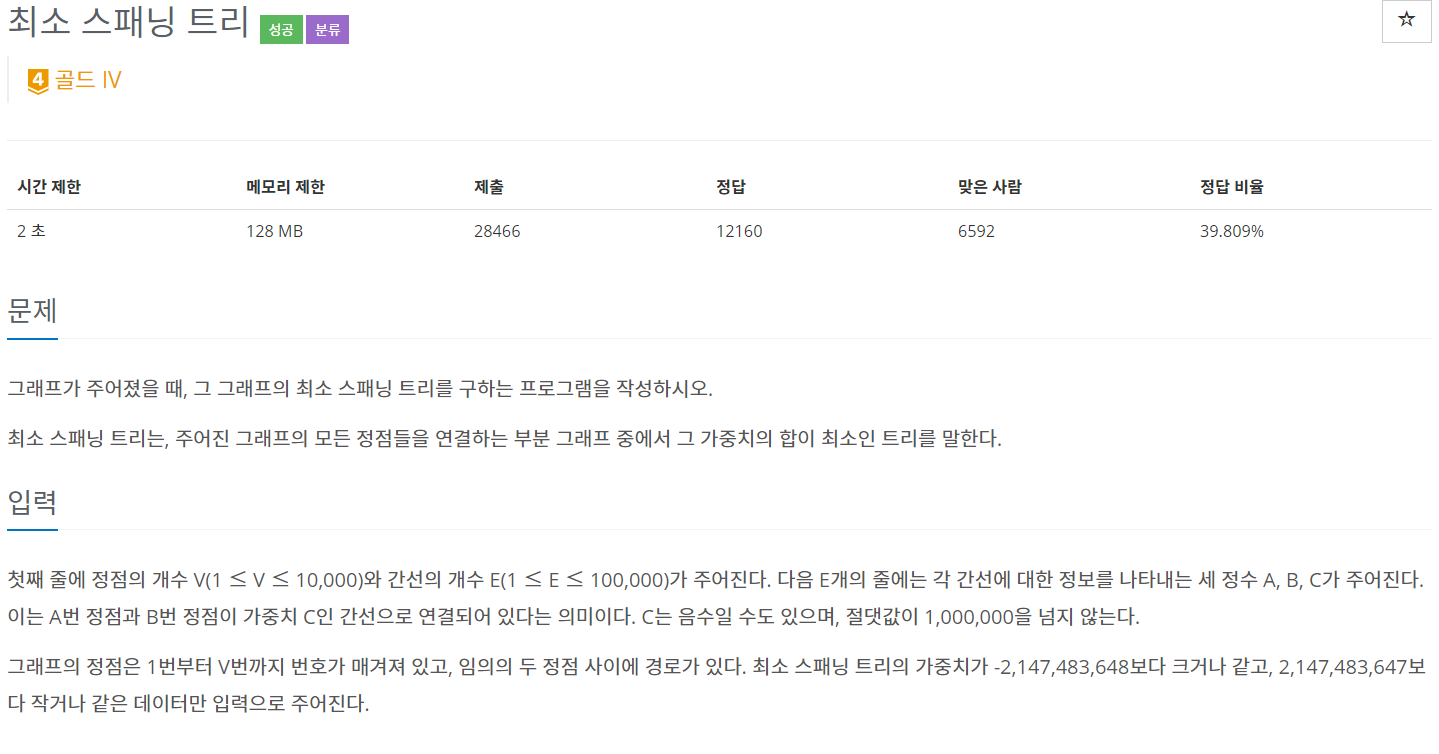
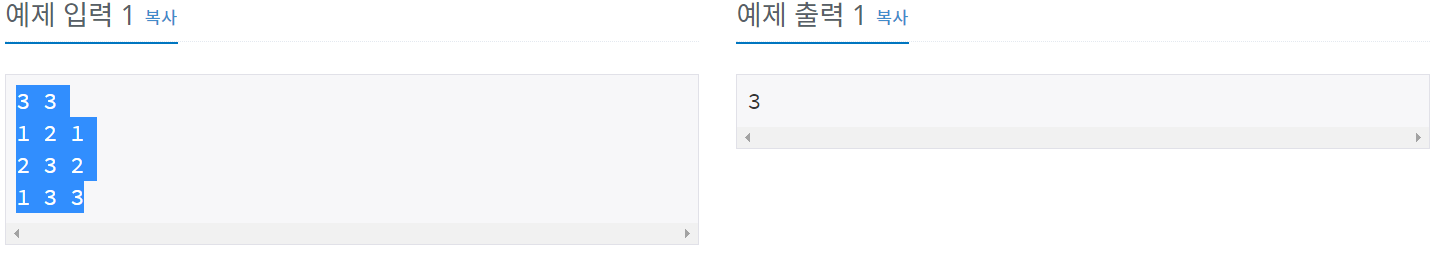
3. 간선을 V-1개 뽑았을 때, 이루는 그래프가 MST이다.백준 1197 - 최소 스패닝 트리
풀이
- 간선 클래스를 만들어 우선순위 큐로 저장한다.
- union find를 사용해 싸이클 검사와 거리를 더해준다.
package package29;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class num1197 {
static int V, E, result=0, cnt=0;
static int[] parent;
static PriorityQueue<Edge> pq = new PriorityQueue<Edge>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] VE = br.readLine().split(" ");
V = stoi(VE[0]);
E = stoi(VE[1]);
parent = new int[V+1];
for(int i=0; i<V+1; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
for(int i=0; i<E; i++) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
pq.add(new Edge(stoi(st.nextToken()),stoi(st.nextToken()),stoi(st.nextToken())));
}
for(int i=0; i<E; i++) {
Edge temp = pq.poll();
int a = temp.s;
int b = temp.e;
if(!union(a, b))
continue;
result+= temp.w;
cnt++;
if(cnt == V-1)
break;
}
System.out.println(result);
}
static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge>{
int s, e, w;
Edge(int s, int e, int w){
this.s = s;
this.e = e;
this.w = w;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge o) {
return o.w >= this.w ? -1: 1;
}
}
public static int find_parent(int num) {
if(parent[num] != num)
return parent[num] = find_parent(parent[num]);
return parent[num];
}
public static boolean union(int a, int b) {
a = find_parent(a);
b = find_parent(b);
if(a==b) {
return false;
}
else if(a < b)
parent[b] = a;
else
parent[a] = b;
return true;
}
public static int stoi(String string) {
return Integer.parseInt(string);
}
}
백준 4386 - 별자리 만들기
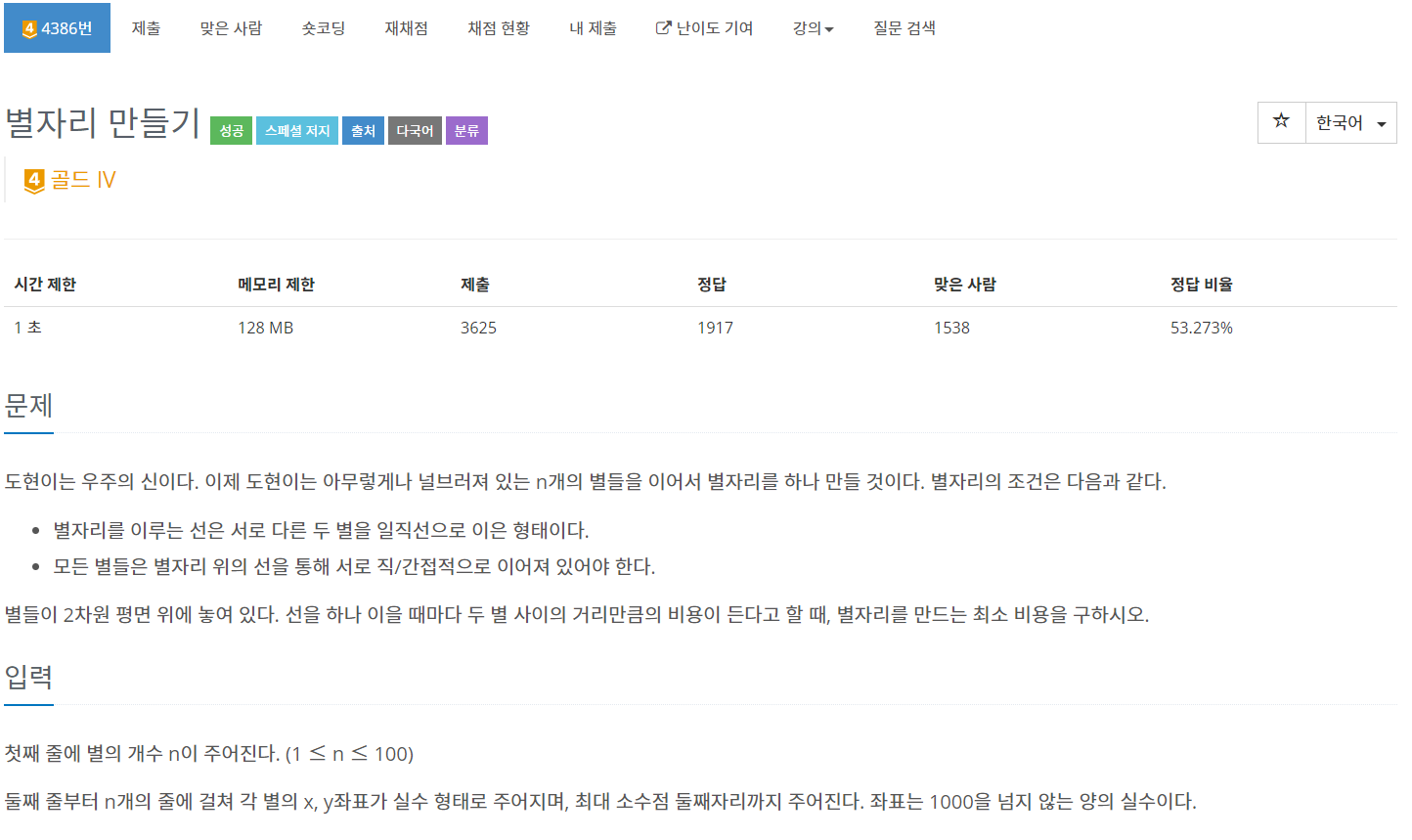
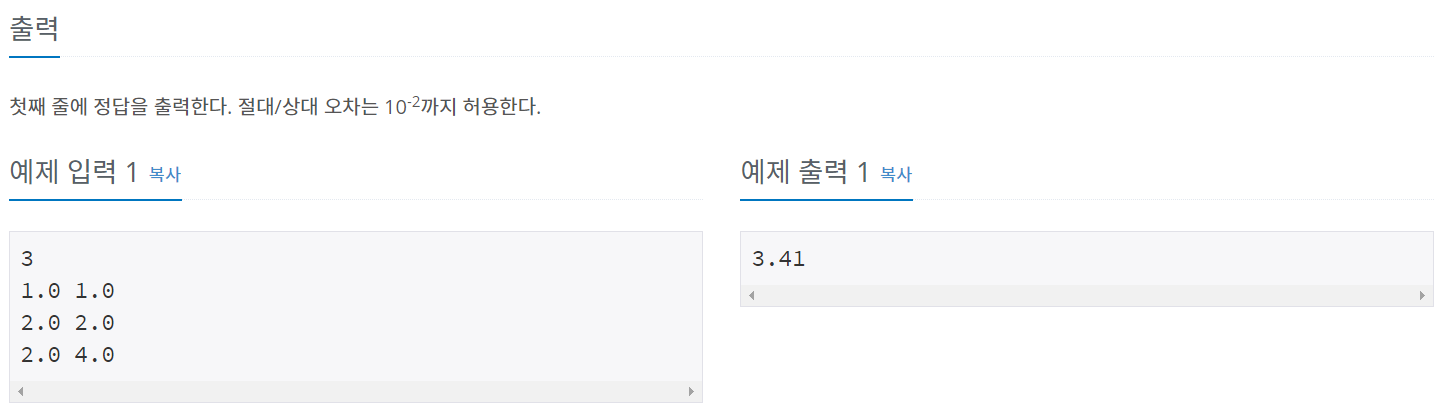
풀이
정점의 x좌표와 y좌표를 저장할 수 있는 클래스를 만들어 사용했다.
위의 문제는 가중치가 주어졌지만, 4386번문제는 가중치를 두 점사이 거리로 계산해서 넣어야 한다.
package package29;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class num4386 {
static int N, cnt=0;
static double result = 0;
static int[] parent;
static PriorityQueue<Edge> pq = new PriorityQueue<Edge>();
static Vertex[] v;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = stoi(br.readLine());
parent = new int[N+1];
v = new Vertex[N+1];
for(int i=1; i<=N+1; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()," ");
v[i] = new Vertex(stod(st.nextToken()), stod(st.nextToken()));
}
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++) {
for(int j=i+1; j<=N; j++) {
pq.add(new Edge(i, j, getDistance(v[i].x, v[j].x, v[i].y, v[j].y)));
}
}
for(int i=0; i<pq.size(); i++) {
Edge temp = pq.poll();
int a = temp.s;
int b = temp.e;
if(!union(a, b))
continue;
result+= temp.w;
cnt++;
if(cnt == N-1)
break;
}
System.out.println(String.format("%.2f", result));
}
static class Vertex{
double x, y;
Vertex(double x, double y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge>{
int s, e;
double w;
Edge(int s, int e, double w){
this.s = s;
this.e = e;
this.w = w;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge o) {
return o.w >= this.w ? -1: 1;
}
}
public static int find_parent(int num) {
if(parent[num] != num)
return parent[num] = find_parent(parent[num]);
return parent[num];
}
public static boolean union(int a, int b) {
a = find_parent(a);
b = find_parent(b);
if(a==b) {
return false;
}
else if(a < b)
parent[b] = a;
else
parent[a] = b;
return true;
}
public static double getDistance(double x1, double x2, double y1, double y2) {
return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(Math.abs(x1 - x2), 2) + Math.pow(Math.abs(y1 - y2), 2));
}
public static int stoi(String string) {
return Integer.parseInt(string);
}
public static double stod(String string) {
return Double.parseDouble(string);
}
}
백준 1647 - 도시 분할 계획
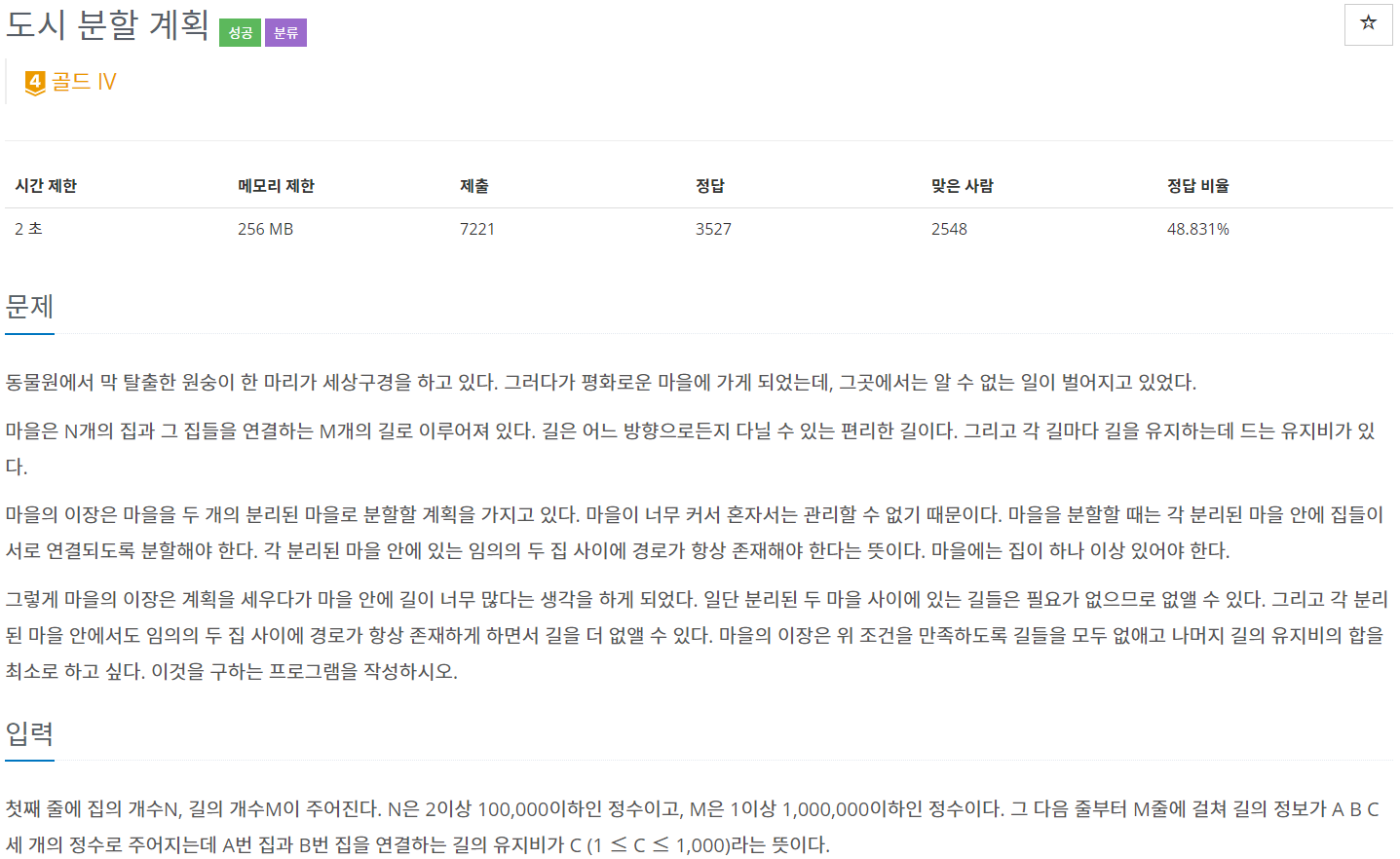
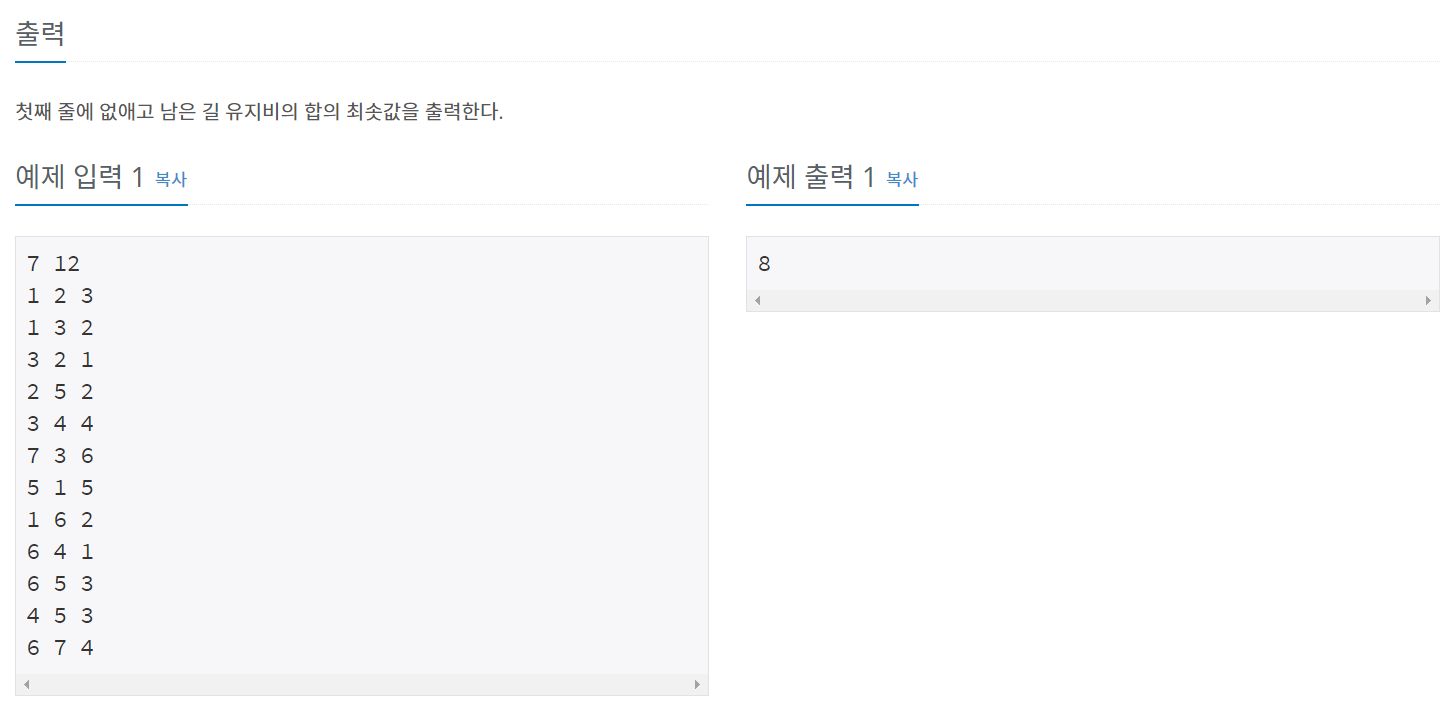
풀이
도시를 2개로 나눈다고 했으니 크루스칼 알고리즘이 끝나는 조건을 N-2로 작성해야 한다.
package MST;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class num1647 {
static int N, M, result=0, cnt=0;
static int[] parent;
static PriorityQueue<Edge> pq = new PriorityQueue<Edge>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st;
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = stoi(st.nextToken());
M = stoi(st.nextToken());
parent = new int[N+1];
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
for(int i=0; i<M; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int s = stoi(st.nextToken()), e = stoi(st.nextToken()), w = stoi(st.nextToken());
pq.add(new Edge(s,e,w));
}
while(!pq.isEmpty()) {
Edge temp = pq.poll();
int a = temp.s;
int b = temp.e;
if(!union(a, b))
continue;
result += temp.w;
cnt++;
if(cnt == N-2)
break;
}
System.out.println(result);
}
static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> {
int s, e, w;
Edge(int s, int e, int w) {
this.s = s;
this.e = e;
this.w = w;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge o) {
return o.w >= this.w ? -1 : 1;
}
}
public static int find_parent(int num) {
if(parent[num] != num)
return parent[num] = find_parent(parent[num]);
return parent[num];
}
public static boolean union(int a, int b) {
a = find_parent(a);
b = find_parent(b);
if(a==b)
return false;
if(a < b)
parent[b] = a;
else
parent[a] = b;
return true;
}
public static int stoi(String string) {
return Integer.parseInt(string);
}
}
백준 1774 - 우주신과의 교감
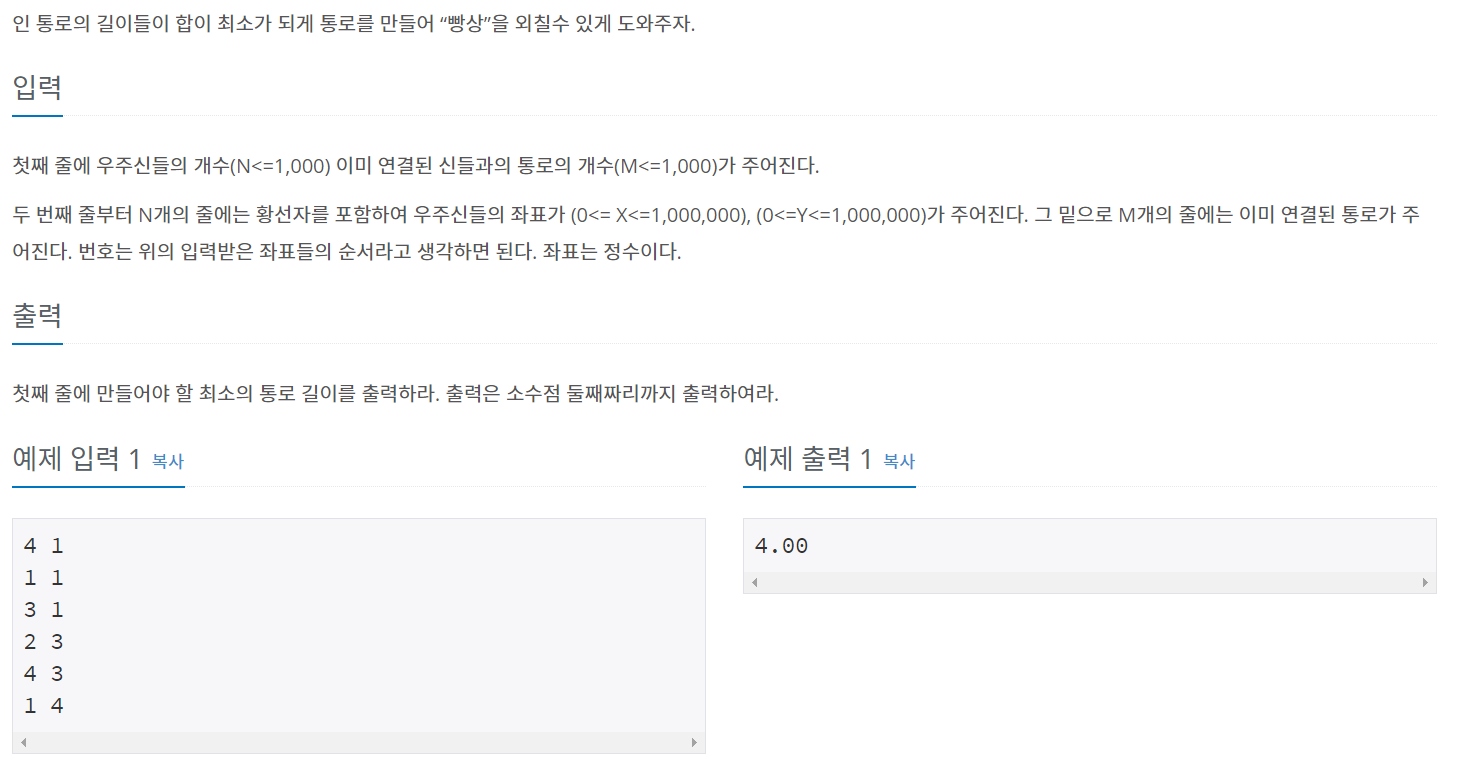
풀이
일반적인 최소 스패닝 트리 문제다. 1197번과 풀이가 동일하다.
package package29;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class num1774 {
static int N, M, cnt = 0;
static PriorityQueue<Edge> pq = new PriorityQueue<Edge>();
static int[] parent;
static Node[] arr;
static double minLen = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] NM = br.readLine().split(" ");
N = stoi(NM[0]);
M = stoi(NM[1]);
Node[] arr = new Node[N+1];
parent = new int[N+1];
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++) {
String[] XY = br.readLine().split(" ");
arr[i] = new Node(stoi(XY[0]), stoi(XY[1]));
}
for(int i=0; i<M; i++) {
String[] se = br.readLine().split(" ");
int s = stoi(se[0]);
int e = stoi(se[1]);
union(s, e);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j <= N; j++) {
pq.add(new Edge(i, j, getDistance(arr[i].x, arr[j].x, arr[i].y, arr[j].y)));
}
}
for(int i=0; i<pq.size(); i++) {
Edge temp = pq.poll();
int a = temp.s;
int b = temp.e;
if(!union(a, b))
continue;
minLen+= temp.w;
}
System.out.println(String.format("%.2f", minLen));
}
static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge>{
int s, e;
double w;
Edge(int s, int e, double w){
this.s = s;
this.e = e;
this.w = w;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge o) {
return o.w >= this.w ? -1: 1;
}
}
public static double getDistance(double x1, double x2, double y1, double y2) {
return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(Math.abs(x1 - x2), 2) + Math.pow(Math.abs(y1 - y2), 2));
}
public static int find_parent(int num) {
if(parent[num] != num)
return parent[num] = find_parent(parent[num]);
return parent[num];
}
public static boolean union(int a, int b) {
a = find_parent(a);
b = find_parent(b);
if(a==b) {
return false;
}
else if(a < b)
parent[b] = a;
else
parent[a] = b;
return true;
}
public static int stoi(String string) {
return Integer.parseInt(string);
}
static class Node{
double x, y;
Node(double x, double y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
}백준 2887 - 행성 터널
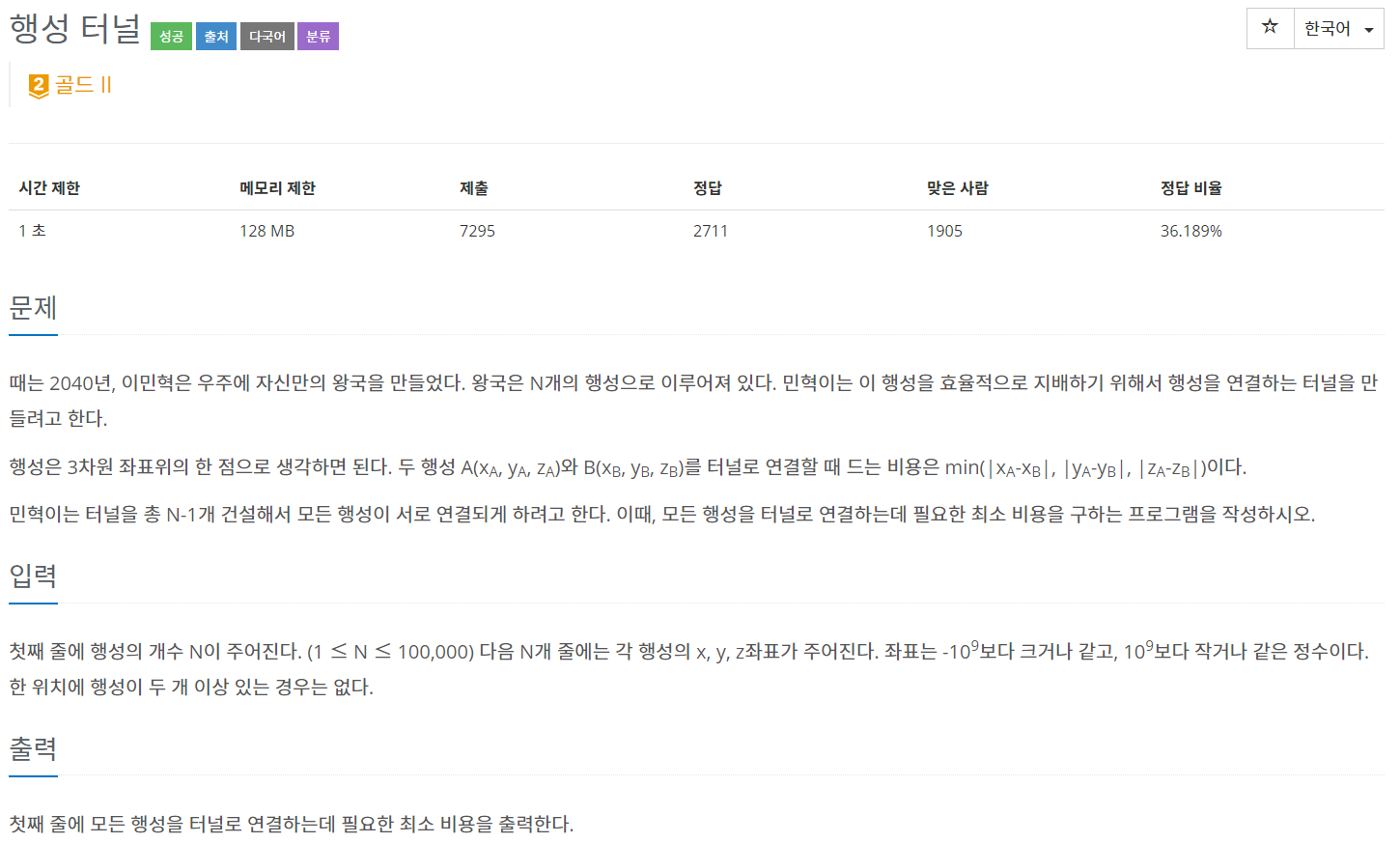
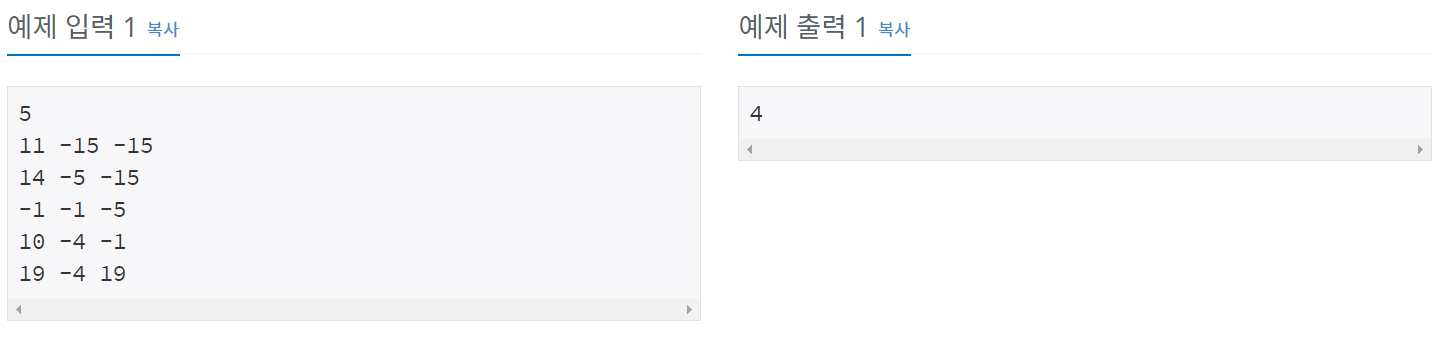
풀이
이 문제가 어려웠다.
N의 개수가 상당히 커서 모든 간선을 추가하면 시간 초과가 나온다.
간선 비용은 문제에 주어진대로 Min(x좌표 차이, y좌표 차이, z좌표 차이)이다.
행성을 연결할 때 드는 비용을 x, y, z을 각각 오름차순으로 정렬하고
인접한 좌표의 비용을 PriorityQueue에 넣는다.
그 뒤 크루스칼 알고리즘을 통해 답을 구한다.
package package29;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class num2887 {
static int N;
static Vertex[] vertexs;
static PriorityQueue<Edge> pq = new PriorityQueue<Edge>(new Comparator<Edge>() {
@Override
public int compare(Edge o1,Edge o2) {
return (o1.w-o2.w);
}
});
static int[] parent;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
vertexs = new Vertex[N];
StringTokenizer st;
for (int i = 0; i < N ; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine().trim(), " ");
int X = stoi(st.nextToken());
int Y = stoi(st.nextToken());
int Z = stoi(st.nextToken());
vertexs[i] = new Vertex(X, Y, Z, i);
}
Arrays.sort(vertexs,new Comparator<Vertex>() {
@Override
public int compare(Vertex o1, Vertex o2) {
return Integer.compare(o1.x, o2.x);
}
});
for (int i = 1; i <N ; i++) {
pq.add(new Edge(vertexs[i-1].id, vertexs[i].id, Math.abs(vertexs[i].x-vertexs[i-1].x)));
}
Arrays.sort(vertexs,new Comparator<Vertex>() {
@Override
public int compare(Vertex o1, Vertex o2) {
return Integer.compare(o1.y, o2.y);
}
});
for (int i = 1; i <N ; i++) {
pq.add(new Edge(vertexs[i-1].id, vertexs[i].id, Math.abs(vertexs[i].y-vertexs[i-1].y)));
}
Arrays.sort(vertexs,new Comparator<Vertex>() {
@Override
public int compare(Vertex o1, Vertex o2) {
return Integer.compare(o1.z, o2.z);
}
});
for (int i = 1; i <N ; i++) {
pq.add(new Edge(vertexs[i-1].id, vertexs[i].id, Math.abs(vertexs[i].z-vertexs[i-1].z)));
}
parent = new int[N+1];
for (int i = 1; i <= N ; i++)
parent[i] = i;
long result=0;
while(!pq.isEmpty()) {
Edge tmp = pq.poll();
if(find_parent(tmp.s)!=find_parent(tmp.e)) {
result +=tmp.w;
union(tmp.s,tmp.e);
}
}
System.out.println(result);
}
static class Vertex {
int x, y, z, id;
Vertex(int x, int y, int z, int id) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.z = z;
this.id = id;
}
}
static class Edge {
int s, e, w;
Edge(int s, int e, int w) {
this.s = s;
this.e = e;
this.w = w;
}
}
public static int find_parent(int num) {
if(parent[num] != num)
return parent[num] = find_parent(parent[num]);
return parent[num];
}
public static boolean union(int a, int b) {
a = find_parent(a);
b = find_parent(b);
if(a==b) {
return false;
}
else if(a < b)
parent[b] = a;
else
parent[a] = b;
return true;
}
public static int stoi(String string) {
return Integer.parseInt(string);
}
}
백준 17472 - 다리 만들기2
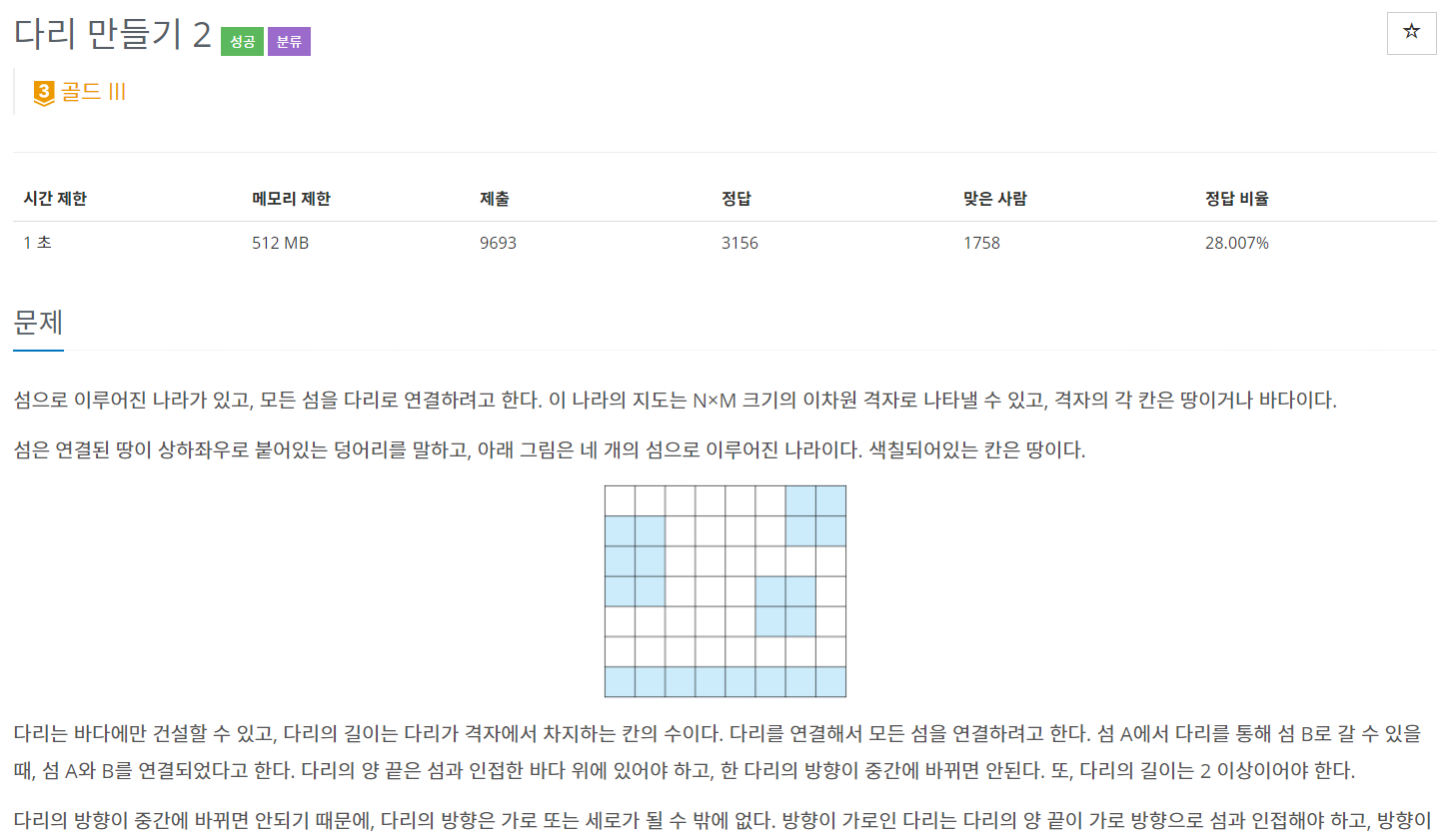
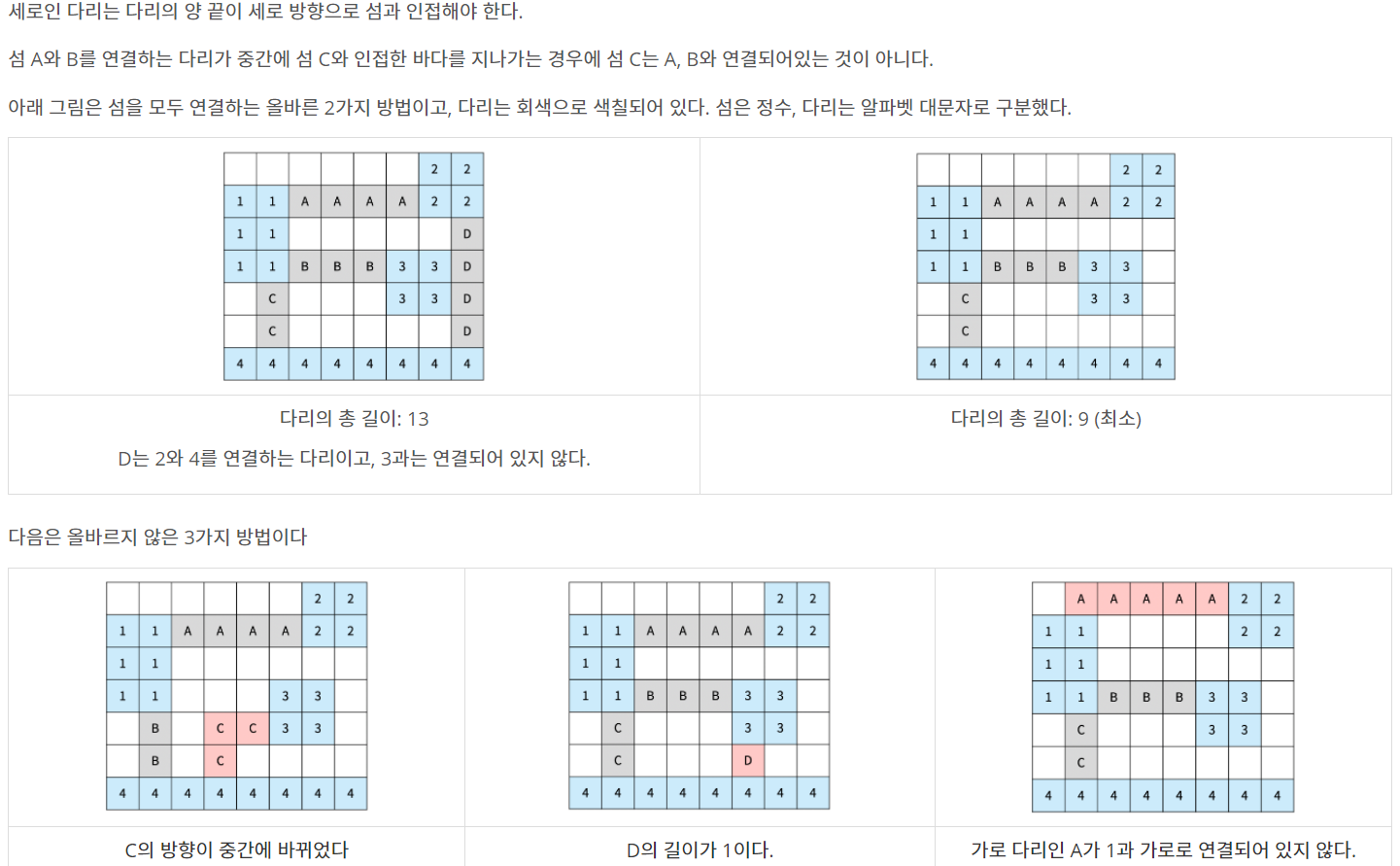
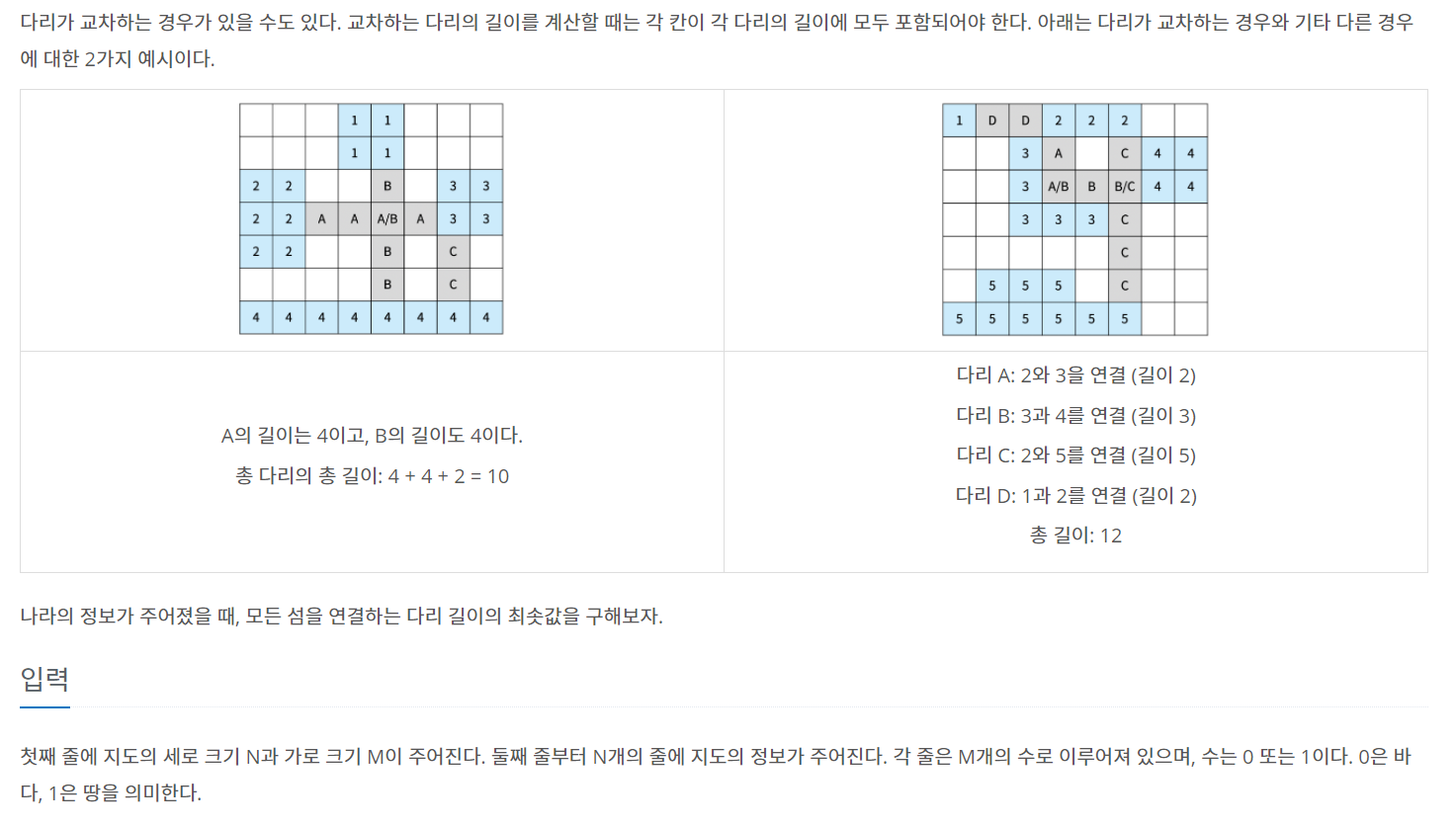
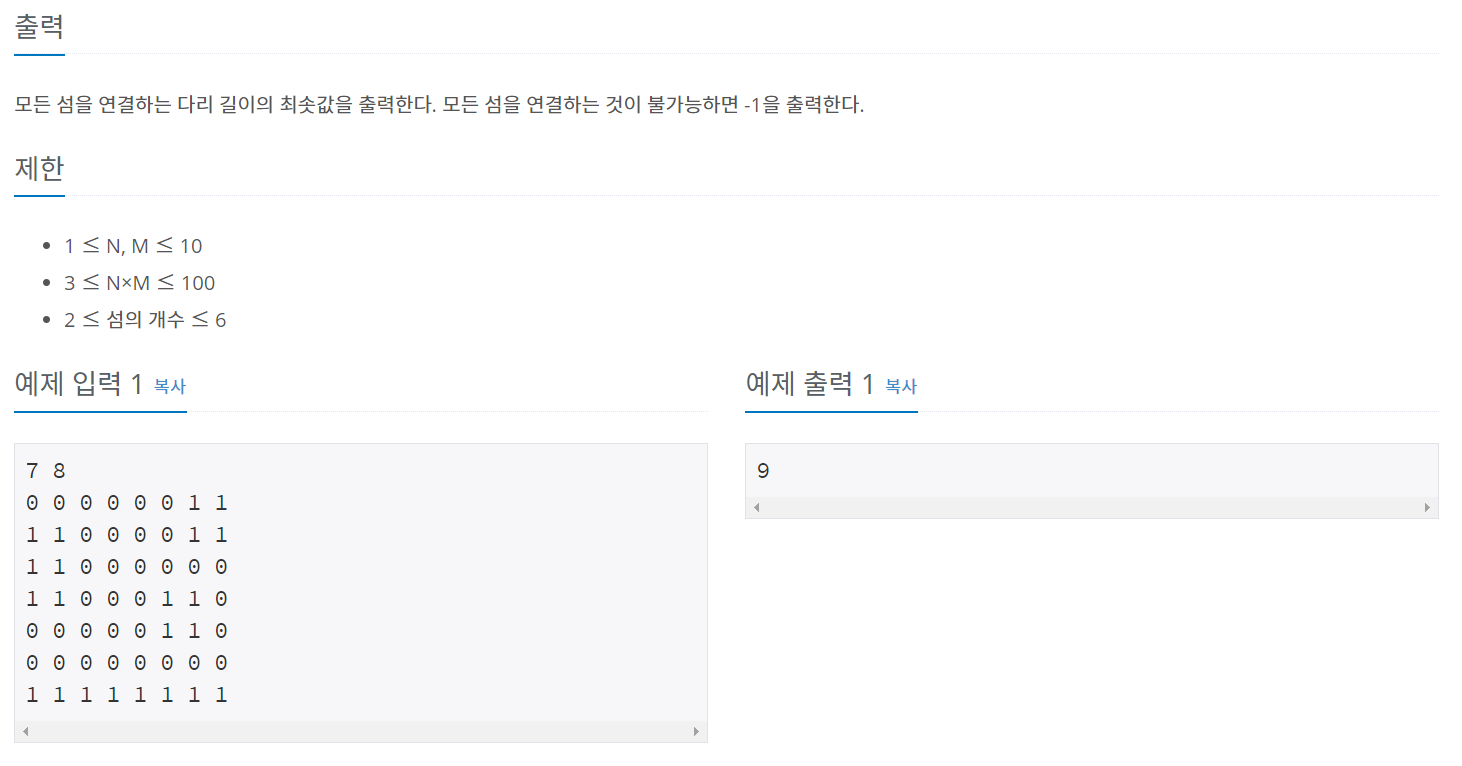
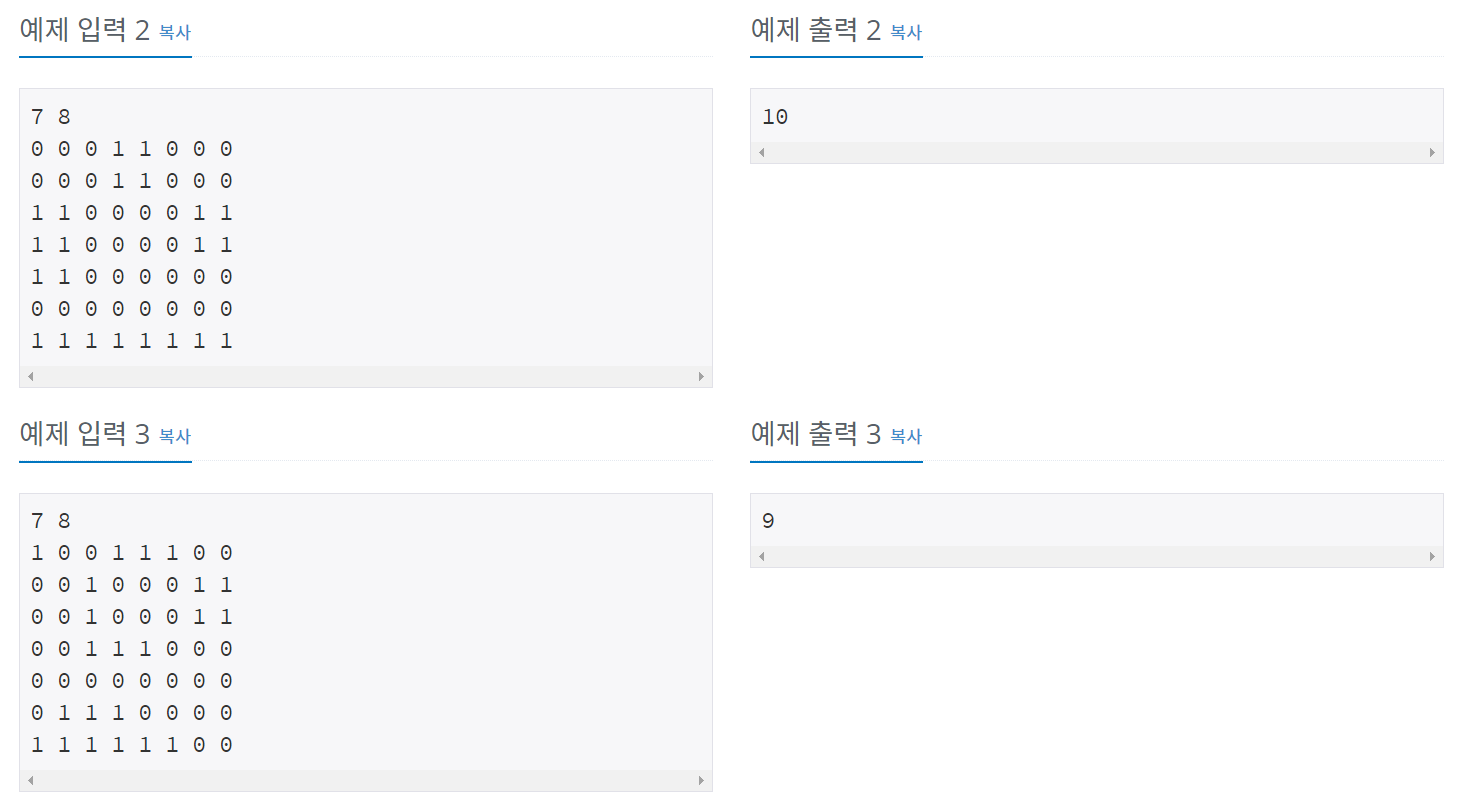
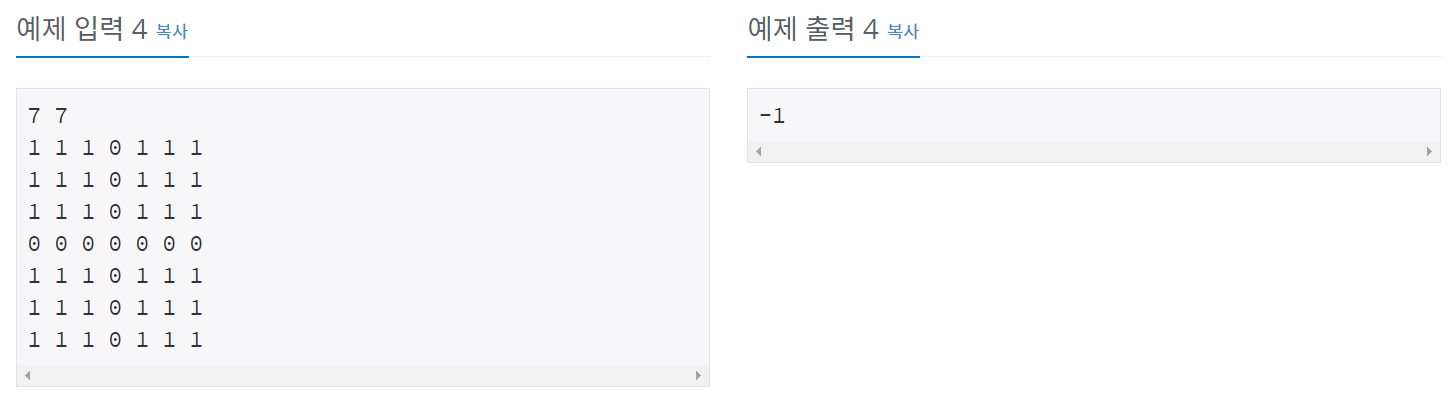
풀이
이전 문제들을 모두 풀어봤으면 어렵진 않은데 삽질을 많이했다.
내가 실수한 부분은 2가지였다.
1. dfs로 체크하는데 자기 자신을 바꾸지 않음
2. for(int i=0; i<pq.size(); i++) 이런식으로 사용어떤 친절하신 분이 반례를 정리해놔서 참고했다.
package package29;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class num17472 {
static int N, M, landCount=0, result = 0, cnt=0;
static int[] parent;
static int[][] map;
static int[] dx = new int[]{0,0,1,-1};
static int[] dy = new int[]{1,-1,0,0};
static PriorityQueue<Edge> pq = new PriorityQueue<Edge>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] NM = br.readLine().split(" ");
N = stoi(NM[0]);
M = stoi(NM[1]);
map = new int[N][M];
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
String[] mapData = br.readLine().split(" ");
for(int j=0; j<M; j++) {
map[i][j] = stoi(mapData[j]);
}
}
checkLand();
parent = new int[landCount+1];
for(int i=0; i<=landCount; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<M; j++) {
if(map[i][j] != 0) {
makeBridge(i, j, map[i][j]);
}
}
}
int size = pq.size();
for(int i=0; i<size; i++) {
Edge temp = pq.poll();
int a = temp.s;
int b = temp.e;
if(!union(a, b))
continue;
union(temp.s, temp.e);
result+= temp.w;
cnt++;
}
if(result == 0 || cnt != landCount-1) {
System.out.println(-1);
} else {
System.out.println(result);
}
}
static void makeBridge(int x, int y, int landNum) {
int newX = x;
int newY = y;
int length = 0;
for(int i=0; i<4; i++) {
while(true) {
newX = newX + dx[i];
newY = newY + dy[i];
if(isPossibleIndex(newX, newY)) {
if(map[newX][newY] == landNum) {
length = 0;
newX = x;
newY = y;
break;
} else if(map[newX][newY] == 0){
length++;
} else {
if(length > 1) {
pq.add(new Edge(landNum, map[newX][newY], length));
}
length = 0;
newX = x;
newY = y;
break;
}
} else {
length = 0;
newX = x;
newY = y;
break;
}
}
}
}
static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge>{
int s, e, w;
Edge(int s, int e, int w){
this.s = s;
this.e = e;
this.w = w;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge o) {
return o.w >= this.w ? -1 : 1;
}
}
public static int find_parent(int num) {
if(parent[num] != num)
return parent[num] = find_parent(parent[num]);
return parent[num];
}
public static boolean union(int a, int b) {
a = find_parent(a);
b = find_parent(b);
if(a==b) {
return false;
}
else if(a < b)
parent[b] = a;
else
parent[a] = b;
return true;
}
public static void checkLand() {
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[N][M];
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<M; j++) {
if(map[i][j] != 0 && !visited[i][j]) {
landCount++;
dfs(i, j, visited);
}
}
}
}
public static void dfs(int x, int y, boolean[][] visited) {
map[x][y] = landCount;
for(int i=0; i<4; i++) {
int newX = x + dx[i];
int newY = y + dy[i];
if(isPossibleIndex(newX, newY) && !visited[newX][newY] && map[newX][newY] != 0) {
visited[x + dx[i]][y + dy[i]] = true;
map[newX][newY] = landCount;
dfs(x + dx[i], y + dy[i], visited);
}
}
}
public static boolean isPossibleIndex(int x, int y) {
return x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < N && y < M ? true : false;
}
public static int stoi(String string) {
return Integer.parseInt(string);
}
}
프림 알고리즘
정점 선택 기반의 알고리즘으로, 하나의 정점에서 연결된 간선들 중에 최소 간선 비용을 가진 정점을 하나씩 선택하면서 MST를 찾는 알고리즘
구현 방법
1. 임의의 정점 하나를 선택해서 시작
2. 선택한 정점과 인접하는 정점들 중에 최소비용의 간선을 가지는 정점을 선택
3. 모든 정점이 선택될 때 까지 반복
주절주절
크루스칼 알고리즘과 프림 알고리즘에 대해 알아보았다. 대부분 최소 신장 트리문제는 크루스칼 알고리즘을 통해 대부분 해결 가능하기 때문에 백준 단계별 문제에 있는 MST문제는 모두 크루스칼 알고리즘을 사용해서 문제를 풀었다.
Reference
이것이 취업을 위한 코딩테스트다 - 나동빈
라이님 블로그
갓킹독님 블로그
주남2님 블로그
두 점 사이의 거리, 좌표평면위의 두 점 사이의 거리
Java - 반올림해서 소수점 n번째 자리까지 출력 - chacha님 블로그