복합체(Composite) 패턴 정리
DesignPattern
2025.11.04.
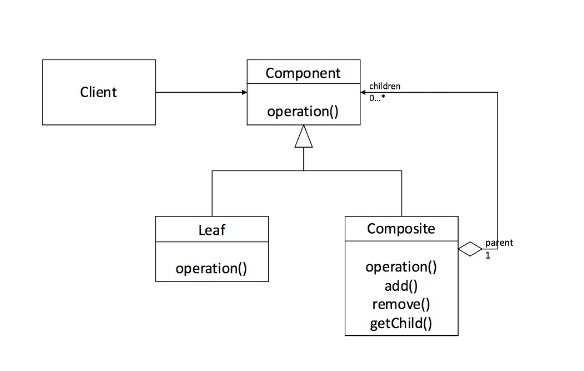
1. 복합체(Composite) 패턴
클라이언트가 그룹 전체와 개별 객체를 동일하게 처리할 수 있게 하는 패턴
- 전체 계층 구조와 전체를 구성하는 부분 계층 구조를 클라이언트 입장에서 동일하게 바라볼 수 있도록 하나의 인터페이스로 구성하는 패턴
- 클라이언트 입장에서는 전체나 부분이나 모두 동일한 컴포넌트로 인식할 수 있는 계층 구조를 만든다.
- 컴포짓 패턴은 트리 구조에 종속적
- Component : Leaf와 Compsite를 묶는 공통 상위 인터페이스
- Composite : 복합 객체로서, Leaf역할이나 Composite역할을 넣어 관리하는 역할
- Component 구현체들을 내부 리스트로 관리
- add와 remove메소드는 내부 리스트에 단일 / 복합 객체를 저장
- Component 인터페이스의 구현 메서드인 operation은 복합 객체에서 호출되면 재귀해, 추가 단일 객체를 저장한 하위 객체를 순회하게 된다.
- Leaf : 단일 객체로서, 단순하게 내용물을 표시하는 역할
- Component인터페이스의 구현 메서드인 operation은 단일 객체에서 호출되면 적절한 값만 반환
- Client : 클라이언트는 Component를 참조해 단일 / 복합 객체를 하나의 객체로 다룬다.
- client 클래스는 leaf와 composite클래스를 직접 참조하지 않고, 공통 인터페이스 component만 참조
- leaf클래스는 component인터페이스를 구현
- composite클래스는 component객체 자식들을 유지하고, operation같은 요청을 통해 자식들에게 전달
2. 복합체(Composite) 구현
composite패턴 적용 전
@Getter
public class Item {
private String name;
private int price;
public Item(String name, int price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
}
@Getter
public class Bag {
private List<Item> items;
public void add(Item item) {
items.add(item);
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Item doranBlade = new Item("도란검", 450);
Item healPotion = new Item("체력 물약", 50);
Bag bag = new Bag();
bag.add(doranBlade);
bag.add(healPotion);
Client client = new Client();
client.printPrice(doranBlade);
client.printPrice(bag);
}
private void printPrice(Item item) {
System.out.println(item.getPrice());
}
private void printPrice(Bag bag) {
System.out.println(bag.getItems().stream().mapToInt(Item::getPrice).sum());
}
}- 클라이언트가 너무 많은 정보를 가지고 있음
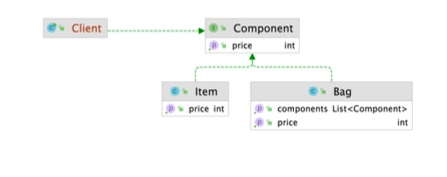
Composite 패턴 적용
- 최상위 component 클래스 정의
public interface Component {
int getPrice();
}- leaf클래스를 통해 component 클래스 구현
@Getter
public class Bag implements Component{
private List<Component> components = new LinkedList<>();
public void add(Component component) {
components.add(component);
}
@Override
public int getPrice() {
return components.stream().mapToInt(Component::getPrice).sum();
}
}
@Getter
public class Item implements Component{
private String name;
private int price;
public Item(String name, int price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public int getPrice(){
return this.price;
}
}- client는 component만 바라봄
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Item doranBlade = new Item("도란검", 450);
Item healPotion = new Item("체력 물약", 50);
Bag bag = new Bag();
bag.add(doranBlade);
bag.add(healPotion);
Client client = new Client();
client.printPrice(doranBlade);
client.printPrice(bag);
}
//클라이언트는 가장 상위를 바라봄 -> 구체적인 방법을 알 필요가 없다
private void printPrice(Component component) {
System.out.println(component.getPrice());
}
}활용 방안
- 객체들 간에 계급 및 계층 구조가 있고, 이를 표현해야 할 때 유용
- 복잡하고 난해한 단일 / 복합 객체 관계를 간편히 단순화하여 균일하게 처리하고 싶을때
3. 복합체(Composite) 패턴 장점 및 단점
장점
- 복잡한 트리 구조를 편하게 사용 가능
- 상위 클래스를 바로보고 있기 때문에 다형성과 재귀를 활용할 수 있습니다. (OCP)
- 클라이언트 코드를 변경하지 않고, 새로운 element타입 추가 가능. 객체들이 모두 같은 타입으로 취급되기 때문에 새로운 클래스 추가가 용이
- 단일 객체 및 집합 객체를 구분하지 않고 코드 작성이 가능해 사용자 코드가 단순해진다.
단점
- 트리를 만들어야 하기 때문에 (공통 인터페이스 정의) 지나치게 인반화 해야하는 경우가 생길 수 있다.
- 설계가 지나치게 범용성을 갖기 때문에 새로운 요소를 추가할 때 복합 객체에서 구성 요소에 제약을 갖기 힘들다.
- 예를들어, 계층형 구조에서 leaf 객체와 composite 객체들을 모두 동일한 인터페이스로 다루어야하는데, 이 공통 인터페이스 설계가 까다로울 수 있다.
- 복합 객체가 가지는 부분 객체의 종류를 제한할 필요가 있을 때
- 수평적 방향으로만 확장이 가능하도록 Leaf를 제한하는 Composite를 만들때
Reference
코딩으로 학습하는 GoF의 디자인 패턴 - 백기선
복합체(Composite) 패턴 - 완벽 마스터하기 - inpa블로그