유형 별 알고리즘 문제 풀이 (그리디, 이분탐색, DP, 구현)
그리디
매번 선택에서 최적의 답을 근시안적으로 택하는 알고리즘
(= 관찰을 통해 탐색범위를 줄임)
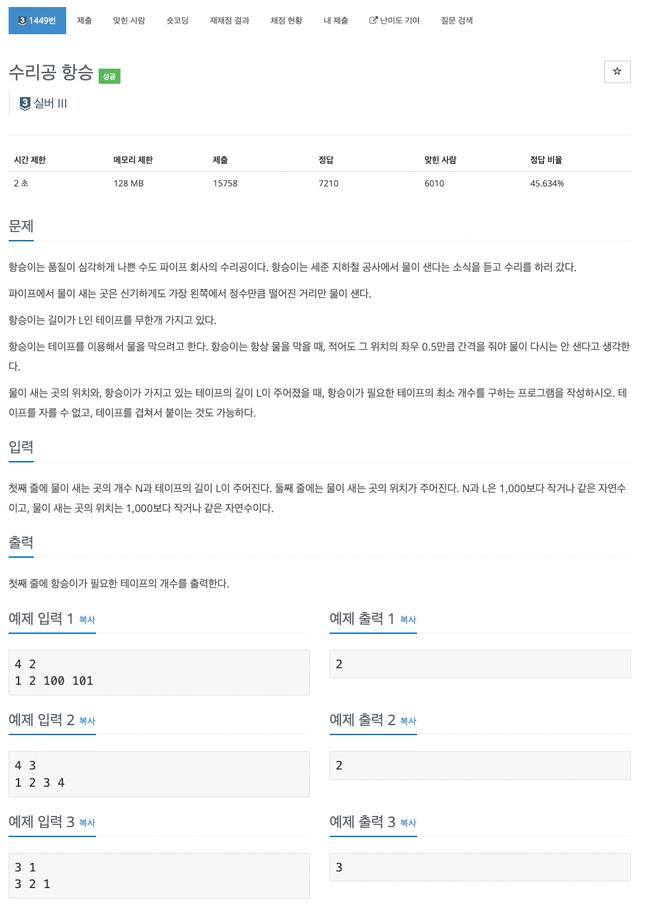
1449번
맨 처음 물이 새는 위치부터 테이프를 붙여주는 처리후에
L값 범위 안으로 처리 가능하면 이전 테이프와 거리차를 더해가며 하나의 테이프로 처리 가능한 부분을 탐색
처리가 불가능 할 경우엔 size 초기화, 테이프 개수 1증가한다
package greedy;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class num1449 {
static int N, L, holes[], cnt = 1;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] NL = br.readLine().split(" ");
N = stoi(NL[0]);
L = stoi(NL[1]);
holes = new int[N];
String[] input = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
holes[i] = stoi(input[i]);
}
Arrays.sort(holes);
int pre = holes[0];
double size = 0.5;
for (int i = 1; i < holes.length; i++) {
double diff = holes[i] - pre;
pre = holes[i];
if (size + diff < L) {
size += diff;
continue;
}
size = 0.5;
cnt++;
}
System.out.println(cnt);
}
public static int stoi(String s) {
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}
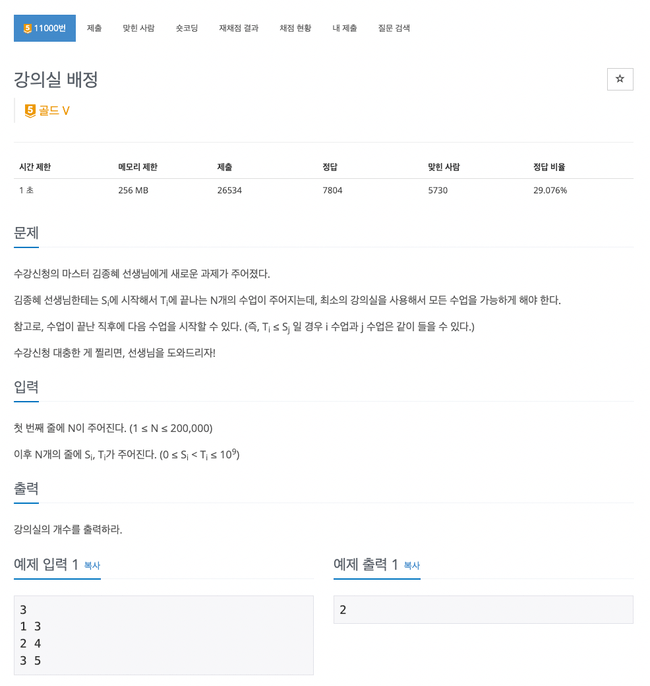
11000번
Priority Queue를 2개 사용해서 처리가 중요
-
start, end 시간을 저장하는 Lesson 클래스를 만들어 시작 시간 오름차순으로 첫번째 Priority Queue에 값을 입력받는다.
-
첫번째 Priority Queue로 반복문을 돌아주면서
-
2.1) 종료 시간을 저장하는 rooms pq를 확인, 현재 Lesson의 시작시간 보다 종료시간이 작은 경우 완료 처리한다.(삭제)
-
2.2) end 시간을 저장하는 rooms pq를 사용해 현재 사용중인 room의 종료 시간을 저장한다.
-
2.3) rooms pq의 사이즈는 현재 사용중인 room의 개수이고, 사용중인 rooms의 최대값을 roomsSize로 관리
-
package greedy;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class num11000 {
static int N;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = stoi(br.readLine());
PriorityQueue<Lesson> q = new PriorityQueue();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
String[] input = br.readLine().split(" ");
q.add(new Lesson(stoi(input[0]), stoi(input[1])));
}
PriorityQueue<Integer> rooms = new PriorityQueue<>();
int roomsSize = 0;
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
Lesson cur = q.poll();
if(rooms.isEmpty()) {
rooms.add(cur.end);
if(roomsSize == 0) {
roomsSize++;
}
continue;
}
// start 시간보다 작을 경우 종료 처리
while(rooms.peek() <= cur.start) {
rooms.poll();
}
rooms.add(cur.end);
roomsSize = roomsSize < rooms.size() ? rooms.size() : roomsSize;
}
System.out.println(roomsSize);
}
static class Lesson implements Comparable<Lesson>{
int start, end;
Lesson(int start, int end) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Lesson o) {
return this.start - o.start;
}
}
public static int stoi(String s) {
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}
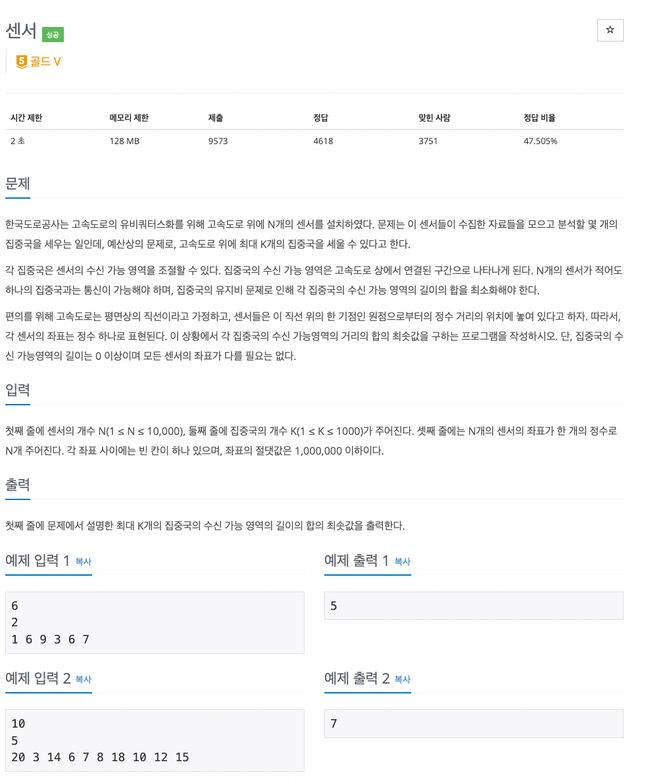
2212번
집중국을 세워 범위를 나눈다.
예제 입력 1을 예시로 들면 K가 2로 범위를 2개로 나눌 수 있다.
센서의 위치는 1, 3, 6, 6, 7, 9 일 때
센서간의 거리는 2, 3, 0, 1, 2가 되는데
센서간의 거리를 정렬해 가장 먼 거리 순으로 제외
예시에선 2개의 범위로 나눌 수 있으니 3을 제거
즉, 센서간의 거리를 가장 큰 K-1개 만큼 제거한 총 합이다.
package greedy;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class num2212 {
static int N, K, senses[], diff[];
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = stoi(br.readLine());
K = stoi(br.readLine());
senses = new int[N];
diff = new int[N - 1];
String[] input = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
senses[i] = stoi(input[i]);
}
Arrays.sort(senses);
int pre = senses[0];
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
int cur = senses[i];
diff[i - 1] = cur - pre;
pre = cur;
}
Arrays.sort(diff);
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < diff.length - K + 1; i++){
sum += diff[i];
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
public static int stoi(String s) {
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}
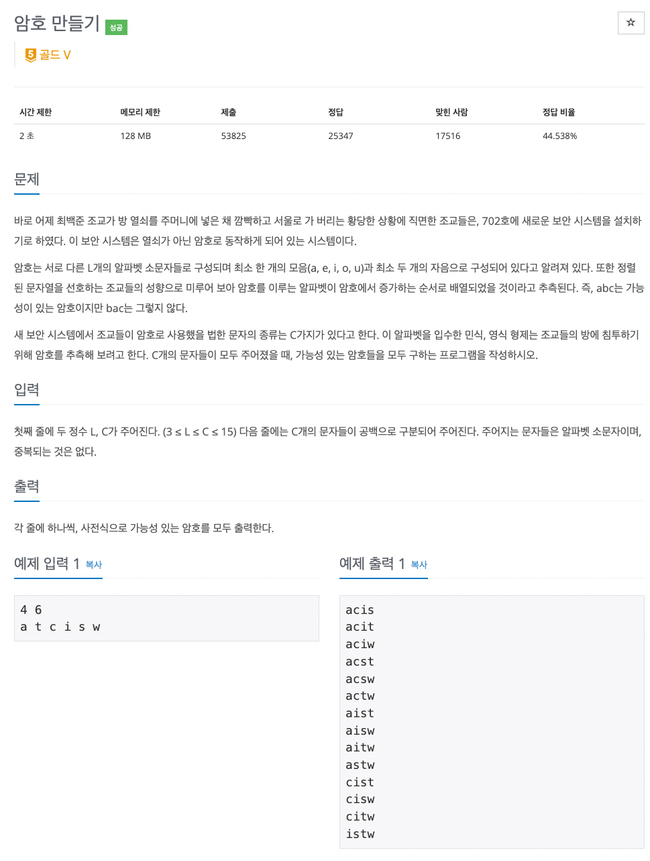
백트래킹
1756번
C개 중 N개를 선택할 수 있는 개수를 구하는 조합문제
조건에 모음 1개, 자음 2개 이상이여야 암호로 사용 가능하다는 조건이 있는데
모음과 자음 개수를 백트래킹 해서 재귀함수 탈출 시 조건 검사 후 맞는 값만 결과에 추가
package backtracking;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class num1759 {
static int L, C;
static String[] list;
static ArrayList<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] input = br.readLine().split(" ");
L = stoi(input[0]);
C = stoi(input[1]);
list = br.readLine().split(" ");
Arrays.sort(list);
getStringList(0, "", 0, new int[]{0, 0});
for (String item : res) {
System.out.println(item);
}
}
public static void getStringList(int depth, String password, int index, int[] check) {
if (depth == L) {
if (check[0] >= 1 && check[1] >= 2) {
res.add(password);
}
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < C; i++) {
int flag = check(list[i]) ? 0 : 1;
check[flag] += 1;
getStringList(depth + 1, password + list[i], i + 1, check);
check[flag] -= 1;
}
return;
}
public static boolean check(String item) {
return item.equals("a") || item.equals("e") || item.equals("i") || item.equals("o") || item.equals("u");
}
public static int stoi(String s) {
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}
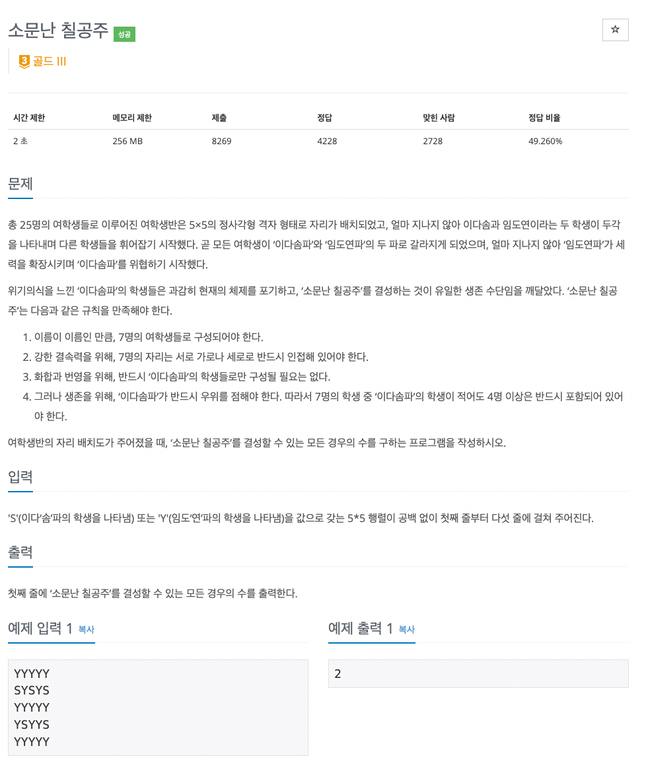
1941번
bfs로 모든 경우를 탐색하기엔 너무 커서 문제에 주어진 대로
25개 중 7개를 선택하는 조합을 bfs로 탐색하면서
- 선택한 모든 경우가 인접하는지
- 선택한 7가지 중 S가 4개 이상
2가지 조건을 확인해 경우의 수를 구하는 문제
package backtracking;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class num1941 {
static char[][] map = new char[5][5];
static boolean[] visited;
static int n = 25, r = 7, res = 0;
static int[] dx = {0, 0, -1, 1}, dy = {1, -1, 0, 0};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
map[i] = br.readLine().toCharArray();
}
combination(0, 0, new int[r]);
System.out.println(res);
}
public static void combination(int idx, int cnt, int[] selected) {
if (cnt == r) {
bfs(selected);
return;
}
for (int i = idx; i < n; i++) {
selected[cnt] = i;
combination(i + 1, cnt + 1, selected);
}
}
public static void bfs(int[] selected) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
visited = new boolean[7];
visited[0] = true;
q.add(selected[0]);
int cnt = 1, s = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int cur = q.poll();
int cx = cur / 5, cy = cur % 5;
if (map[cx][cy] == 'S') s++;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
for (int next = 1; next < 7; next++) {
if(check(cx + dx[i]) && check(cy + dy[i])) {
if (!visited[next] && selected[next] / 5 == cx + dx[i] && selected[next] % 5 == cy + dy[i]) {
visited[next] = true;
q.add(selected[next]);
cnt++;
}
}
}
}
}
if (cnt == 7 && s >= 4) {
res++;
}
}
}
}
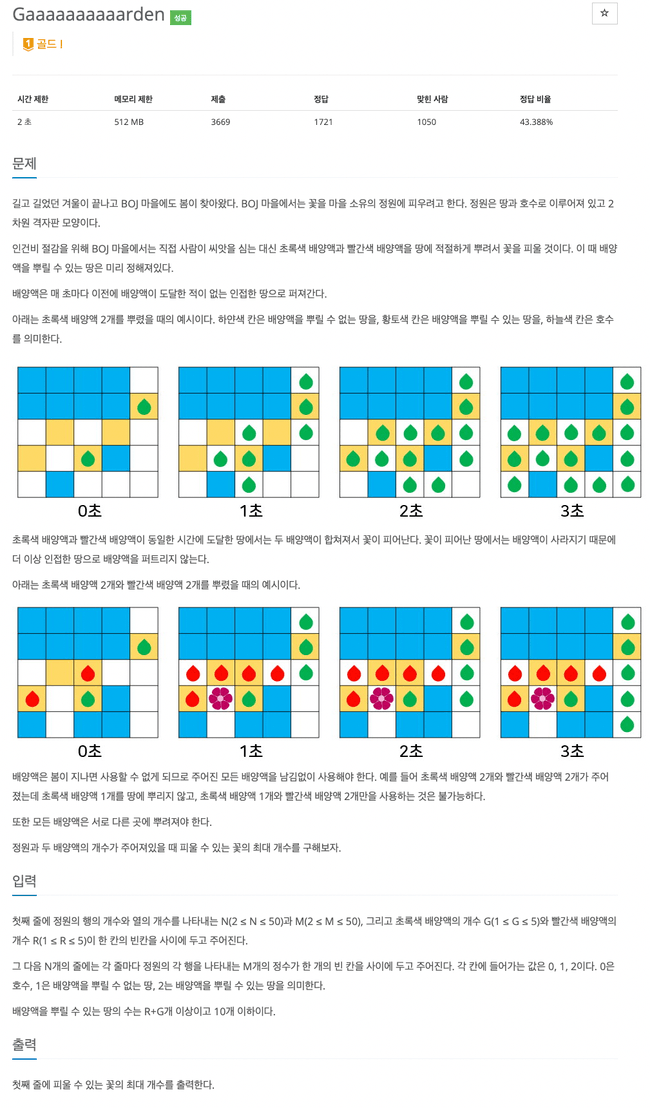
18809번
1) map값을 입력 받을 때 배양액을 뿌릴 수 있는 곳을 ArrayList로 추가, 전부 추가 후 list길이 계산
2) 배양액을 놓을 수 있는 위치에 초록색 G개, 빨강색 R개를 고른 조합 구한다.
3) bfs로 탐색
3.1) 배양액을 뿌린 초록색 G개, R개 큐에 추가, 방문 처리
3.2) 문제 조건에 맞춰 bfs탐색을 하는데 주의 할 조건으로 같은 시간에 방문한 값들만 꽃이 핀 처리package backtracking;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class num18809 {
static int N, M, G, R, len, res = 0;
static int[] arrG, arrR;
static int[] X = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
static int[] Y = {0, 1, 0, -1};
static int[][] map;
static Pos[][] visited;
static ArrayList<Pos> list = new ArrayList<>();
static Queue<Pos> q = new LinkedList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] input = br.readLine().split(" ");
N = stoi(input[0]);
M = stoi(input[1]);
G = stoi(input[2]);
R = stoi(input[3]);
map = new int[N][M];
arrG = new int[G];
arrR = new int[R];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
input = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
map[i][j] = stoi(input[j]);
if (map[i][j] == 2) {
list.add(new Pos(i, j, 0));
}
}
}
len = list.size();
combination(0, 0, 0);
System.out.println(res);
}
static void bfs() {
visited = new Pos[N][M];
for (int i = 0; i < G; i++) {
Pos p = list.get(arrG[i]);
q.offer(p);
visited[p.x][p.y] = new Pos(p.time, 'G');
}
for (int i = 0; i < R; i++) {
Pos p = list.get(arrR[i]);
q.offer(p);
visited[p.x][p.y] = new Pos(p.time, 'R');
}
int cnt = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Pos cur = q.poll();
int time = visited[cur.x][cur.y].time;
char color = visited[cur.x][cur.y].color;
// Flower가 된 경우에 배양액을 확장시키면 안됨
if (visited[cur.x][cur.y].color == 'F')
continue;
for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
int nx = cur.x + X[d];
int ny = cur.y + Y[d];
if (!check(nx, ny))
continue;
if (visited[nx][ny] == null) {
visited[nx][ny] = new Pos(cur.time + 1, color);
q.offer(new Pos(nx, ny, cur.time + 1));
} else if (visited[nx][ny].color == 'G' && color == 'R' && visited[nx][ny].time == time + 1) {
cnt++;
visited[nx][ny].color = 'F';
} else if (visited[nx][ny].color == 'R' && color == 'G' && visited[nx][ny].time == time + 1) {
cnt++;
visited[nx][ny].color = 'F';
}
}
}
res = Math.max(res, cnt);
}
static boolean check(int x, int y) {
return x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < N && y < M && map[x][y] != 0;
}
static void combination(int idx, int g, int r) {
if (g == G && r == R) {
bfs();
return;
}
if (g < G) {
for (int i = idx; i < len; i++) {
arrG[g] = i;
combination(i + 1, g + 1, r);
}
}
if (r < R) {
for (int i = idx; i < len; i++) {
arrR[r] = i;
combination(i + 1, g, r + 1);
}
}
}
static class Pos {
int x, y, time;
char color;
public Pos(int time, char color) {
this.time = time;
this.color = color;
}
public Pos(int x, int y, int time) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.time = time;
}
}
public static int stoi(String s) {
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}분할정복
DP
주어진 문제를 여러개의 부분 문제들로 나누어 푼 다음, 결과들로 주어진 문제 풀이
분할 정복과 비슷하지만
겹치는 문제가 발생하기 때문에 메모제이션 활용
2193번
package DP;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class num2193 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
long [] dp = new long[n+1];
dp[0] = 0;
dp[1] = 1;
for(int i=2; i<=n; i++)
dp[i] = dp[i-1]+dp[i-2];
System.out.println(dp[n]);
}
}
2240번
package DP;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class num2240 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] TW = br.readLine().split(" ");
int T = stoi(TW[0]);
int W = stoi(TW[1]);
// [이동횟수][시간]
int[][] dp = new int[W + 1][T + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= T; i++) {
// 1번 나무, 2번 나무
int cur = stoi(br.readLine());
// 이동하지 않고 자리에 그대로 있는 경우 처리
if (cur == 1){
dp[0][i] = dp[0][i - 1] + 1;
} else {
dp[0][i] = dp[0][i - 1];
}
// 움직인 횟수에 대한 받은 자두 값 갱신
for (int j = 1; j <= W; j++) {
// 나무 1
if (j % 2 == 0) {
if (cur == 1) {
dp[j][i] = Math.max(dp[j - 1][i - 1], dp[j][i - 1] + 1);
} else {
dp[j][i] = Math.max(dp[j - 1][i - 1] + 1, dp[j][i - 1]);
}
}
// 나무 2
else {
if (cur == 1) {
dp[j][i] = Math.max(dp[j - 1][i - 1] + 1, dp[j][i - 1]);
} else {
dp[j][i] = Math.max(dp[j - 1][i - 1], dp[j][i - 1] + 1);
}
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= W; i++)
ans = Math.max(ans, dp[i][T]);
System.out.println(ans);
}
public static int stoi(String s) {
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}
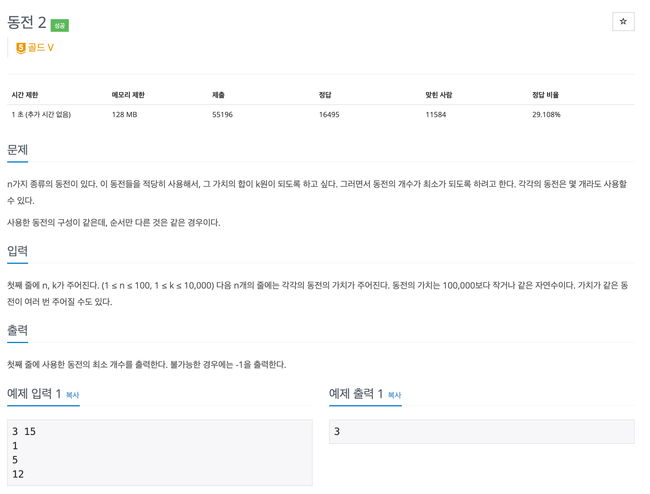
2294번
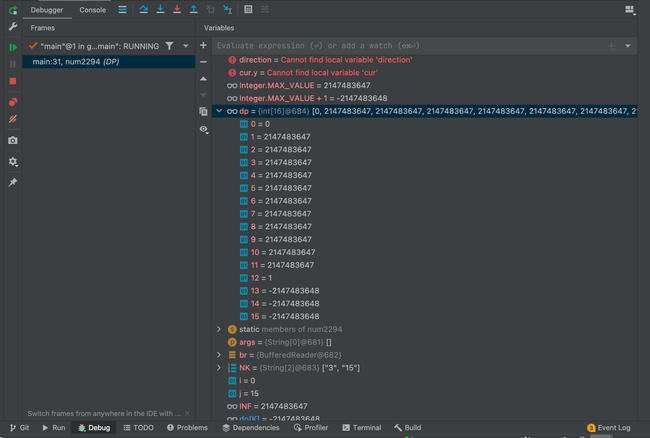
N 개의 동전으로 K 값을 만드는데 최소 값을 찾는다.
동전을 선택해 값을 만들 수 있는 방법을 배열에 저장하고 갱신하면서 배열에 최소 값을 저장한다.
주의 할 부분으로 dp배열을 초기화 할 때 INF 값으로 초기화 하면
입력
3 15
12
5
1
출력
-2147483648
와같이 출력이 되는데
위 사진과 같이 INF + 1이 되면서 오버플로우가나 Integer.MIN_VALUE값이 저장되어 제대로 갱신되지 않는다
INF - 1 한 값을 사용하거나 적당한 값으로 계산해야 함
package DP;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class num2294 {
static int N, K, coins[], dp[], INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 1, res;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] NK = br.readLine().split(" ");
N = stoi(NK[0]);
K = stoi(NK[1]);
coins = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
coins[i] = stoi(br.readLine());
}
dp = new int[K + 1];
Arrays.fill(dp, INF);
dp[0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = coins[i]; j <= K; j++) {
dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j], dp[j - coins[i]] + 1);
}
}
System.out.println(dp[K] == INF? -1 : dp[K]);
}
public static int stoi(String s) {
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}
구현
14499번
생각보다 구현이 빡세다
풀이 핵심은 6개의 값을 가진 주사위 클래스를 만들어
-
Command 마다 주사위 면의 값 변경
-
지도의 면과 맞닿은 bottom 값 처리이다.
package implementation;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class num14499 {
static int N, M, x, y, K, map[][], commands[];
static ArrayList<Integer> results = new ArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] input = br.readLine().split(" ");
N = stoi(input[0]);
M = stoi(input[1]);
x = stoi(input[2]);
y = stoi(input[3]);
K = stoi(input[4]);
map = new int[N][M];
commands = new int[K];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
input = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
map[i][j] = stoi(input[j]);
}
}
input = br.readLine().split(" ");
Dice dice = new Dice(x, y);
for(int i = 0; i < K; i++) {
commands[i] = stoi(input[i]) - 1;
int res = dice.run(commands[i]);
if(res == -1) {
continue;
}
results.add(res);
}
for(int result : results) {
System.out.println(result);
}
}
static class Dice {
// 동, 서, 북, 남
int[] dx = {0, 0, -1, 1}, dy = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int x, y; // 현재 좌표
int top, left, right, up, down, bottom;
Dice(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
top = 0;
}
public int run(int command) {
int nx = this.x + dx[command];
int ny = this.y + dy[command];
// 맵 범위에 벗어나면 명령 무시
if(!checkMapPoint(nx, ny)) {
return -1;
}
x = nx;
y = ny;
// 동
if(command == 0) {
// 주사위 이동
int tmp = left;
left = bottom;
bottom = right;
right = top;
top = tmp;
}
// 서
else if(command == 1){
int tmp = right;
right = bottom;
bottom = left;
left = top;
top = tmp;
}
// 북
else if(command == 2) {
int tmp = up;
up = top;
top = down;
down = bottom;
bottom = tmp;
}
// 남
else if(command == 3) {
int tmp = down;
down = top;
top = up;
up = bottom;
bottom = tmp;
}
// 주사위 처리
if(map[nx][ny] != 0) {
bottom = map[nx][ny];
map[nx][ny] = 0;
} else {
map[nx][ny] = bottom;
}
return top;
}
public boolean checkMapPoint(int x, int y){
return x >= 0 && y >= 0 && y < M && x < N;
}
}
public static int stoi(String s) {
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}
17142번
map의 정보를 입력받을 때 바이러스의 위치와 빈 공간의 수를 따로 저장한다.
2로 입력받은 바이러스의 총 수에서 M개 만큼 선택해 bfs로 탐색하며 최소 시간을 구해준다.
탐색 시 바이러스를 둘 수 있는 공간은 빈 공간으로 계산하지 않는게 중요
package implementation;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class num17142 {
static int N, M, map[][], min = Integer.MAX_VALUE, originEmptyCnt = 0;
static int[] dx = new int[]{1, -1, 0, 0}, dy = new int[]{0, 0, 1, -1};
static boolean[][] visited;
static ArrayList<Virus> viruses = new ArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] NM = br.readLine().split(" ");
N = stoi(NM[0]);
M = stoi(NM[1]);
map = new int[N][N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
String[] input = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
map[i][j] = stoi(input[j]);
if (map[i][j] == 2) {
viruses.add(new Virus(i, j, 0));
}else if (map[i][j] == 0) {
originEmptyCnt++;
}
}
}
selectVirus(0, 0, new Virus[M]);
if (originEmptyCnt == 0) {
System.out.println(0);
return;
}
System.out.println(min == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : min);
}
static void selectVirus(int idx, int cnt, Virus[] selected) {
if (cnt == M) {
searchVirus(selected, originEmptyCnt);
return;
}
for (int i = idx; i < viruses.size(); i++) {
selected[cnt] = viruses.get(i);
selectVirus(i + 1, cnt + 1, selected);
}
}
static void searchVirus(Virus[] list, int emptyCnt) {
Queue<Virus> q = new LinkedList<>();
visited = new boolean[N][N];
for (Virus virus : list) {
q.add(virus);
visited[virus.x][virus.y] = true;
}
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Virus cur = q.poll();
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
int nx = cur.x + dx[j];
int ny = cur.y + dy[j];
if (!checkMapArea(nx, ny)) continue;
if (visited[nx][ny] || map[nx][ny] == 1) continue;
if (map[nx][ny] == 0) {
emptyCnt--;
}
if (emptyCnt == 0) {
min = Math.min(min, cur.time + 1);
return;
}
q.add(new Virus(nx, ny, cur.time + 1));
visited[nx][ny] = true;
}
}
}
static boolean checkMapArea(int x, int y) {
return x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < N && y < N;
}
static class Virus {
int x, y, time;
Virus(int x, int y, int time) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.time = time;
}
}
public static int stoi(String s) {
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}21608번
전처리 할게 좀 많다.
값을 입력 받을 때
- student index 배열
- student index로 친한 친구(HashSet)을 저장 할 map
을 입력 받고 값을 받을 때 마다 자리에 넣어준다.
나머진 조건대로 하면 되는데 좋아하는 학생이 동일 할 경우 우선순위를 정하기 위해
Priority Queue를 활용해 값을 입력받는다.
package implementation;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
public class num21608 {
static int N, studentLen, res = 0;
static Student students[];
static HashMap<Integer, HashSet> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
static int[][] resultMap; // 최종 결과 저장
static int[][] checkValueMap; //
static int[] dx = new int[]{1, -1, 0, 0}, dy = new int[]{0, 0, 1, -1};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = stoi(br.readLine());
studentLen = N * N;
students = new Student[studentLen];
resultMap = new int[N][N];
for (int i = 0; i < studentLen; i++) {
HashMap<Integer, HashSet<Integer>> student = new HashMap<Integer, HashSet<Integer>>();
String[] input = br.readLine().split(" ");
HashSet<Integer> favoriteFriend = new HashSet<>();
for (int j = 1; j < input.length; j++) {
favoriteFriend.add(stoi(input[j]));
}
students[i] = new Student(stoi(input[0]), favoriteFriend);
hashMap.put(stoi(input[0]) , favoriteFriend);
}
for (int i = 0; i < studentLen; i++) {
// 하나씩 넣음
searchStudentPosition(i);
}
calcResult();
// 결과
System.out.println(res);
}
public static void searchStudentPosition(int idx) {
checkValueMap = new int[N][N];
Student student = students[idx];
PriorityQueue<Point> possiblePoint = new PriorityQueue<>();
int max = 0;
// 조건 1. 비어있는 칸 중에서 좋아하는 학생이 인접한 칸에 가장 많은 칸으로 자리를 정한다.
for (int i = 0; i < studentLen; i++) {
int x = i / N, y = i % N, cx, cy;
int blankCount = 0;
// 현재 앉은 자리 있으면 pass
if (resultMap[x][y] != 0) {
continue;
}
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
cx = dx[j] + x;
cy = dy[j] + y;
if (checkMapRange(cx, cy)) {
// 현재 좌표가 좋아하는 친구인지
if (student.favoriteList.contains(resultMap[cx][cy])) {
checkValueMap[x][y] += 1;
}
if(resultMap[cx][cy] == 0) {
blankCount++;
}
}
}
if (checkValueMap[x][y] > max) {
max = checkValueMap[x][y];
// 선택 가능한 좌표 리스트 초기화
possiblePoint.clear();
possiblePoint.add(new Point(x, y, blankCount, checkValueMap[x][y]));
} else if (checkValueMap[x][y] == max) {
possiblePoint.add(new Point(x, y, blankCount, checkValueMap[x][y]));
}
}
Point selected = possiblePoint.remove();
resultMap[selected.x][selected.y] = student.num;
}
public static void calcResult() {
for (int i = 0; i < studentLen; i++) {
int x = i / N, y = i % N, cx, cy;
int count = 0;
HashSet map = hashMap.get(resultMap[x][y]);
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
cx = dx[j] + x;
cy = dy[j] + y;
if (checkMapRange(cx, cy) && map.contains(resultMap[cx][cy])) {
count++;
}
}
if(count == 1) {
res += 1;
} else if (count == 2) {
res += 10;
} else if (count == 3) {
res += 100;
} else if (count == 4) {
res += 1000;
}
}
}
static class Point implements Comparable<Point> {
int x, y, blank, like;
Point(int x, int y, int blank, int like) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.blank = blank;
this.like = like;
}
public int compareTo(Point o) {
// like 많은 순 -> blank 많은 순 -> y 작은 순 -> x 작은 순
if (this.like != o.like) {
return o.like - this.like;
}
if (this.blank != o.blank) {
return o.blank - this.blank;
}
if (this.y != o.y) {
return this.y - o.y;
}
return this.x - o.x;
}
}
static class Student {
int num;
HashSet<Integer> favoriteList;
Student(int n, HashSet list) {
this.num = n;
this.favoriteList = list;
}
}
public static boolean checkMapRange(int x, int y) {
return x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < N && y < N;
}
public static int stoi(String s) {
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}
이분탐색
2467번
left, right 2개 인덱스를 사용해서 값을 더하고 절대값이 가장 작은 값을 찾는다.
절대 값이 기존 값보다 작을 경우 left, right값을 따로 저장
더한 값이 0보다 크면 right감소 0보다 작으면 left 증가
package binarySearch;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class num2467 {
static int N;
static long[] list;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = stoi(br.readLine());
list = new long[N];
String[] input = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < input.length; i++) {
list[i] = stol(input[i]);
}
int left = 0;
int right = N - 1;
int minIdx = 0, maxIdx = 0;
long min = Long.MAX_VALUE;
while (left < right) {
long sum = list[left] + list[right];
if (min > Math.abs(sum)) {
min = Math.abs(sum);
minIdx = left;
maxIdx = right;
}
if (sum >= 0) {
right--;
} else {
left++;
}
}
System.out.println(list[minIdx] + " " + list[maxIdx]);
}
public static long stol(String s){
return Long.parseLong(s);
}
public static int stoi(String s) {
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}
14921번
이전 문제와 거의 비슷한데 이전 문제에선 0에 가장 가까운 min값을 저장할 때 절대값의 값을 그대로 저장했는데
이 문제는 0에 가장 가까운 값을 그대로 출력해야 해서 비교 시 abs계산을 한다
package binarySearch;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class num14921 {
static int N;
static long[] list;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = stoi(br.readLine());
list = new long[N];
String[] input = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < input.length; i++) {
list[i] = stol(input[i]);
}
int left = 0;
int right = N - 1;
long min = Long.MAX_VALUE;
while (left < right) {
long sum = list[left] + list[right];
if (Math.abs(min) > Math.abs(sum)) {
min = sum;
}
if (sum >= 0) {
right--;
} else {
left++;
}
}
System.out.println(min);
}
public static long stol(String s){
return Long.parseLong(s);
}
public static int stoi(String s) {
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}
2473번
기존 이분탐색에서 바같에 for문을 추가해 용액의 개수 - 2만큼 돌면서 첫번째 인덱스로 사용 (총 3개 인덱스 사용)
left를 첫번째 인덱스 + 1부터 시작해 3개 합을 구해서 이분탐색
package binarySearch;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class num2473 {
static int N;
static long[] list;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = stoi(br.readLine());
list = new long[N];
String[] input = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < input.length; i++) {
list[i] = stol(input[i]);
}
Arrays.sort(list);
int minIdx = 0, maxIdx = 0, midIdx = 0;
long min = Long.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < N - 2; i++) {
int left = i + 1;
int right = N - 1;
while (left < right) {
long sum = list[i] + list[left] + list[right];
if (min > Math.abs(sum)) {
min = Math.abs(sum);
minIdx = i;
midIdx = left;
maxIdx = right;
}
if (sum >= 0) {
right--;
} else {
left++;
}
}
}
System.out.println(list[minIdx] + " " + list[midIdx] + " " + list[maxIdx]);
}
public static long stol(String s) {
return Long.parseLong(s);
}
public static int stoi(String s) {
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}
Reference
[실전 알고리즘] 0x11강 - 그리디 / BaaaaaaaarkingDog
동적 계획법(Dynamic Programming) (수정: 2019-02-07) / Ries