알고리즘 문제 풀이 (정렬, 그리디, 해시, 스택, BFS, DFS)
코딩 테스트 준비가 부족해서 유형별로 풀고 정리해보려고 한다.
정렬, 그리디, 해시맵, 스택, BFS, DFS, 그래프 탐색 문제 풀이
빠킹독 공개 문제집, 백준 단계별 문제 여기 있는 문제들로 골랐다.
정렬
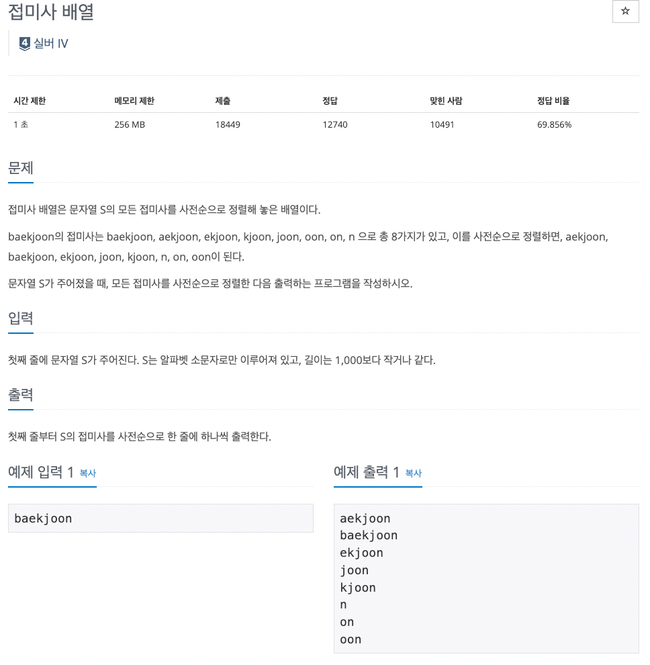
11656번
String 배열을 잘라서 접미사 배열을 만들어 주고 정렬하면 된다.
package sort;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class num11656 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String input = br.readLine();
String[] res = new String[input.length()];
for(int i=0; i<input.length(); i++){
res[i] = input.substring(i);
}
Arrays.sort(res);
for(String item : res){
System.out.println(item);
}
}
}
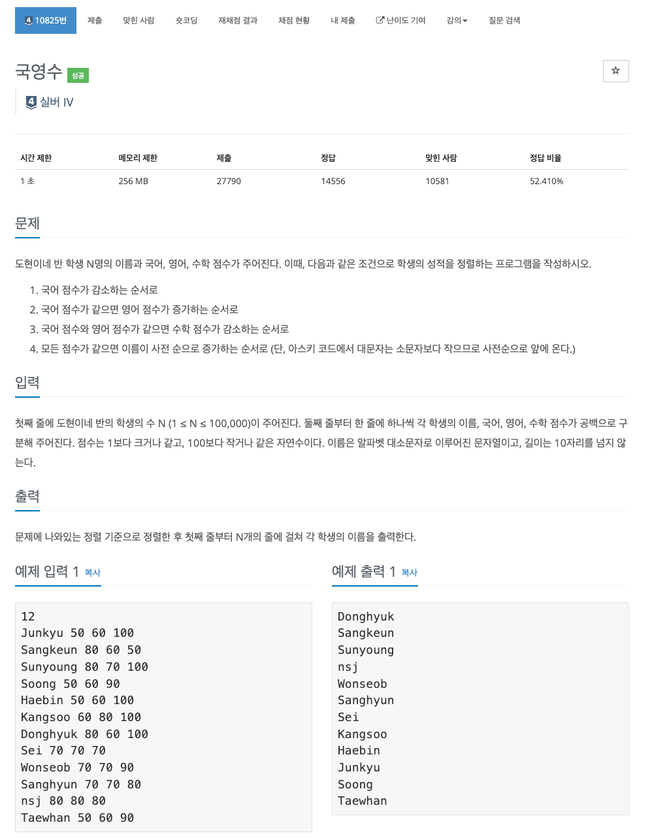
10825번
사람마다 점수를 저장할 객체 생성, compareTo 함수를 문제에 주어진 조건에 맞게 구현하면 된다
package sort;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class num10825 {
static int N;
static ArrayList<Person> list = new ArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = stoi(br.readLine());
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
String[] input = br.readLine().split(" ");
list.add(new Person(input[0], stoi(input[1]), stoi(input[2]), stoi(input[3])));
}
Collections.sort(list);
for(Person person : list){
System.out.println(person.name);
}
}
static class Person implements Comparable<Person> {
String name;
int kor, eng, math;
public Person(String name, int kor, int eng, int math) {
this.name = name;
this.kor = kor;
this.eng = eng;
this.math = math;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Person o) {
// 국어 (내림차순)
if(this.kor > o.kor)
return -1;
else if(this.kor < o.kor)
return 1;
// 영어 (오름차순)
if(this.eng > o.eng)
return 1;
else if(this.eng < o.eng)
return -1;
// 수학 (내림차순)
if(this.math > o.math)
return -1;
else if(this.math < o.math)
return 1;
// 이름 (오름차순)
return this.name.compareTo(o.name);
}
}
public static int stoi(String s){
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}
그리디
매번 선택에서 지금 가장 최적인 답을 근시안적으로 택하는 알고리즘
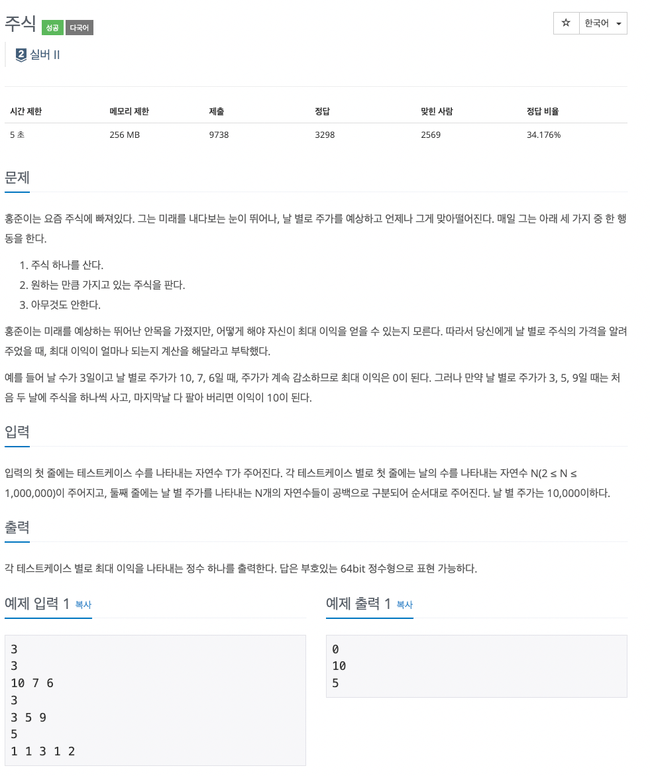
11501번
값을 뒤에서부터 확인하며 max값을 갱신
-
max 값보다 크면 max값 갱신
-
max 값보다 작으면 샀을 때 max - 현재 값 만큼 이익
package greedy;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class num11501 {
static int T, N;
static int[] list;
static long[] res;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
T = stoi(br.readLine());
res = new long[T];
for (int i = 0; i < T; i++) {
N = stoi(br.readLine());
String[] input = br.readLine().split(" ");
list = new int[N];
int max = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
list[j] = stoi(input[j]);
}
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
if (list[N - j] > max) {
max = list[N - j];
} else {
res[i] += (max - list[N - j]);
}
}
}
for (long item : res) {
System.out.println(item);
}
}
public static int stoi(String s) {
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}
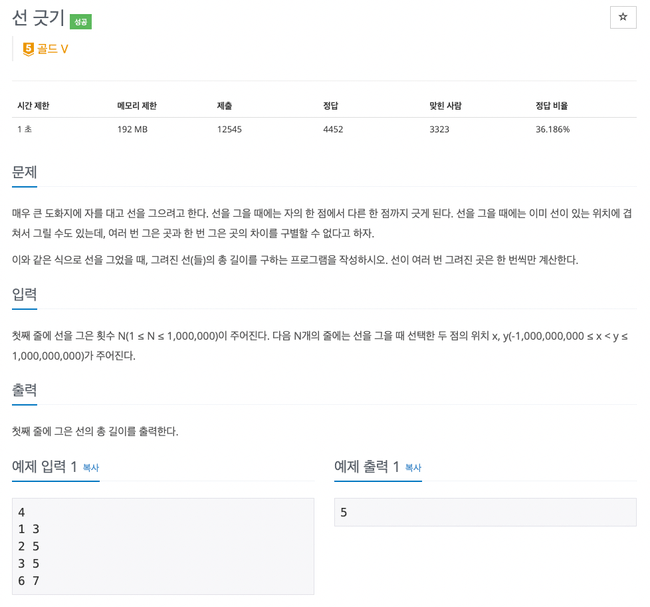
2170번
선을 그릴 때 조건을 나눠보면
- 다음 선이 이전 선에 포함되는 경우
- 다음 선이 이전 선과 일부분 포함되는 경우
- 다음 선이 이전 선과 포함되지 않는 경우
3가지로 나눠진다.
값을 입력받을 때 선의 시작 지점을 기준으로 오름차순인 우선순위 큐를 선언하고
선을 하나씩 빼며 위 조건에 맞춰 선의 길이를 계속 더하면 된다.
package greedy;
import javax.sound.sampled.Line;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class num2170 {
static int N, res = 0;
static PriorityQueue<Line> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = stoi(br.readLine());
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
String[] input = br.readLine().split(" ");
pq.add(new Line(stoi(input[0]), stoi(input[1])));
}
// 초기값 설정
Line cur = pq.poll();
if (cur != null) {
res = cur.end - cur.start;
}
while(!pq.isEmpty()) {
Line next = pq.poll();
// 1. 선이 작은 경우 pass
if(next.end <= cur.end) {
continue;
}
// 2. 겹치는 경우
if(next.start <= cur.end) {
res += next.end - cur.end;
} else { // 3. 겹치는 영역이 없는 경우
res += next.end - next.start;
}
cur = next;
}
System.out.println(res);
}
static class Line implements Comparable<Line> {
int start, end;
public Line(int s, int e){
this.start = s;
this.end = e;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Line o) {
return this.start - o.start;
}
}
public static int stoi(String s){
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}
해시맵
key - value 형태의 자료구조, 탐색을 O(1)으로 줄여주기 위해 사용
1351번
dp문제다. 문제에 주어진 대로 점화식을 재귀함수로 구현해주고
메모제이션을 해시맵으로 저장해 사용하면 된다
package HashMap;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class num1351 {
static long n, p, q;
static HashMap<Long, Long> map = new HashMap<Long, Long>();
static long search(long n) {
if (n == 0)
return 1;
if (map.containsKey(n))
return map.get(n);
map.put(n, search(n / p) + search(n / q));
return map.get(n);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] input = br.readLine().split(" ");
n = stol(input[0]);
p = stol(input[1]);
q = stol(input[2]);
System.out.println(search(n));
}
public static long stol(String s){
return Long.parseLong(s);
}
}16928번
사다리, 뱀으로 이동하는 부분을 해시맵으로 저장하고
bfs돌면서 탐색
package BFSDFS;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class num16928 {
static int N, K, res = 0;
static HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
static boolean[] visited = new boolean[101];
static LinkedList<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] NK = br.readLine().split(" ");
N = stoi(NK[0]);
K = stoi(NK[1]);
for (int i = 0; i < N + K; i++) {
String[] input = br.readLine().split(" ");
int key = stoi(input[0]);
int value = stoi(input[1]);
map.put(key, value);
}
bfs();
System.out.println(res);
}
public static void bfs() {
q.add(new int[]{1, 0});
visited[1] = true;
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] cur = q.poll();
if (cur[0] == 100) {
res = cur[1];
return;
}
for(int i=1; i<=6; i++){
int next = cur[0] + i;
if(next > 100) break;
if(visited[next]) continue;
if(map.containsKey(next)) {
next = map.get(next);
if(visited[next]) continue;
}
visited[next] = true;
q.add(new int[] {next, cur[1] + 1});
}
}
}
public static int stoi(String s) {
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}20166번
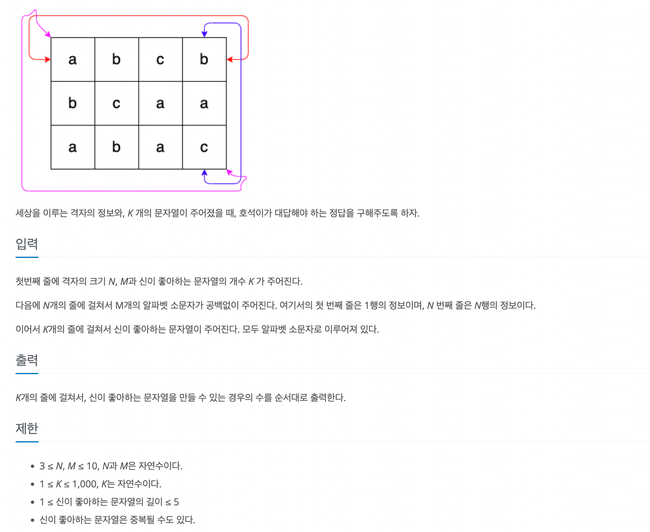
검사해야 할 문자들을 hashMap에 저장하고
dfs로 만들 수 있는 문자열을 모두 만들어 확인
보통 map의 밖으로 나가면 검사하지 않는데 이 문제는 map의 반대로 넘어가는 처리 필요
쓸데없이 시간을 많이 썼는데 생각없이 hashMap에 저장된 값들을 그대로 출력하게 짜서 왜맞틀을 시전했다…
입력받은 순서대로 출력할 수 있게 순서대로 배열을 저장시켜 출력한다.
package BFSDFS;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class num20166 {
static int N, M, K, fsLen = 0;
static String keys[];
static HashMap<String, Integer> favoriteStrings = new HashMap<>();
static String[][] map;
static int[] dx = {0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1};
static int[] dy = {1, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1, 0, 1};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] NMK = br.readLine().split(" ");
N = stoi(NMK[0]);
M = stoi(NMK[1]);
K = stoi(NMK[2]);
map = new String[N][M];
keys = new String[K];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
String[] input = br.readLine().split("");
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
map[i][j] = input[j];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < K; i++) {
String inputString = br.readLine();
fsLen = Math.max(fsLen, inputString.length());
favoriteStrings.put(inputString, 0);
keys[i] = inputString;
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
makeString(i, j, 1, map[i][j]);
}
}
for(String key : keys){
System.out.println(favoriteStrings.get(key));
}
}
public static void makeString(int x, int y, int depth, String item) {
if(favoriteStrings.containsKey(item)){
favoriteStrings.put(item, favoriteStrings.get(item) + 1);
}
// 종료 조건
if (depth == fsLen) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < dx.length; i++) {
int cx = checkMapValue(dx[i] + x, N);
int cy = checkMapValue(dy[i] + y, M);
String cItem = item + map[cx][cy];
makeString(cx, cy, depth + 1, cItem);
}
}
public static int checkMapValue(int value, int checkValue) {
if(value >= checkValue) {
return 0;
}else if(value < 0) {
return checkValue - 1;
}
return value;
}
public static int stoi(String s) {
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}
스택
현재 값을 기준으로 과거 값을 처리하는 유형
3986
문자 나눠서 같은 경우 스택에서 제거하고, 다른경우 스택에 추가해서
스택이 비었는지 확인 후에 결과값에 추가
package stack;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Stack;
public class num3986 {
static int N, res;
static Stack<String> stack;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = stoi(br.readLine());
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
String[] input = br.readLine().split("");
stack = new Stack<String>();
for(int j=0; j<input.length; j++){
if(stack.empty()){
stack.push(input[j]);
continue;
}
if(stack.peek().equals(input[j]))
stack.pop();
else
stack.push(input[j]);
}
if(stack.empty())
res++;
}
System.out.println(res);
}
public static int stoi(String s){
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}
2841
라인별로 스택을 생성하고 누르고 있는 숫자를 스택에 저장한다
- stack.top > now 인 경우 -> 손가락 뗴야함 -> 값 제거, 결과 + 1
- stack.top < now 인 경우 -> 눌러야 함 -> 값 추가 , 결과 + 1
- stack.top == now 인 경우 -> pass
로 케이스를 나눠 처리하면 된다.
2493
stack에 [높이, 인덱스]값을 추가하는데
스택엔 새로 추가한 탑의 높이보다 큰 탑을 가지고 있으면 된다
package stack;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Stack;
public class num2493 {
static long N;
static Stack<Long[]> stack = new Stack<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
N = stol(br.readLine());
String[] input = br.readLine().split(" ");
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
long item = stol(input[i]);
while(!stack.empty()){
if(stack.peek()[0] >= item) {
sb.append(stack.peek()[1] + " ");
break;
}
stack.pop();
}
if(stack.isEmpty()) {
sb.append("0 ");
}
stack.push(new Long[] {item, (long) i + 1});
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
public static long stol(String s){
return Long.parseLong(s);
}
}
3015번
풀이가 좀 어려웠다ㅜ
값의 범위 때문에 long 형태를 사용하고
값을 스택에 저장하는데 [길이, 횟수] 를 저장해야 한다 (길이가 같은 값을 처리하기 위해)
값이 추가 되면서 이전 값들과 짝을 이룰 수 있는 지 확인 하는 형태로 반복문이 진행되는데
케이스는 총 3개로 나눠 생각해야 한다
- stack.top > now인 경우
-> stack의 top인 사람과 쌍을 지을 수 있다. (이전 값들은 가려져서 보이지 않음) - stack.top < now인 경우
-> 스택에 담겨 있을 필요 없는 값들 제거하며 값 증가 - stack.top == now인 경우
-> 같은 키를 갖는 사람들과 모두 쌍을 지을 수 있어 같은 높이를 가진 사람을 모두 더해주고
-> (스택에 값이 있으니) 자기 자신을 하나 추가해 스택에 값 추가
2412251을 예시로 설명하면
| 단계 | 추가 값 | stack | res |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | <2,1> | 0 |
| 2 | 4 | <4,1> | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | <4,1>, <1,1> | 2 |
| 4 | 2 | <4,1>, <2,1> | 4 |
| 5 | 2 | <4,1>, <2,2> | 6 |
| 6 | 5 | <5,1> | 9 |
| 7 | 1 | <5,1>, <1,1> | 10 |
위 표와같이 진행되는데
값 추가 시 result값이 먼저 계산되고 stack에 추가된다
package stack;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Stack;
public class num3015 {
static long N, res;
static Stack<long[]> stack = new Stack<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = stol(br.readLine());
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
long input = stol(br.readLine());
// 0 = 높이, 1 = 개수
long[] now = new long[]{input, 1};
long[] top;
// 스택에 담겨 있을 필요 없는 값들 제거하며 값 증가
while(!stack.empty() && stack.peek()[0] <= now[0]){
top = stack.pop();
res += top[1];
// 키가 같을 경우 같은 키를 가진사람과 모두 쌍을 지을 수 있음
if(top[0] == input){
now[1] += top[1];
}
}
// 스택에 값이 있으면 현재 값과 매칭 가능
if(!stack.empty()) {
res++;
}
stack.push(now);
}
System.out.println(res);
}
public static long stol(String s){
return Long.parseLong(s);
}
}
DFS, BFS
DFS - 재귀, 스택 / BFS - 큐 으로 구현 방문 처리 필요
5427번
Queue를 2개 사용해서 불, 사람을 이동 시킨다.
package BFSDFS;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class num5427 {
static int N, w, h, result;
static int[] dx = {1, -1, 0, 0}, dy = {0, 0, 1, -1};
static Queue<Position> personQueue;
static Queue<Position> fireQueue;
static String map[][], res[];
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = stoi(br.readLine());
res = new String[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
String[] wh = br.readLine().split(" ");
w = stoi(wh[0]);
h = stoi(wh[1]);
// h : 행 / w : 열
map = new String[h][w];
personQueue = new LinkedList<>();
fireQueue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < h; j++) {
String[] input = br.readLine().split("");
for (int k = 0; k < w; k++) {
if (input[k].equals("@")) {
personQueue.add(new Position(j, k));
} else if (input[k].equals("*")) {
fireQueue.add(new Position(j, k));
}
map[j][k] = input[k];
}
}
result = 0;
bfs();
res[i] = result == 0 ? "IMPOSSIBLE" : Integer.toString(result);
}
for (String item : res) {
System.out.println(item);
}
}
public static void bfs() {
int cnt = 0;
while (!personQueue.isEmpty()) {
// 1. 먼저 불 전파
int fSize = fireQueue.size();
// 현재 q에 들어있는 것들 전파
for (int i = 0; i < fSize; i++) {
Position cur = fireQueue.poll();
for(int j=0; j<4; j++){
int cx = cur.x + dx[j];
int cy = cur.y + dy[j];
if(checkValue(cx, cy)) {
if(map[cx][cy].equals("@") || map[cx][cy].equals(".")) {
map[cx][cy] = ("*");
fireQueue.add(new Position(cx, cy));
}
}
}
}
// 2. 사람 이동
int pSize = personQueue.size();
for(int i=0; i<pSize; i++){
Position cur = personQueue.poll();
for(int j=0; j<4; j++){
int cx = cur.x + dx[j];
int cy = cur.y + dy[j];
if(!checkValue(cx, cy)) {
result = cnt + 1;
return;
}
if(checkValue(cx, cy)) {
if(map[cx][cy].equals(".")) {
map[cx][cy] = ("@");
personQueue.add(new Position(cx, cy));
}
}
}
}
cnt++;
}
}
static boolean checkValue(int x, int y) {
return x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < h && y < w;
}
public static class Position {
int x, y;
Position(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
public static int stoi(String s) {
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}
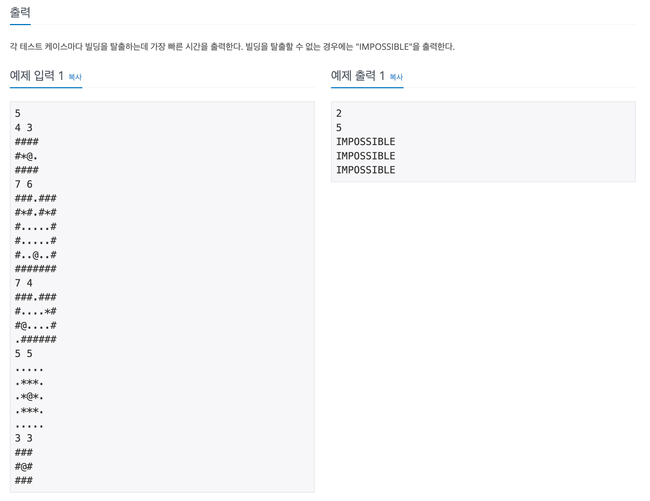
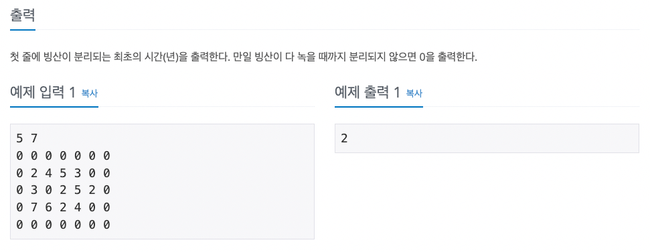
2573번
… 좀 지저분하게 짰는데 핵심은 빙산의 덩어리를 먼저 계산
-> 빙산 처리를 할 때 visited배열을 써서 기존에 빙산이 있던 곳은 0으로 계산하지 않게 처리
curHeight <= 0 을 curHeight < 0 처리해서 좀 오래걸렸다… ㅋㅋ;
package BFSDFS;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class num2573 {
static int N, M, map[][], res, time, part;
static int[] dx = {1, -1, 0, 0}, dy = {0, 0, -1, 1};
static boolean flag = false, visited[][];
static Queue<Point> q = new LinkedList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] NM = br.readLine().split(" ");
N = stoi(NM[0]);
M = stoi(NM[1]);
map = new int[N][M];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
String[] input = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
int item = stoi(input[j]);
if (item != 0) {
q.add(new Point(i, j));
}
map[i][j] = item;
}
}
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
visited = new boolean[N][M];
// 빙산 개수
part = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
if (!visited[i][j] && map[i][j] > 0) {
dfs(i, j);
part++;
}
}
}
if(part > 1){
flag = true;
break;
} else if(part == 0) {
break;
}
int size = q.size();
time++;
visited = new boolean[N][M];
// 빙산 처리
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Point cur = q.poll();
int curHeight = map[cur.x][cur.y];
int cnt = 0;
visited[cur.x][cur.y] = true;
for (int add = 0; add < 4; add++) {
int cx = cur.x + dx[add];
int cy = cur.y + dy[add];
if (checkValue(cx, cy)) {
if (!visited[cx][cy] && map[cx][cy] == 0) {
cnt++;
}
}
}
curHeight -= cnt;
if (curHeight <= 0) {
curHeight = 0;
} else {
q.add(new Point(cur.x, cur.y));
}
map[cur.x][cur.y] = curHeight;
}
}
System.out.println(flag ? time : 0);
}
public static void dfs(int x, int y) {
visited[x][y] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int cx = x + dx[i];
int cy = y + dy[i];
if (checkValue(cx, cy)) {
if (!visited[cx][cy] && map[cx][cy] != 0) {
dfs(cx, cy);
}
}
}
}
public static boolean checkValue(int x, int y) {
return x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < N && y < M;
}
public static class Point {
int x, y;
Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
public static int stoi(String s) {
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}
9019번
문제에 주어진 1. 현재 숫자 2. command 대로 동작하는 클래스를 하나 만들어주고
bfs값 탐색 후에 순서대로 출력
package BFSDFS;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class num9019 {
static int T;
static String[] res;
static String[] go = new String[]{"D", "S", "L", "R"};
static Queue<Register> q;
static boolean[] visit = new boolean[10000];
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
T = stoi(br.readLine());
res = new String[T];
for (int i = 0; i < T; i++) {
String[] AB = br.readLine().split(" ");
int A = stoi(AB[0]);
int B = stoi(AB[1]);
q = new LinkedList<>();
visit = new boolean[10000];
search(A, B, i);
}
for (String item : res) {
System.out.println(item);
}
}
public static void search(int A, int B, int index) {
q.add(new Register(A, ""));
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
for (int si = 0; si < size; si++) {
Register cur = q.poll();
if (cur.num == B) {
res[index] = cur.command;
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int cx = cur.run(go[i]);
if (!visit[cx]) {
q.add(new Register(cx, cur.command + go[i]));
visit[cx] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
static class Register {
int num;
String command;
Register(int num, String command) {
this.num = num;
this.command = command;
}
int run (String run) {
if(run.equals("D")){
return (num * 2) % 10000;
}else if(run.equals("S")){
return num == 0 ? 9999 : num - 1;
}else if(run.equals("L")){
return num % 1000 * 10 + num / 1000;
}else if(run.equals("R")){
return num % 10 * 1000 + num / 10;
}
return 0;
}
}
public static int stoi(String s) {
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}
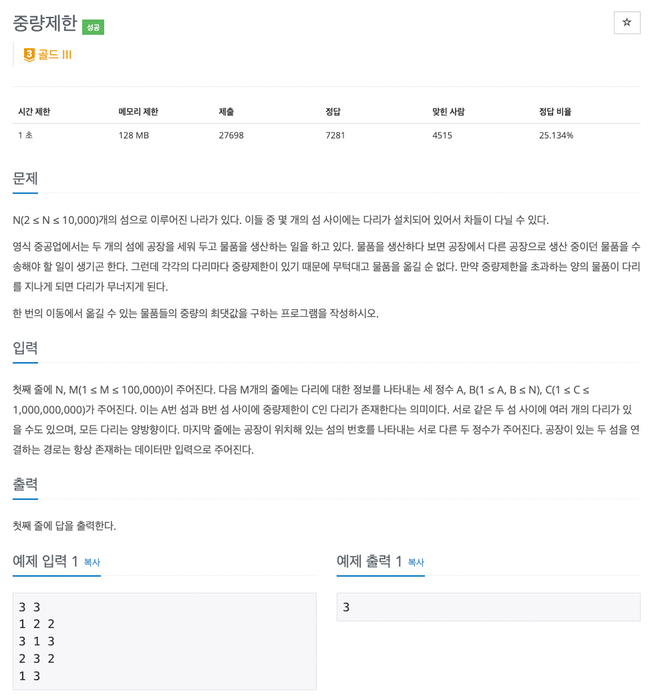
그래프
1939번
… 오래 걸렸다
실수한 부분은 2가지
-
별 생각 안하고 DFS로 탐색하는 방법으로 풀었는데 정점(N), 간선(M)값이 100000으로 O(V+E) 시간 초과 -> 이분 탐색으로 탐색이 가능한지 확인
-
dfs시 visited배열을 재사용 하지 않고 false로 바꿔주면서 사용하니 메모리 초과 -> 인자값으로 넘겨줘 재사용
추가로 다익스트라, 크루스칼 알고리즘으로 풀이가 가능한데 유형2 정리하면서 풀이 추가할 예정
package BFSDFS;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class num1939 {
static int N, M;
static long res = 0, max = 0;
static boolean visited[];
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Edge>> Vertex = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Edge>>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] NM = br.readLine().split(" ");
N = stoi(NM[0]);
M = stoi(NM[1]);
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) {
Vertex.add(new ArrayList<Edge>());
}
visited = new boolean[N + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
String[] input = br.readLine().split(" ");
int s = stoi(input[0]);
int e = stoi(input[1]);
long w = stol(input[2]);
Vertex.get(s).add(new Edge(s, e, w));
Vertex.get(e).add(new Edge(e, s, w));
max = Math.max(max, w);
}
String[] se = br.readLine().split(" ");
int s = stoi(se[0]);
int e = stoi(se[1]);
long left = 0;
long right = max;
while (right >= left) {
long mid = (left + right) / 2;
visited = new boolean[N + 1];
if (dfs(s, e, mid, visited)) {
left = mid + 1;
res = Math.max(res, mid);
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
System.out.println(res);
}
public static boolean dfs(int s, int e, long mid, boolean[] visited) {
if (visited[s]) {
return false;
}
visited[s] = true;
if (s == e) {
return true;
}
for (Edge item : Vertex.get(s)) {
if (item.w >= mid) {
if (dfs(item.e, e, mid, visited)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
public static class Edge {
int s, e;
long w;
Edge(int s, int e, long w) {
this.s = s;
this.e = e;
this.w = w;
}
}
public static long stol(String s) {
return Long.parseLong(s);
}
public static int stoi(String s) {
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}